BFSP1 rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YT6349
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- BFSP1
- Gene Name:
- BFSP1
- Protein Name:
- BFSP1
- Human Gene Id:
- 631
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q12934
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 12075
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- A2AMT1
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25394
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q02435
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human BFSP1 AA range: 494-544
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of BFSP1 at Human/Mouse/Rat
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 73kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a lens-specific intermediate filament-like protein named filensin. The encoded protein is expressed in lens fiber cells after differentiation has begun. This protein functions as a component of the beaded filament which is a cytoskeletal structure found in lens fiber cells. Mutations in this gene are the cause of autosomal recessive cortical juvenile-onset cataract. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in BFSP1 are the cause of autosomal recessive cortical juvenile-onset cataract [MIM:611391]. Cataract is the most frequent cause of visual impairment and blindness worldwide. While congenital cataracts are less frequent than age related cataracts, if not treated promptly they can result in irreversible neural blindness. The frequency of non-syndromic congenital cataract is estimated to be 1-6 cases per 10'000 children with one additional case being diagnosed during childhood. Developmental or juvenile onset cataract is distinguished from congenital cataract by initial clarity of the lens at birth and development of opacities progressively with maturation during childhood or adolescence. Approximately 25% of non-syndromic cataracts are inherited, and they are phenotypically and genetically heterogeneous, with autosomal dominant generally considered to be more common than a
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein ; Cytoplasmic side . Cytoplasm . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Cytoplasm, cell cortex .
- Expression:
- Expressed in the cortex and nucleus of the retina lens (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
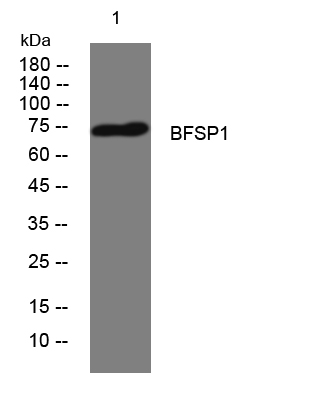
- Western blot analysis of lysates from Hela cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night



