RARα Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT4007
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- RARα
- Fields:
- >>Th17 cell differentiation;>>Estrogen signaling pathway;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Transcriptional misregulation in cancer;>>Acute myeloid leukemia
- Gene Name:
- RARA
- Protein Name:
- Retinoic acid receptor alpha
- Human Gene Id:
- 5914
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P10276
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 19401
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P11416
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Retinoic Acid Receptor alpha. AA range:46-95
- Specificity:
- RARα Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of RARα protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- RARA;NR1B1;Retinoic acid receptor alpha;RAR-alpha;Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group B member 1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 51kD
- Background:
- This gene represents a nuclear retinoic acid receptor. The encoded protein, retinoic acid receptor alpha, regulates transcription in a ligand-dependent manner. This gene has been implicated in regulation of development, differentiation, apoptosis, granulopoeisis, and transcription of clock genes. Translocations between this locus and several other loci have been associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this locus.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010],
- Function:
- disease:Chromosomal aberrations involving RARA may be a cause of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) [MIM:612376]. Translocation t(11;17)(q32;q21) with ZBTB16/PLZF; translocation t(15;17)(q21;q21) with PML; translocation t(5;17)(q32;q11) with NPM.,domain:Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal steroid-binding domain.,function:This is a receptor for retinoic acid. This metabolite has profound effects on vertebrate development. Retinoic acid is a morphogen and is a powerful teratogen. This receptor controls cell function by directly regulating gene expression.,online information:Retinoic acid receptor entry,PTM:Phosphorylated. Phosphorylation does not change during cell cycle. Phosphorylation on Ser-77 is crucial for transcriptional activity.,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family.,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Nuclear localization depends on ligand binding, phosphorylation and sumoylation (PubMed:19850744). Translocation to the nucleus in the absence of ligand is dependent on activation of PKC and the downstream MAPK phosphorylation (By similarity). Increased nuclear localization upon pulsatile shear stress (PubMed:28167758). .
- Expression:
- Expressed in monocytes.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
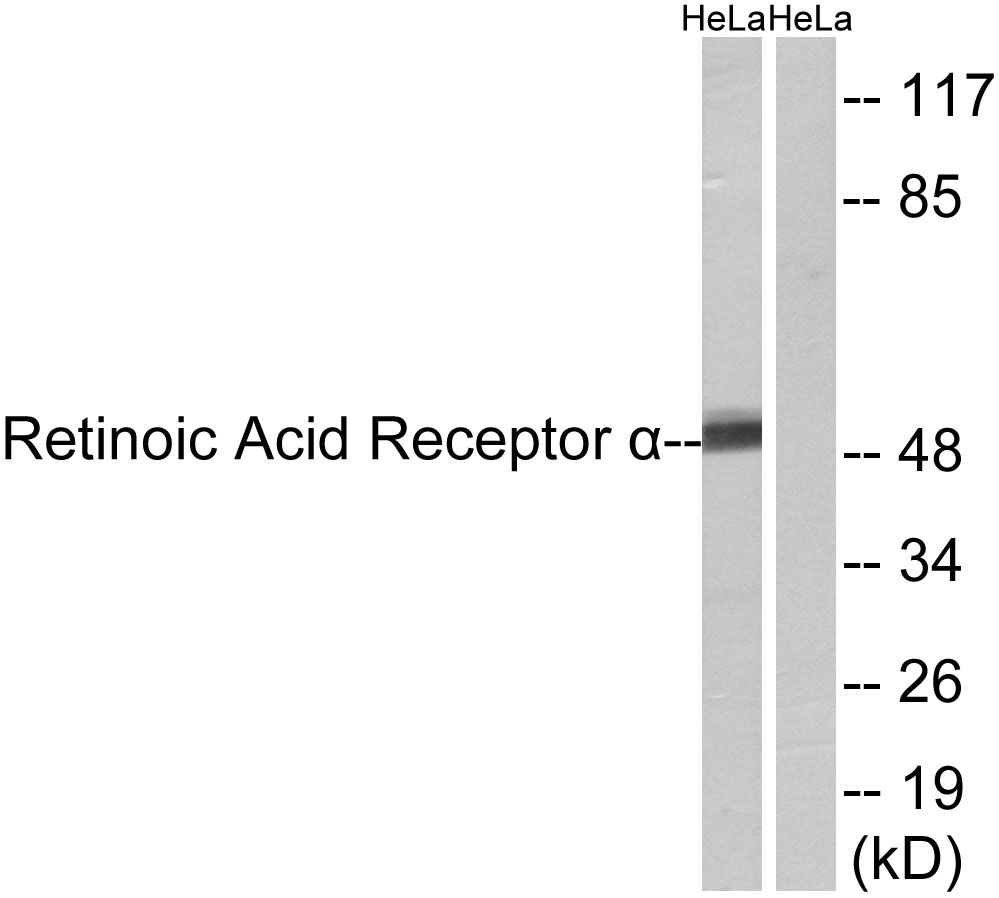
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa cells, using Retinoic Acid Receptor alpha Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.

- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HepG2 cells using Retinoic Acid Receptor α antibody.
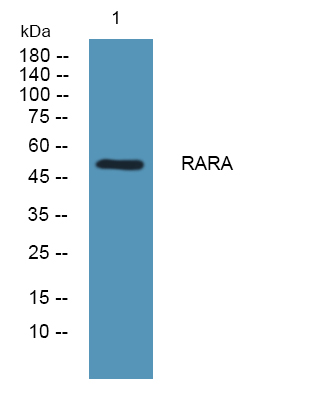
- Western blot analysis of lysates from KB cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night

- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human small intestinal carcinoma tissue. 1,primary Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Sodium citrate pH 6.0 was used for antigen retrieval(>98°C,20min). 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200


