KIR2.1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT2473
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat
- Target:
- KIR2.1
- Fields:
- >>Cholinergic synapse;>>Oxytocin signaling pathway;>>Renin secretion;>>Gastric acid secretion
- Gene Name:
- KCNJ2
- Protein Name:
- Inward rectifier potassium channel 2
- Human Gene Id:
- 3759
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P63252
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P35561
- Rat Gene Id:
- 29712
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q64273
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human KCNJ2. AA range:81-130
- Specificity:
- KIR2.1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of KIR2.1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- KCNJ2;IRK1;Inward rectifier potassium channel 2;Cardiac inward rectifier potassium channel;Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir2.1;IRK-1;hIRK1;Potassium channel; inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 2
- Observed Band(KD):
- 48kD
- Background:
- Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, probably participates in establishing action potential waveform and excitability of neuronal and muscle tissues. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Andersen syndrome, which is characterized by periodic paralysis, cardiac arrhythmias, and dysmorphic features. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in KCNJ2 are the cause of long QT syndrome type 7 (LQT7) [MIM:170390]; also called Andersen syndrome or Andersen cardiodysrhythmic periodic paralysis. Long QT syndromes are heart disorders characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the ECG and polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias. They cause syncope and sudden death in response to excercise or emotional stress. LQT7 manifests itself as a clinical triad consisting of potassium-sensitive periodic paralysis, ventricular ectopy and dysmorphic features.,disease:Defects in KCNJ2 are the cause of short QT syndrome type 3 (SQT3) [MIM:609622]. Short QT syndromes are heart disorders characterized by idiopathic persistently and uniformly short QT interval on ECG in the absence of structural heart disease in affected individuals. They cause syncope and sudden death. SQT3 has a unique ECG phenotype characterized by asymmetrical T wave
- Subcellular Location:
- Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane; Lipid-anchor .
- Expression:
- Heart, brain, placenta, lung, skeletal muscle, and kidney. Diffusely distributed throughout the brain.
The use of antibody modified liposomes loaded with AMO-1 to deliver oligonucleotides to ischemic myocardium for arrhythmia therapy. BIOMATERIALS Biomaterials. 2014 Apr;35:3697 IHC Rat 1:100 left ventricle
The use of antibody modified liposomes loaded with AMO-1 to deliver oligonucleotides to ischemic myocardium for arrhythmia therapy. BIOMATERIALS Biomaterials. 2014 Apr;35:3697 IHC Rat 1:100 left ventricle
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
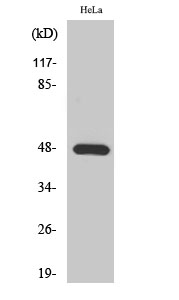
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using KIR2.1 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
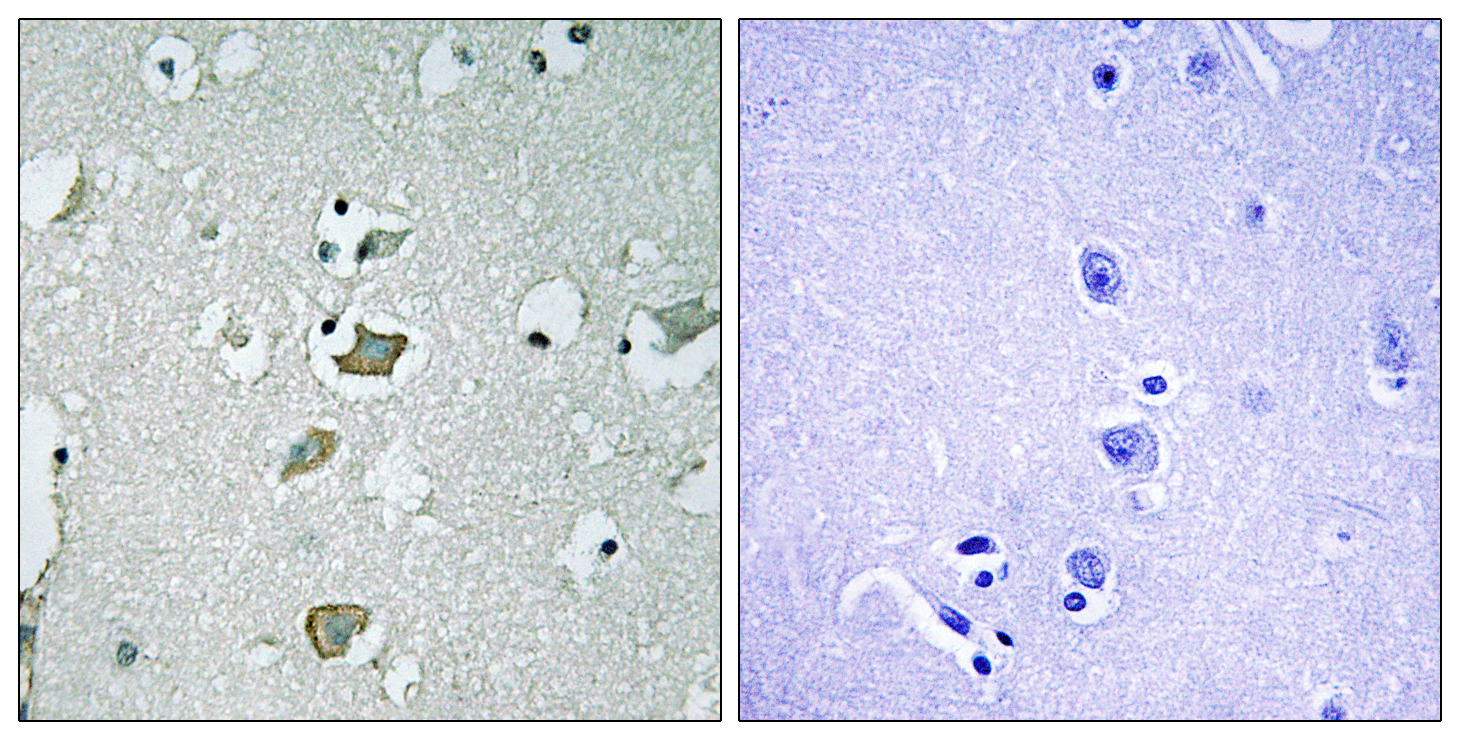
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using KCNJ2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



