SODE rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YT6859
- Applications:WB;ELISA;IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- SODE
- Gene Name:
- SOD3
- Protein Name:
- SODE
- Human Gene Id:
- 6649
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P08294
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 20657
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O09164
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25352
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q08420
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human SODE AA range: 67-117
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of SODE at Human/Mouse/Rat
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:50-300; ELISA 2000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 26kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) protein family. SODs are antioxidant enzymes that catalyze the conversion of superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, which may protect the brain, lungs, and other tissues from oxidative stress. Proteolytic processing of the encoded protein results in the formation of two distinct homotetramers that differ in their ability to interact with the extracellular matrix (ECM). Homotetramers consisting of the intact protein, or type C subunit, exhibit high affinity for heparin and are anchored to the ECM. Homotetramers consisting of a proteolytically cleaved form of the protein, or type A subunit, exhibit low affinity for heparin and do not interact with the ECM. A mutation in this gene may be associated with increased heart disease risk. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:2 superoxide + 2 H(+) = O(2) + H(2)O(2).,cofactor:Binds 1 copper ion per subunit.,cofactor:Binds 1 zinc ion per subunit.,function:Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems.,function:Protect the extracellular space from toxic effect of reactive oxygen intermediates by converting superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen.,online information:Superoxide dismutase entry,polymorphism:The variant Gly-231 which is found in about 2.2% of individual displays a 10-fold increased plasma EC-SOD content due to reduced heparin-binding affinity and thus the impairment of its binding ability to endothelial cell surface.,similarity:Belongs to the Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase family.,subcellular location:99% of EC-SOD is anchored to heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the tissue interstitium, and 1% is located in the v
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted, extracellular space. Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network . 99% of EC-SOD is anchored to heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the tissue interstitium, and 1% is located in the vasculature in equilibrium between the plasma and the endothelium.
- Expression:
- Expressed in blood vessels, heart, lung, kidney and placenta. Major SOD isoenzyme in extracellular fluids such as plasma, lymph and synovial fluid.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
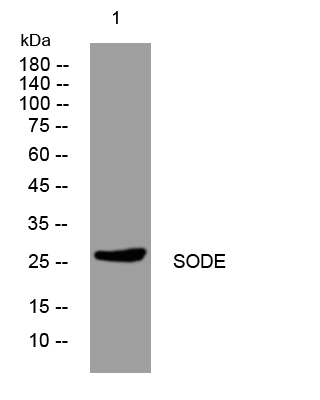
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HpeG2 cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night
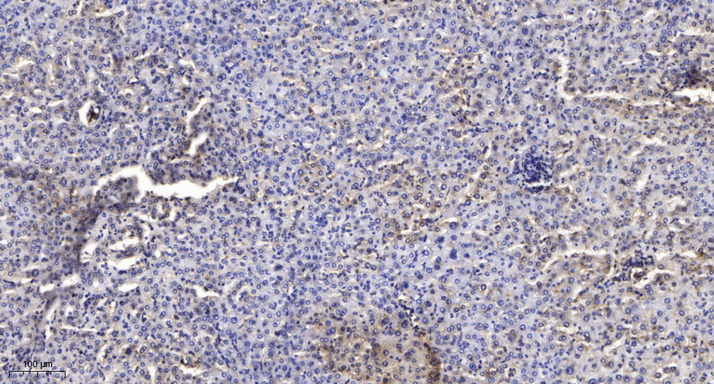
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



