PEPCK-C Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT5236
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- PEPCK-C
- Fields:
- >>Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis;>>Citrate cycle (TCA cycle);>>Pyruvate metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>PPAR signaling pathway;>>FoxO signaling pathway;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>AMPK signaling pathway;>>Insulin signaling pathway;>>Adipocytokine signaling pathway;>>Glucagon signaling pathway;>>Insulin resistance;>>Proximal tubule bicarbonate reclamation
- Gene Name:
- PCK1
- Protein Name:
- Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase cytosolic [GTP]
- Human Gene Id:
- 5105
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P35558
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 18534
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9Z2V4
- Rat Gene Id:
- 362282
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P07379
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human PCK1. AA range:491-540
- Specificity:
- PEPCK-C Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PEPCK-C protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC: 1:100-300 ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PCK1;PEPCK1;Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, cytosolic [GTP];PEPCK-C;Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
- Observed Band(KD):
- 65kD
- Background:
- This gene is a main control point for the regulation of gluconeogenesis. The cytosolic enzyme encoded by this gene, along with GTP, catalyzes the formation of phosphoenolpyruvate from oxaloacetate, with the release of carbon dioxide and GDP. The expression of this gene can be regulated by insulin, glucocorticoids, glucagon, cAMP, and diet. Defects in this gene are a cause of cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase deficiency. A mitochondrial isozyme of the encoded protein also has been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:GTP + oxaloacetate = GDP + phosphoenolpyruvate + CO(2).,cofactor:Binds 1 manganese ion per subunit.,disease:Defects in PCK1 are the cause of cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase deficiency (cytosolic PEPCK deficiency) [MIM:261680]. PEPCK deficiency is a metabolic disorder resulting from impaired gluconeogenesis. It is a rare disease with less than 10 cases reported in the literature. Clinical characteristics include hypotonia, hepatomegaly, failure to thrive, lactic acidosis and hypoglycaemia. Autoposy reveals fatty infiltration of both the liver and kidneys. The disorder is transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait.,enzyme regulation:Activity is affected by a number of hormones regulating this metabolic process (such as glucagon, insulin, or glucocorticoids).,function:Catalyzes the conversion of oxaloacetate (OAA) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the rate-limiti
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytosol . Endoplasmic reticulum . Phosphorylation at Ser-90 promotes translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum. .
- Expression:
- Major sites of expression are liver, kidney and adipocytes.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
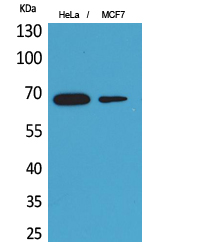
- Western Blot analysis of HeLa, MCF7 cells using PEPCK-C Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
.jpg)
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat-liver, antibody was diluted at 1:100

- Western blot analysis of lysate from HeLa cells, using PCK1 Antibody.



