ASAH3 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5672
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- ASAH3
- Fields:
- >>Sphingolipid metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Sphingolipid signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- ACER1
- Protein Name:
- Alkaline ceramidase 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 125981
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8TDN7
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8R4X1
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from ASAH3 . at AA range: 100-180
- Specificity:
- ASAH3 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of ASAH3 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ACER1;ASAH3;Alkaline ceramidase 1;AlkCDase 1;Alkaline CDase 1;Acylsphingosine deacylase 3;N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase 3
- Observed Band(KD):
- 34kD
- Background:
- Ceramides are synthesized during epidermal differentiation and accumulate within the interstices of the stratum corneum, where they represent critical components of the epidermal permeability barrier. Excess cellular ceramide can trigger antimitogenic signals and induce apoptosis, and the ceramide metabolites sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) are important bioregulatory molecules. Ceramide hydrolysis in the nucleated cell layers regulates keratinocyte proliferation and apoptosis in response to external stress. Ceramide hydrolysis also occurs at the stratum corneum, releasing free sphingoid base that functions as an endogenous antimicrobial agent. ACER1 is highly expressed in epidermis and catalyzes the hydrolysis of very long chain ceramides to generate sphingosine (Houben et al., 2006 [PubMed 16477081]; Sun et al., 2008 [PubMed 17713573]).[supplied by OMIM, Jul 2010],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:N-acylsphingosine + H(2)O = a carboxylate + sphingosine.,enzyme regulation:Inhibited by sphingosine.,function:Hydrolyzes the sphingolipid ceramide into sphingosine and free fatty acid at an optimal pH of 8.0. Has a highly restricted substrate specificity for the natural stereoisomer of ceramide with D-erythro-sphingosine but not D-ribo-phytosphingosine or D-erythro-dihydrosphingosine as a backbone. May have a role in regulating the levels of bioactive lipids ceramide and sphingosine 1-phosphate, as well as complex sphingolipids.,similarity:Belongs to the alkaline ceramidase family.,tissue specificity:Mainly expressed in epidermis.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Mainly expressed in epidermis.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
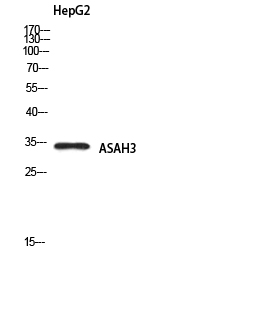
- Western blot analysis of HepG2 using ASAH3 antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000



