- Home
- About
- Promotions
-
Products
-
Elisa Kits
- |
-
Primary antibodies
- |
-
Secondary antibodies
- |
-
Proteins
- |
-
IHC reagents
- |
-
WB reagents
- PonceauS Staining Solution
- PBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- 1.5M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH8.8
- 1M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH6.8
- 10% SDS Solution
- Prestained Protein Marker
- TBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- SDS PAGE Loading Buffer, 5X
- Stripping Buffered Solution
- Tris Buffer, pH7.4, 10X
- Total Protein Extraction Kit
- Running Buffer, 10X
- Transfer Buffer, 10X
- 30% Acr-Bis(29:1) Solution
- Tris电泳液速溶颗粒
- PBS(1X, premixed powder)
- TBS(1X, premixed powder)
- 快速封闭液
- 转膜液速溶颗粒
- Chemical reagents
- News
- Distributor
- Resources
- Contact
- Home
- >
- Info
- >
- H2B1L rabbit pAb
- >
- Go Back
H2B1L rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YT7551
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human
- Fields:
- >>Neutrophil extracellular trap formation;>>Alcoholism;>>Viral carcinogenesis;>>Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BL H2BFC
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human H2B1L AA range: 34-84
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of H2B1L at Human
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 14kD
- Background:
- Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Two molecules of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) form an octamer, around which approximately 146 bp of DNA is wrapped in repeating units, called nucleosomes. The linker histone, H1, interacts with linker DNA between nucleosomes and functions in the compaction of chromatin into higher order structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a replication-dependent histone that is a member of the histone H2B family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails but instead contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is found in the small histone gene cluster on chromosome 6p22-p21.3. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015],
- Function:
- function:Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.,PTM:Monoubiquitination of Lys-121 by the RNF20/40 complex gives a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation and is also prerequisite for histone H3 'Lys-4' and 'Lys-79' methylation. It also functions cooperatively with the FACT dimer to stimulate elongation by RNA polymerase II.,PTM:Phosphorylated on Ser-15 by STK4/MST1 during apoptosis; which facilitates apoptotic chromatin condensation. Also phosphorylated on Ser-15 in response to DN
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Chromosome.
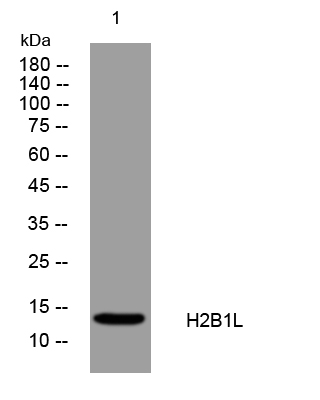
- Western blot analysis of lysates from Hela cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night




