V-ATPase C2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4859
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- V-ATPase C2
- Fields:
- >>Oxidative phosphorylation;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Phagosome;>>mTOR signaling pathway;>>Synaptic vesicle cycle;>>Collecting duct acid secretion;>>Vibrio cholerae infection;>>Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection;>>Human papillomavirus infection;>>Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gene Name:
- ATP6V1C2
- Protein Name:
- V-type proton ATPase subunit C 2
- Human Gene Id:
- 245973
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8NEY4
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q99L60
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human ATP6V1C2. AA range:121-170
- Specificity:
- V-ATPase C2 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of V-ATPase C2 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ATP6V1C2;V-type proton ATPase subunit C 2;V-ATPase subunit C 2;Vacuolar proton pump subunit C 2
- Observed Band(KD):
- 48kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A,three B, and two G subunits, as well as a C, D, E, F, and H subunit. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. This gene encodes alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different V1 domain C subunit isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- function:Subunit of the peripheral V1 complex of vacuolar ATPase. Subunit C is necessary for the assembly of the catalytic sector of the enzyme and is likely to have a specific function in its catalytic activity. V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying a variety of intracellular compartments in eukaryotic cells.,similarity:Belongs to the V-ATPase C subunit family.,subunit:V-ATPase is an heteromultimeric enzyme composed of a peripheral catalytic V1 complex (components A to H) attached to an integral membrane V0 proton pore complex (components: a, c, c', c'' and d).,tissue specificity:Kidney and placenta.,
- Subcellular Location:
- vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain,lysosomal membrane,cytosol,proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain,extracellular exosome,
- Expression:
- Kidney and placenta.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
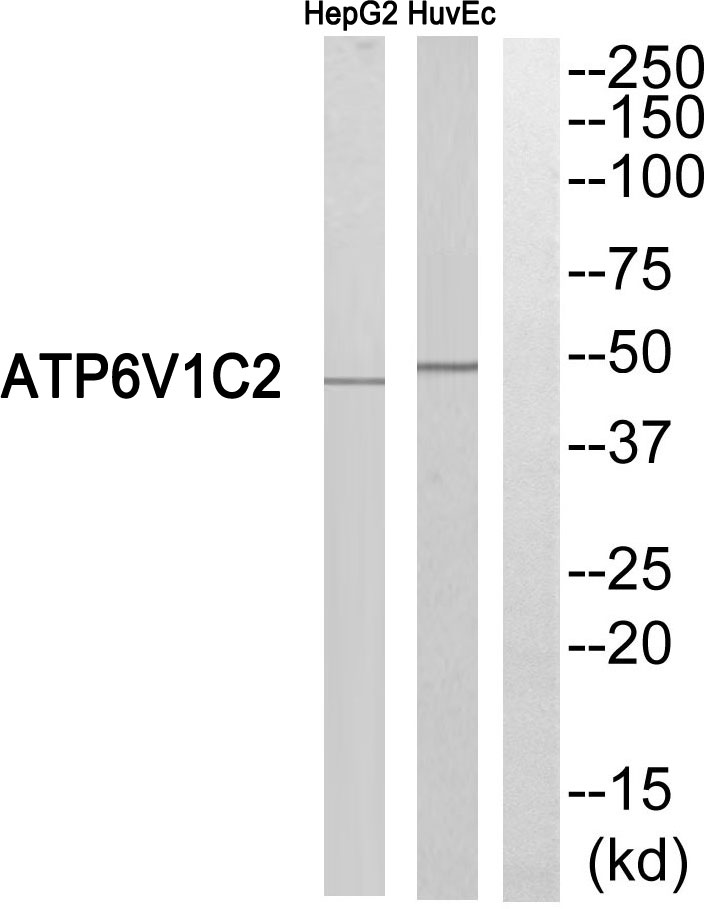
- Western blot analysis of ATP6V1C2 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the ATP6V1C2 peptide.

- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HT-29 cells using ATP6V1C2 antibody.



