SEMA4A Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4235
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;Monkey
- Target:
- SEMA4A
- Fields:
- >>Axon guidance
- Gene Name:
- SEMA4A
- Protein Name:
- Semaphorin-4A
- Human Gene Id:
- 64218
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9H3S1
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 20351
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q62178
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human SEMA4A. AA range:501-550
- Specificity:
- SEMA4A Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of SEMA4A protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SEMA4A;SEMAB;SEMB;Semaphorin-4A;Semaphorin-B;Sema B
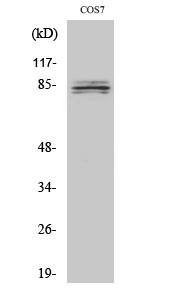
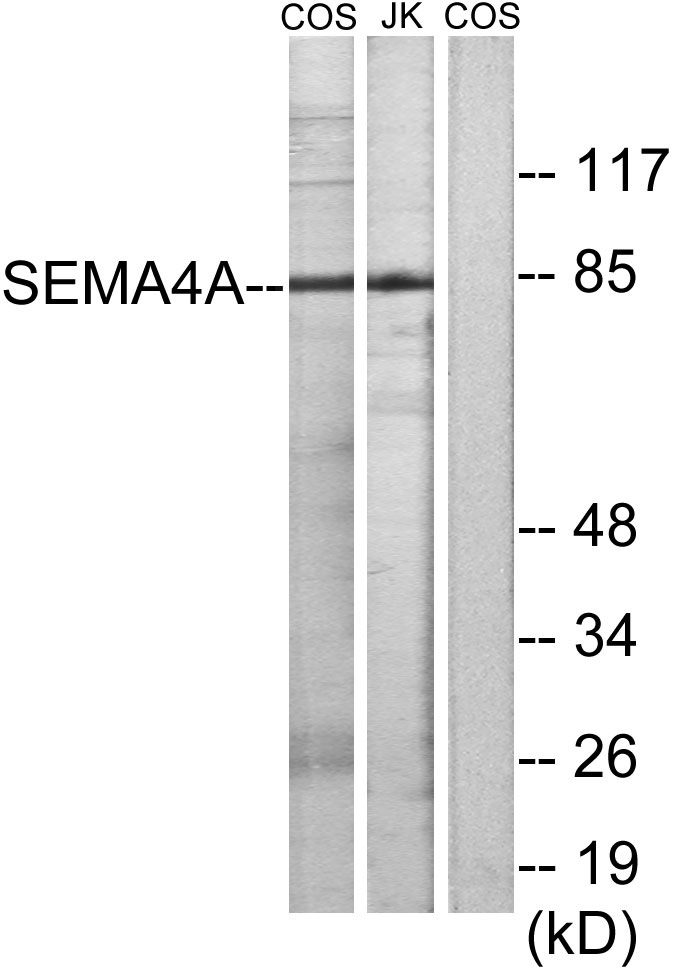
- Observed Band(KD):
- 84kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the semaphorin family of soluble and transmembrane proteins. Semaphorins are involved in numerous functions, including axon guidance, morphogenesis, carcinogenesis, and immunomodulation. The encoded protein is a single-pass type I membrane protein containing an immunoglobulin-like C2-type domain, a PSI domain and a sema domain. It inhibits axonal extension by providing local signals to specify territories inaccessible for growing axons. It is an activator of T-cell-mediated immunity and suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated endothelial cell migration and proliferation in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo. Mutations in this gene are associated with retinal degenerative diseases including retinitis pigmentosa type 35 (RP35) and cone-rod dystrophy type 10 (CORD10). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identif
