KV1.5 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT2507
- Applications:WB;ELISA;IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- KV1.5
- Gene Name:
- KCNA5
- Protein Name:
- Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 5
- Human Gene Id:
- 3741
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P22460
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 16493
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q61762
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25470
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P19024
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human KCNA5. AA range:253-302
- Specificity:
- KV1.5 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of KV1.5 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:50-300; ELISA 2000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- KCNA5;Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 5;HPCN1;Voltage-gated potassium channel HK2;Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv1.5
- Observed Band(KD):
- 68kD
- Background:
- Potassium channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ino channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. Four sequence-related potassium channel genes - shaker, shaw, shab, and shal - have been identified in Drosophila, and each has been shown to have human homolog(s). This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, shaker-related subfamily. This member contains six membrane-spanning domains with a shaker-type repeat in the fourth segment. It belongs to the delayed rectifier class, the function of which could restore the resting membrane potential of beta cells after depolarization and thereby contribute to the regulation of
- Function:
- disease:Defects in KCNA5 are the cause of atrial fibrillation familial type 7 (ATFB7) [MIM:612240]. Atrial fibrillation is a common disorder of cardiac rhythm that is hereditary in a small subgroup of patients. It is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity, progressive deterioration of atrial electromechanical function and ineffective pumping of blood into the ventricles. It can be associated with palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure.,domain:The amino terminus may be important in determining the rate of inactivation of the channel while the C-terminal PDZ-binding motif may play a role in modulation of channel activity and/or targeting of the channel to specific subcellular compartments.,domain:The segment S4 is probably the voltage-sensor and is characterized by a series of positively charged amino acids at every third position.,func
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Pancreatic islets and insulinoma.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
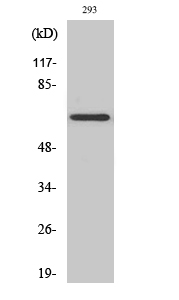
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using KV1.5 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
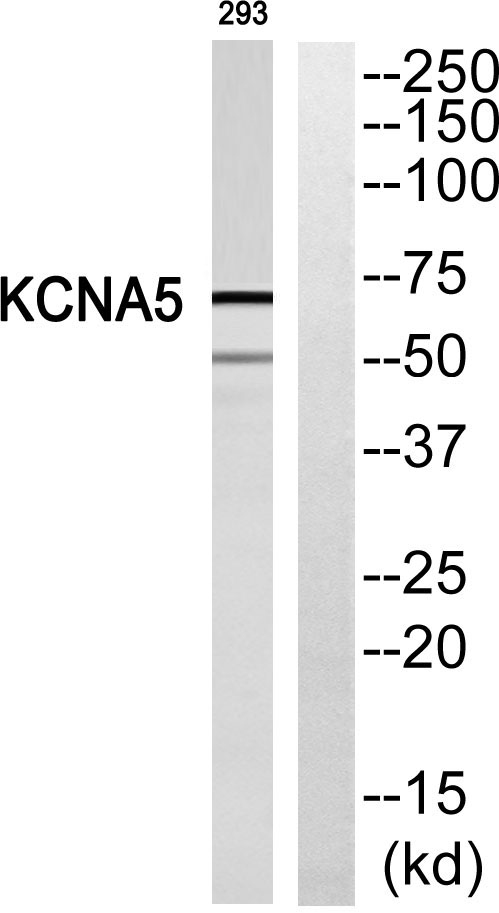
- Western blot analysis of KCNA5 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the KCNA5 peptide.

- Western blot analysis of 293T with KV1.5 Rabbit pAb diluted at 1:2,000.
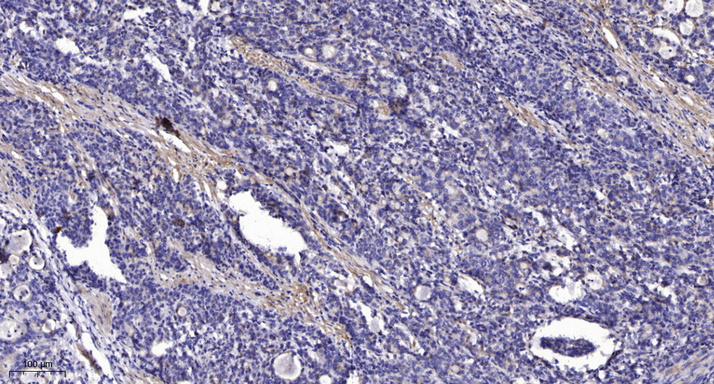
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human Gastric adenocarcinoma. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



