MLL Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0444
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- MLL
- Fields:
- >>Lysine degradation;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Cushing syndrome;>>Transcriptional misregulation in cancer
- Gene Name:
- MLL
- Protein Name:
- Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL
- Human Gene Id:
- 4297
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q03164
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P55200
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of MLL (aa3751-3968) expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- MLL Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of MLL protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- MLL;ALL1;CXXC7;HRX;HTRX;KMT2A;MLL1;TRX1;Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL;ALL-1;CXXC-type zinc finger protein 7;Lysine N-methyltransferase 2A;KMT2A;Trithorax-like protein;Zinc finger protein HRX
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 432kD
- References:
- 1. Genet Couns. 2006;17(2):155-9.
2. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006 Jul 15;168(2):162-7
3. Leukemia. 2007 Feb;21(2):360-2. Epub 2007 Jan 4.
- Background:
- This gene encodes a transcriptional coactivator that plays an essential role in regulating gene expression during early development and hematopoiesis. The encoded protein contains multiple conserved functional domains. One of these domains, the SET domain, is responsible for its histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase activity which mediates chromatin modifications associated with epigenetic transcriptional activation. This protein is processed by the enzyme Taspase 1 into two fragments, MLL-C and MLL-N. These fragments reassociate and further assemble into different multiprotein complexes that regulate the transcription of specific target genes, including many of the HOX genes. Multiple chromosomal translocations involving this gene are the cause of certain acute lymphoid leukemias and acute myeloid leukemias. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefS
- Function:
- catalytic activity:S-adenosyl-L-methionine + histone L-lysine = S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + histone N(6)-methyl-L-lysine.,similarity:Contains 1 post-SET domain.,similarity:Contains 1 SET domain.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus .; [MLL cleavage product N320]: Nucleus.; [MLL cleavage product C180]: Nucleus. Localizes to a diffuse nuclear pattern when not associated with MLL cleavage product N320.
- Expression:
- Heart, lung, brain and T- and B-lymphocytes.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
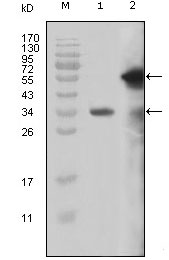
- Western Blot analysis using MLL Monoclonal Antibody against truncated MLL recombinant protein (1) and truncated GFP-MLL(aa3714-3969) transfected Cos7 cell lysate (2).
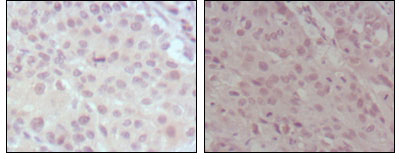
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer (left) and esophagus cancer (right), showing nuclear localization with DAB staining using MLL Monoclonal Antibody.