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SEMA4A are the cause of cone-rod dystrophy type 10 (CORD10) [MIM:610283]. CORDs are inherited retinal dystrophies belonging to the group of pigmentary retinopathies. CORDs are characterized by retinal pigment deposits visible on fundus examination, predominantly in the macular region, and initial loss of cone photoreceptors followed by rod degeneration. This leads to decreased visual acuity and sensitivity in the central visual field, followed by loss of peripheral vision. Severe loss of vision occurs earlier than in retinitis pigmentosa.,disease:Defects in SEMA4A are the cause of retinitis pigmentosa type 35 (RP35) [MIM:610282]. RP leads to degeneration of retinal photoreceptor cells. Patients typically have night vision blindness and loss of midperipheral visual field. As their condition progresses, they lose their far peripheral visual field and eventually central v
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Colon,Mammary gland,Placenta,Salivary gland,Tongue,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using SEMA4A Polyclonal Antibody
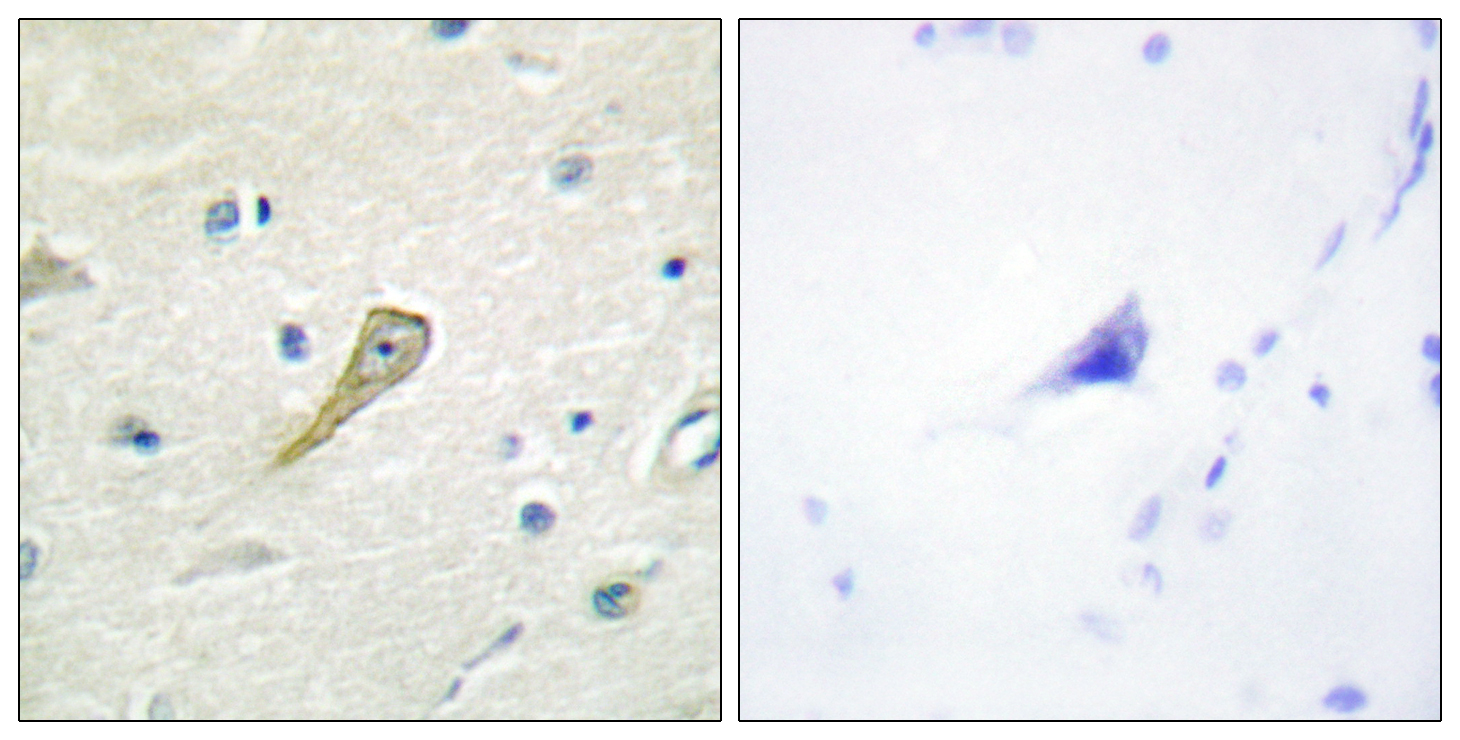
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using SEMA4A Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
- Western blot analysis of lysates from COS7 and Jurkat cells, using SEMA4A Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



