MaxiKβ Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT2667
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- MaxiKβ
- Fields:
- >>cGMP-PKG signaling pathway;>>Vascular smooth muscle contraction;>>Insulin secretion
- Gene Name:
- KCNMB4
- Protein Name:
- Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-4
- Human Gene Id:
- 27345
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q86W47
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 58802
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9JIN6
- Rat Gene Id:
- 66016
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9ESK8
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human MaxiKbeta. AA range:70-119
- Specificity:
- MaxiKβ Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of MaxiKβ protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- KCNMB4;Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-4;BK channel subunit beta-4;BKbeta4;Hbeta4;Calcium-activated potassium channel; subfamily M subunit beta-4;Charybdotoxin receptor subunit beta-4;K(VCA)beta-4;Maxi K channel sub
- Observed Band(KD):
- 24kD
- Background:
- MaxiK channels are large conductance, voltage and calcium-sensitive potassium channels which are fundamental to the control of smooth muscle tone and neuronal excitability. MaxiK channels can be formed by 2 subunits: the pore-forming alpha subunit and the modulatory beta subunit. The protein encoded by this gene is an auxiliary beta subunit which slows activation kinetics, leads to steeper calcium sensitivity, and shifts the voltage range of current activation to more negative potentials than does the beta 1 subunit. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:Resistance to charybdotoxin (CTX) toxin is mediated by the extracellular domain.,function:Regulatory subunit of the calcium activated potassium KCNMA1 (maxiK) channel. Modulates the calcium sensitivity and gating kinetics of KCNMA1, thereby contributing to KCNMA1 channel diversity. Decreases the gating kinetics and calcium sensitivity of the KCNMA1 channel, but with fast deactivation kinetics. May decrease KCNMA1 channel openings at low calcium concentrations but increases channel openings at high calcium concentrations. Makes KCNMA1 channel resistant to 100 nM charybdotoxin (CTX) toxin concentrations.,miscellaneous:Treatment with okadaic acid reduces its effect on KCNMA1.,PTM:N-glycosylated. A highly glycosylated form is promoted by KCNMA1. Glycosylation, which is not required for the interaction with KCNMA1 and subcellular location, increases protection against charybdotoxin.,PT
- Subcellular Location:
- Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
- Expression:
- Predominantly expressed in brain. In brain, it is expressed in the cerebellum, cerebral cortex, medulla, spinal cord, occipital pole, frontal lobe, temporal lobe, putamen, amygdala, caudate nucleus, corpus callosum, hippocampus, substantia nigra and thalamus. Weakly or not expressed in other tissues.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using MaxiKβ Polyclonal Antibody
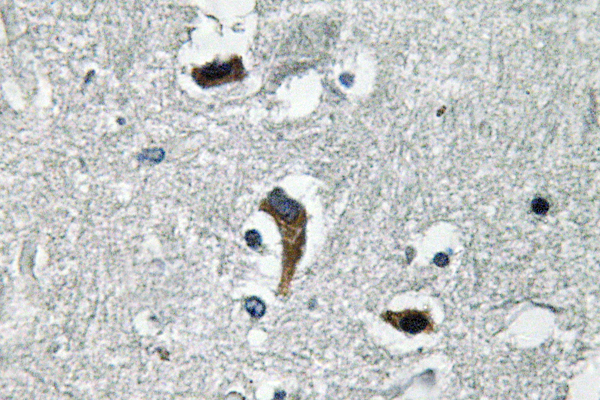
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of MaxiKβ antibody in paraffin-embedded human brain tissue.

- Western blot analysis of lysate from HepG2 cells, using MaxiKβ antibody.



