RKIP Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4150
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- RKIP
- Gene Name:
- PEBP1
- Protein Name:
- Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 5037
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P30086
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P70296
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human PEBP1. AA range:105-154
- Specificity:
- RKIP Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of RKIP protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:5000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PEBP1;PBP;PEBP;Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1;PEBP-1;HCNPpp;Neuropolypeptide h3;Prostatic-binding protein;Raf kinase inhibitor protein;RKIP
- Observed Band(KD):
- 23kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the phosphatidylethanolamine-binding family of proteins and has been shown to modulate multiple signaling pathways, including the MAP kinase (MAPK), NF-kappa B, and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) signaling pathways. The encoded protein can be further processed to form a smaller cleavage product, hippocampal cholinergic neurostimulating peptide (HCNP), which may be involved in neural development. This gene has been implicated in numerous human cancers and may act as a metastasis suppressor gene. Multiple pseudogenes of this gene have been identified in the genome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015],
- Function:
- disease:Stomatin is deficient in overhydrated hereditary stomatocytosis (OHS); also known as cryohydrocytosis or hereditary stomatocytosis. OHS results in red cell anomaly associated with hemolytic anemia. There is increased Na(+)/K(+)-permeability and hence a disorder of cell volume control. The nature of the molecular defect underlying OHS is unknown.,function:Binds ATP, opioids and phosphatidylethanolamine. Has lower affinity for phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine. Serine protease inhibitor which inhibits thrombin, neuropsin and chymotrypsin but not trypsin, tissue type plasminogen activator and elastase.,function:HCNP may be involved in the function of the presynaptic cholinergic neurons of the central nervous system. HCNP increases the production of choline acetyltransferase but not acetylcholinesterase. Seems to be mediated by a specific receptor.,function:Thought to regu
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm .
- Expression:
- Bone marrow,Brain,Cajal-Retzius cell,Epithelium,Erythrocyte
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using RKIP Polyclonal Antibody
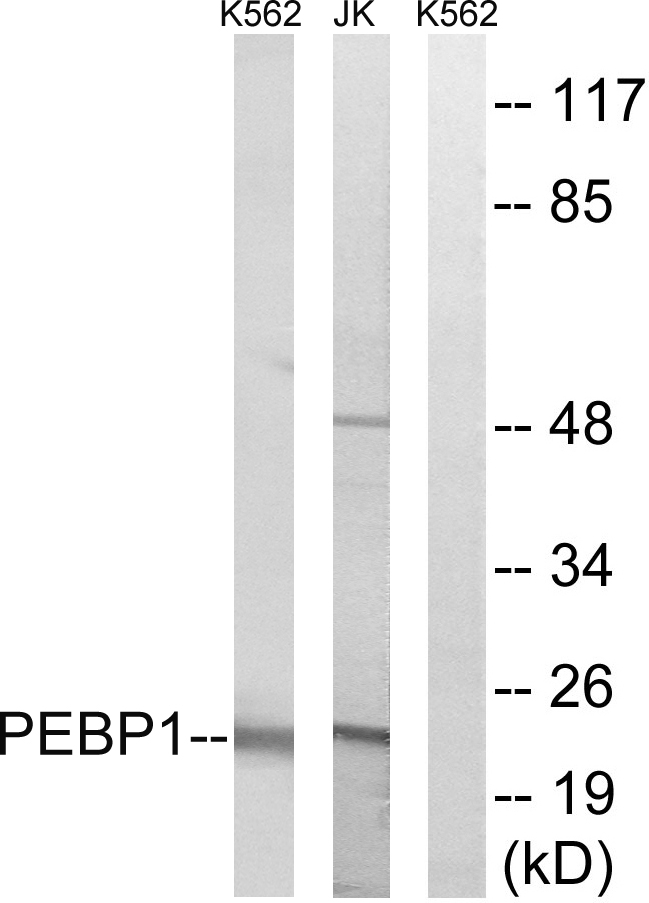
- Western blot analysis of lysates from Jurkat and K562 cells, using PEBP1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
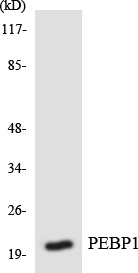
- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HepG2 cells using PEBP1 antibody.
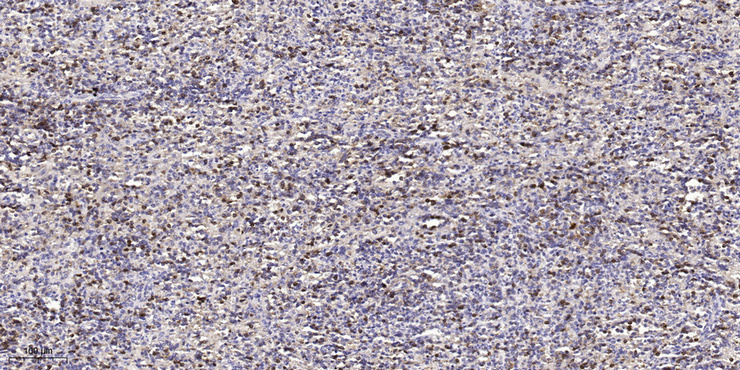
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human spleen tissue. 1,primary Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antigen retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 30min) Negtive control was used by secondary antibody only.)



