GALE rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YT6716
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- GALE
- Fields:
- >>Galactose metabolism;>>Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Biosynthesis of nucleotide sugars
- Gene Name:
- GALE
- Protein Name:
- GALE
- Human Gene Id:
- 2582
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q14376
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 74246
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8R059
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P18645
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human GALE AA range: 104-154
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of GALE at Human/Mouse/Rat
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 38kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes UDP-galactose-4-epimerase which catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose, and the epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine. The bifunctional nature of the enzyme has the important metabolic consequence that mutant cells (or individuals) are dependent not only on exogenous galactose, but also on exogenous N-acetylgalactosamine as a necessary precursor for the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids. Mutations in this gene result in epimerase-deficiency galactosemia, also referred to as galactosemia type 3, a disease characterized by liver damage, early-onset cataracts, deafness and mental retardation, with symptoms ranging from mild ('peripheral' form) to severe ('generalized' form). Multiple alternatively spliced transcripts encoding the same protein have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:UDP-glucose = UDP-galactose.,cofactor:NAD.,disease:Defects in GALE are the cause of epimerase-deficiency galactosemia (EDG) [MIM:230350]; also known as galactosemia type 3. Clinical features include early-onset cataracts, liver damage, deafness and mental retardation. There are two clinically distinct forms of EDG. (1) A benign, or 'peripheral' form with no detectable GALE activity in red blood cells and characterized by mild symptoms. Some patients may suffer no symptoms beyond raised levels of galactose-1-phosphate in the blood. (2) A much rarer 'generalized' form with undetectable levels of GALE activity in all tissues and resulting in severe features such as restricted growth and mental development.,function:Catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose and the epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-ace
- Subcellular Location:
- cytosol,extracellular exosome,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
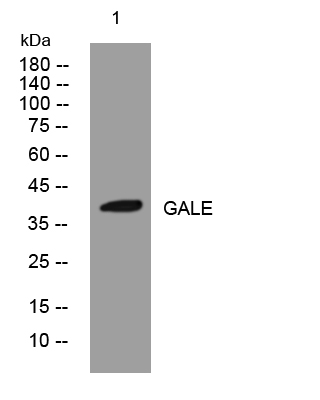
- Western blot analysis of lysates from PC-12 cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night



