PAH Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT3568
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- PAH
- Fields:
- >>Phenylalanine metabolism;>>Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis;>>Folate biosynthesis;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Biosynthesis of amino acids
- Gene Name:
- PAH
- Protein Name:
- Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase
- Human Gene Id:
- 5053
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P00439
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 18478
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P16331
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P04176
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human PAH. AA range:351-400
- Specificity:
- PAH Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PAH protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:40000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PAH;Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase;PAH;Phe-4-monooxygenase
- Observed Band(KD):
- 51kD
- Background:
- PAH encodes the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase that is the rate-limiting step in phenylalanine catabolism. Deficiency of this enzyme activity results in the autosomal recessive disorder phenylketonuria. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:L-phenylalanine + tetrahydrobiopterin + O(2) = L-tyrosine + 4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin.,cofactor:Fe(2+) ion.,disease:Defects in PAH are the cause of hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) [MIM:261600]. HPA is the mildest form of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.,disease:Defects in PAH are the cause of non-phenylketonuria hyperphenylalaninemia (Non-PKU HPA) [MIM:261600]. Non-PKU HPA is a mild form of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency characterized by phenylalanine levels persistently below 600 mumol, which allows normal intellectual and behavioral development without treatment. Non-PKU HPA is usually caused by the combined effect of a mild hyperphenylalaninemia mutation and a severe one.,disease:Defects in PAH are the cause of phenylketonuria (PKU) [MIM:261600]. PKU is an autosomal recessive inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism, due to severe phenylalanine hydroxylas
- Subcellular Location:
- cytosol,extracellular exosome,
- Expression:
- Liver,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
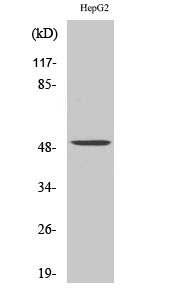
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using PAH Polyclonal Antibody
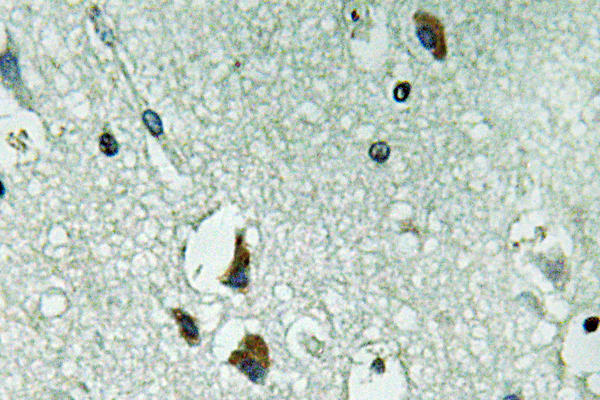
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of PAH antibody in paraffin-embedded human brain tissue.

- Western blot analysis of lysate from HepG2 cells, using PAH antibody.



