Neurofibromin Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT3065
- Applications:WB;IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Neurofibromin
- Fields:
- >>EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance;>>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Ras signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- NF1
- Protein Name:
- Neurofibromin
- Human Gene Id:
- 4763
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P21359
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 18015
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q04690
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24592
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P97526
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human NF1. AA range:1551-1600
- Specificity:
- Neurofibromin Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Neurofibromin protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:50-300
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- NF1;Neurofibromin;Neurofibromatosis-related protein NF-1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 319kD
- Background:
- This gene product appears to function as a negative regulator of the ras signal transduction pathway. Mutations in this gene have been linked to neurofibromatosis type 1, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia and Watson syndrome. The mRNA for this gene is subject to RNA editing (CGA>UGA->Arg1306Term) resulting in premature translation termination. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have also been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- alternative products:Experimental confirmation may be lacking for some isoforms,caution:Was originally (PubMed:8807336) thought to be associated with LEOPARD (LS), an autosomal dominant syndrome.,disease:Defects in NF1 are a cause of familial spinal neurofibromatosis (spinal NF) [MIM:162210]. Familial spinal NF is considered to be an alternative form of neurofibromatosis, showing multiple spinal tumors.,disease:Defects in NF1 are a cause of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) [MIM:607785]. JMML is a pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome that constitutes approximately 30% of childhood cases of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and 2% of leukemia. Germline mutations of NF1 account for the association of JMML with type 1 neurofibromatosis (NF1).,disease:Defects in NF1 are a cause of neurofibromatosis-Noonan syndrome (NFNS) [MIM:601321]. NFNS is characterized by manifestations of both NF1 and
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Nucleus, nucleolus .
- Expression:
- Detected in brain, peripheral nerve, lung, colon and muscle.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
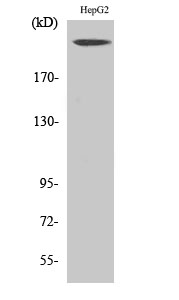
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Neurofibromin Polyclonal Antibody
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of HepG2 cells using Neurofibromin Polyclonal Antibody
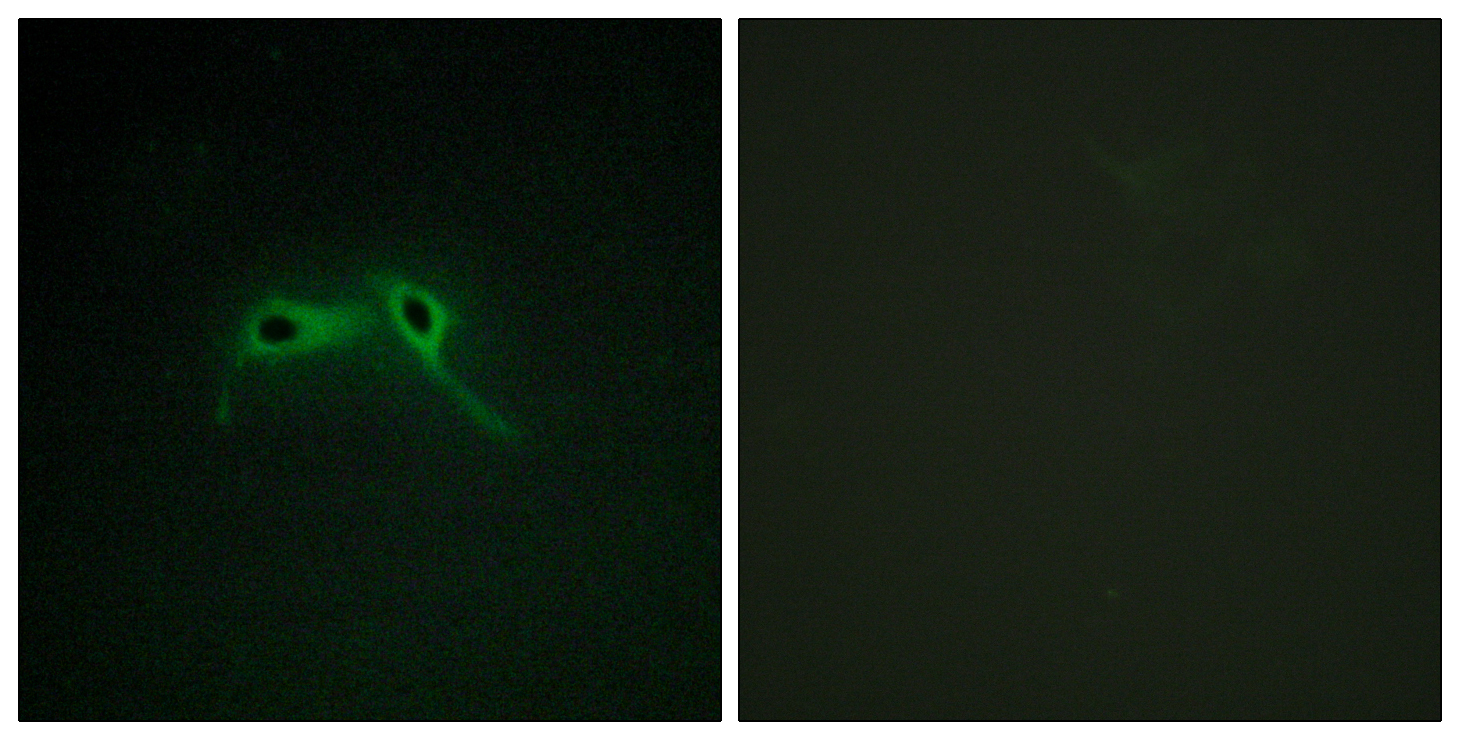
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HepG2 cells, using NF1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
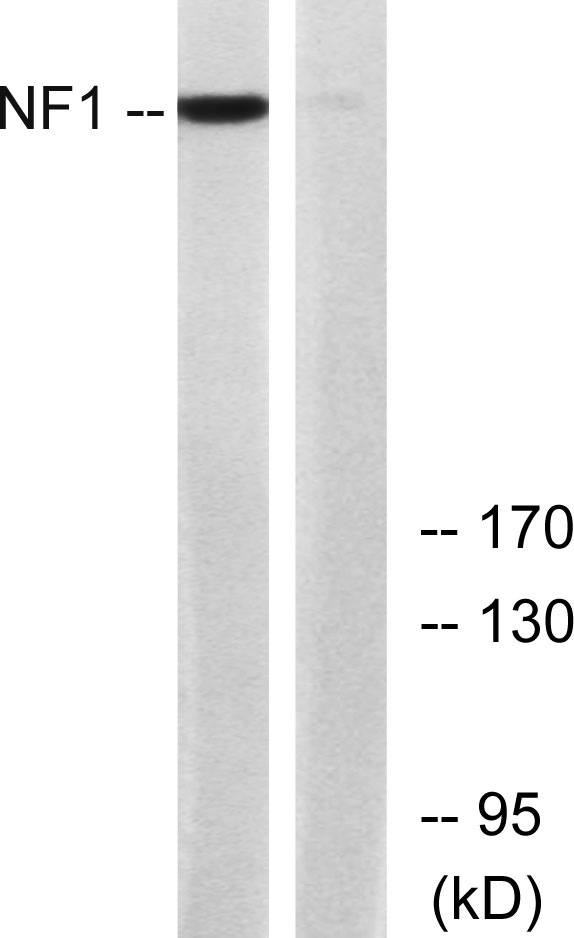

- Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2 cells, using NF1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
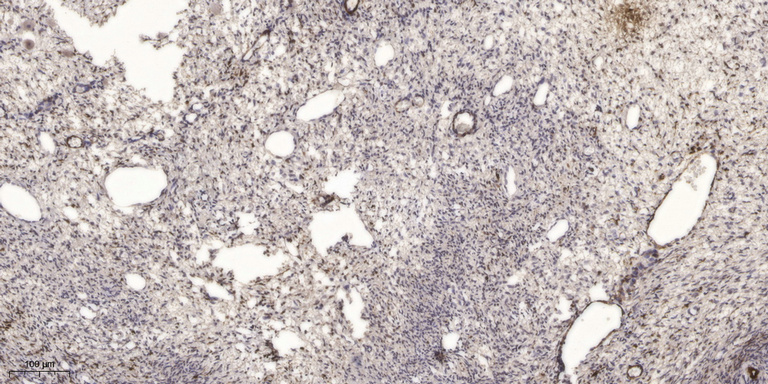
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human oophoroma. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



