- Home
- About
- Promotions
-
Products
-
Elisa Kits
- |
-
Primary antibodies
- |
-
Secondary antibodies
- |
-
Proteins
- |
-
IHC reagents
- |
-
WB reagents
- PonceauS Staining Solution
- PBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- 1.5M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH8.8
- 1M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH6.8
- 10% SDS Solution
- Prestained Protein Marker
- TBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- SDS PAGE Loading Buffer, 5X
- Stripping Buffered Solution
- Tris Buffer, pH7.4, 10X
- Total Protein Extraction Kit
- Running Buffer, 10X
- Transfer Buffer, 10X
- 30% Acr-Bis(29:1) Solution
- Tris电泳液速溶颗粒
- PBS(1X, premixed powder)
- TBS(1X, premixed powder)
- 快速封闭液
- 转膜液速溶颗粒
- Chemical reagents
- News
- Distributor
- Resources
- Contact
- Home
- >
- Info
- >
- ALG1 rabbit pAb
- >
- Go Back
ALG1 rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YT6940
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Fields:
- >>N-Glycan biosynthesis;>>Various types of N-glycan biosynthesis;>>Metabolic pathways
- Gene Name:
- ALG1 HMAT1 HMT1 PSEC0061 UNQ861/PRO1870
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human ALG1 AA range: 180-230
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of ALG1 at Human/Mouse
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 51kD
- Background:
- The enzyme encoded by this gene catalyzes the first mannosylation step in the biosynthesis of lipid-linked oligosaccharides. This gene is mutated in congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ik. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:GDP-mannose + chitobiosyldiphosphodolichol = GDP + beta-1,4-D-mannosylchitobiosyldiphosphodolichol.,disease:Defects in ALG1 are the cause of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1K (CDG1K) [MIM:608540]. CDGs are a family of severe inherited diseases caused by a defect in protein N-glycosylation. They are characterized by under-glycosylated serum proteins. These multisystem disorders present with a wide variety of clinical features, such as disorders of the nervous system development, psychomotor retardation, dysmorphic features, hypotonia, coagulation disorders, and immunodeficiency. The broad spectrum of features reflects the critical role of N-glycoproteins during embryonic development, differentiation, and maintenance of cell functions.,function:Participates in the formation of the lipid-linked precursor oligosaccharide for N-glycosylation. Involved in assembli
- Subcellular Location:
- Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein .
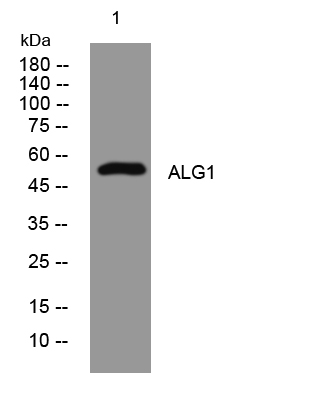
- Western blot analysis of lysates from Jurkat cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night




