FAF1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1658
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- FAF1
- Fields:
- >>Necroptosis
- Gene Name:
- FAF1
- Protein Name:
- FAS-associated factor 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 11124
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9UNN5
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14084
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P54731
- Rat Gene Id:
- 140657
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q924K2
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human FAF1. AA range:531-580
- Specificity:
- FAF1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of FAF1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:5000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- FAF1;UBXD12;UBXN3A;CGI-03;FAS-associated factor 1;hFAF1;UBX domain-containing protein 12;UBX domain-containing protein 3A
- Observed Band(KD):
- 75kD
- Background:
- Interaction of Fas ligand (TNFSF6) with the FAS antigen (TNFRSF6) mediates programmed cell death, also called apoptosis, in a number of organ systems. The protein encoded by this gene binds to FAS antigen and can initiate apoptosis or enhance apoptosis initiated through FAS antigen. Initiation of apoptosis by the protein encoded by this gene requires a ubiquitin-like domain but not the FAS-binding domain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- function:Potentiates but cannot initiate FAS-induced apoptosis.,similarity:Contains 1 UBX domain.,subunit:Specifically interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of FAS.,tissue specificity:Most abundant in testis, slightly less abundant in skeletal muscle and heart, followed by prostate, thymus, ovary, small intestine, and colon. Not detected in the peripheral blood leukocytes.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus .
- Expression:
- Most abundant in testis, slightly less abundant in skeletal muscle and heart, followed by prostate, thymus, ovary, small intestine, and colon. Not detected in the peripheral blood leukocytes.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
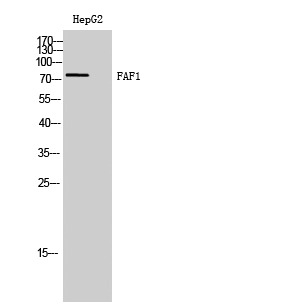
- Western Blot analysis of HepG2 cells using FAF1 Polyclonal Antibody



