TIRAP Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4667
- Applications:IHC;IF;WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- TIRAP
- Fields:
- >>NF-kappa B signaling pathway;>>Toll-like receptor signaling pathway;>>Alcoholic liver disease;>>Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection;>>Salmonella infection;>>Pertussis;>>Tuberculosis;>>Hepatitis B;>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer;>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- TIRAP
- Protein Name:
- Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein
- Human Gene Id:
- 114609
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P58753
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 117149
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q99JY1
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human TIRAP. AA range:52-101
- Specificity:
- TIRAP Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of TIRAP protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- TIRAP;MAL;Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein;TIR domain-containing adapter protein;Adaptor protein Wyatt;MyD88 adapter-like protein
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 24kD
- Background:
- The innate immune system recognizes microbial pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Different TLRs recognize different pathogen-associated molecular patterns and all TLRs have a Toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain, which is responsible for signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a TIR adaptor protein involved in the TLR4 signaling pathway of the immune system. It activates NF-kappa-B, MAPK1, MAPK3 and JNK, which then results in cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants; however, not all variants have been fully described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- function:Adapter involved in the TLR4 signaling pathway in the innate immune response. Acts via IRAK2 and TRAF-6, leading to the activation of NF-kappa-B, MAPK1, MAPK3 and JNK, resulting in cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response.,polymorphism:Genetic variation in TIRAP can influence susceptibility or resistance to invasive pneumococcal disease, bacteremia, malaria and tuberculosi.,similarity:Contains 1 TIR domain.,subunit:Homodimer. Also forms heterodimers with MyD88. Binds to TLR4 and IRAK2 via their respective TIR domains. Binds to PKR and TBK1. Does not interact with IRAK1, nor TLR9.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in liver, kidney, spleen, skeletal muscle and heart. Also detected in peripheral blood leukocytes, lung, placenta, small intestine, thymus, colon and brain.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Cell membrane . Membrane . Colocalizes with DAB2IP at the plasma membrane.
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in liver, kidney, spleen, skeletal muscle and heart. Also detected in peripheral blood leukocytes, lung, placenta, small intestine, thymus, colon and brain.
Phycocyanin Exerts Anti-Proliferative Effects through Down-Regulating TIRAP/NF-κB Activity in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cells Cells-Basel. 2019 Jun;8(6):588 WB Human H1975 cell, H1650 cell,LTEP-a2 cell
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
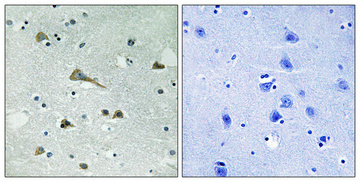
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human brain. Antibody was diluted at 1:100(4° overnight). High-pressure and temperature Tris-EDTA,pH8.0 was used for antigen retrieval. Negetive contrl (right) obtaned from antibody was pre-absorbed by immunogen peptide.


