MLH3 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT2781
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- MLH3
- Fields:
- >>Mismatch repair
- Gene Name:
- MLH3
- Protein Name:
- DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh3
- Human Gene Id:
- 27030
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9UHC1
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human MLH3. AA range:521-570
- Specificity:
- MLH3 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of MLH3 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:40000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- MLH3;DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh3;MutL protein homolog 3
- Observed Band(KD):
- 164kD
- Background:
- This gene is a member of the MutL-homolog (MLH) family of DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes. MLH genes are implicated in maintaining genomic integrity during DNA replication and after meiotic recombination. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a heterodimer with other family members. Somatic mutations in this gene frequently occur in tumors exhibiting microsatellite instability, and germline mutations have been linked to hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer type 7 (HNPCC7). Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified, but the full-length nature of only two transcript variants has been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in MLH3 are a cause of somatic colorectal cancer (CRC) [MIM:114500].,disease:Defects in MLH3 are the cause of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer type 7 (HNPCC7) [MIM:604395]. Mutations in more than one gene locus can be involved alone or in combination in the production of the HNPCC phenotype (also called Lynch syndrome). Most families with clinically recognized HNPCC have mutations in either MLH1 or MSH2 genes. HNPCC is an autosomal, dominantly inherited disease associated with marked increase in cancer susceptibility. It is characterized by a familial predisposition to early onset colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and extra-colonic cancers of the gastrointestinal, urological and female reproductive tracts. HNPCC is reported to be the most common form of inherited colorectal cancer in the Western world, and accounts for 15% of all colon cancers. Cancers in HNPCC origina
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus .
- Expression:
- Ubiquitous.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
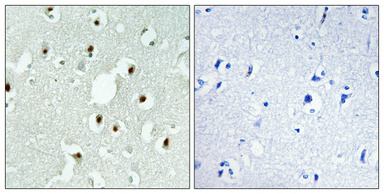
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Human brain. Antibody was diluted at 1:100(4° overnight). High-pressure and temperature Tris-EDTA,pH8.0 was used for antigen retrieval. Negetive contrl (right) obtaned from antibody was pre-absorbed by immunogen peptide.

- Western blot analysis of lysates from K562 and HT-29 cells, using MLH3 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



