EYA1/EYA4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT6050
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- EYA1/EYA4
- Fields:
- >>Transcriptional misregulation in cancer
- Gene Name:
- EYA3/4
- Protein Name:
- Eyes absent homolog 3/4
- Human Gene Id:
- 2138/2140
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q99502/O95677
- Immunogen:
- Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 271-320
- Specificity:
- The antibody detects endogenous EYA1/EYA4
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:50-200, ELISA 1:10000-20000. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Background:
- EYA transcriptional coactivator and phosphatase 1(EYA1) Homo sapiens This gene encodes a member of the eyes absent (EYA) family of proteins. The encoded protein may play a role in the developing kidney, branchial arches, eye, and ear. Mutations of this gene have been associated with branchiootorenal dysplasia syndrome, branchiootic syndrome, and sporadic cases of congenital cataracts and ocular anterior segment anomalies. A similar protein in mice can act as a transcriptional activator. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:Protein tyrosine phosphate + H(2)O = protein tyrosine + phosphate.,cofactor:Binds 1 Mg(2+) ion per subunit.,developmental stage:Detected in cytoplasm of somite cells at the beginning of fourth week of development. Detected in cytoplasm of limb bud cell between the sixth and eighth week of development.,disease:Defects in EYA1 are the cause of branchiootic syndrome type 1 (BOS1) [MIM:602588]; also known as BO syndrome type 1 or branchiootic dysplasia. Individuals with BOS1 are affected by the same branchial and otic anomalies as those seen in individuals with BOR1, but lack renal anomalies.,disease:Defects in EYA1 are the cause of branchiootorenal syndrome type 1 (BOR1) [MIM:113650]; also known as Melnick-Fraser syndrome. BOR is an autosomal dominant disorder manifested by various combinations of preauricular pits, branchial fistulae or cysts, lacrimal duct stenosis, hea
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs). .
- Expression:
- In the embryo, highly expressed in kidney with lower levels in brain. Weakly expressed in lung. In the adult, highly expressed in heart and skeletal muscle. Weakly expressed in brain and liver. No expression in eye or kidney.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
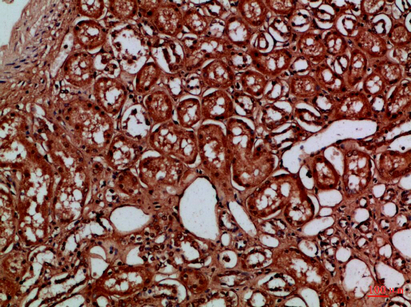
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-kidney, antibody was diluted at 1:100

- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-kidney, antibody was diluted at 1:100

- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-brain, antibody was diluted at 1:100

- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human-brain, antibody was diluted at 1:100



