GlyRβ Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1935
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- GlyRβ
- Fields:
- >>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction
- Gene Name:
- GLRB
- Protein Name:
- Glycine receptor subunit beta
- Human Gene Id:
- 2743
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P48167
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14658
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P48168
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25456
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P20781
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human GLRB. AA range:211-260
- Specificity:
- GlyRβ Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of GlyRβ protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:40000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GLRB;Glycine receptor subunit beta;Glycine receptor 58 kDa subunit
- Observed Band(KD):
- 56kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes the beta subunit of the glycine receptor, which is a pentamer composed of alpha and beta subunits. The receptor functions as a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel, which produces hyperpolarization via increased chloride conductance due to the binding of glycine to the receptor. Mutations in this gene cause startle disease, also known as hereditary hyperekplexia or congenital stiff-person syndrome, a disease characterized by muscular rigidity. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in GLRB are a cause of startle disease (STHE) [MIM:149400]; also known as hereditary hyperekplexia or congenital stiff-person syndrome. STHE is a genetically heterogeneous neurologic disorder characterized by muscular rigidity of central nervous system origin, particularly in the neonatal period, and by an exaggerated startle response to unexpected acoustic or tactile stimuli. Inheritance can be autosomal dominant or recessive.,function:The glycine receptor is a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel. Binding of glycine to its receptor increases the chloride conductance and thus produces hyperpolarization (inhibition of neuronal firing).,similarity:Belongs to the ligand-gated ionic channel (TC 1.A.9) family.,subunit:Pentamer composed of alpha and beta subunits. Interacts with GPHN.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell junction, synapse . Cell projection, dendrite . Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cytoplasm . Retained in the cytoplasm upon heterologous expression by itself. Coexpression with GPHN promotes expression at the cell membrane (PubMed:12684523). Coexpression with GLRA1, GLRA2 or GLRA3 promotes expression at the cell membrane. .
- Expression:
- Brain,Hippocampus,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
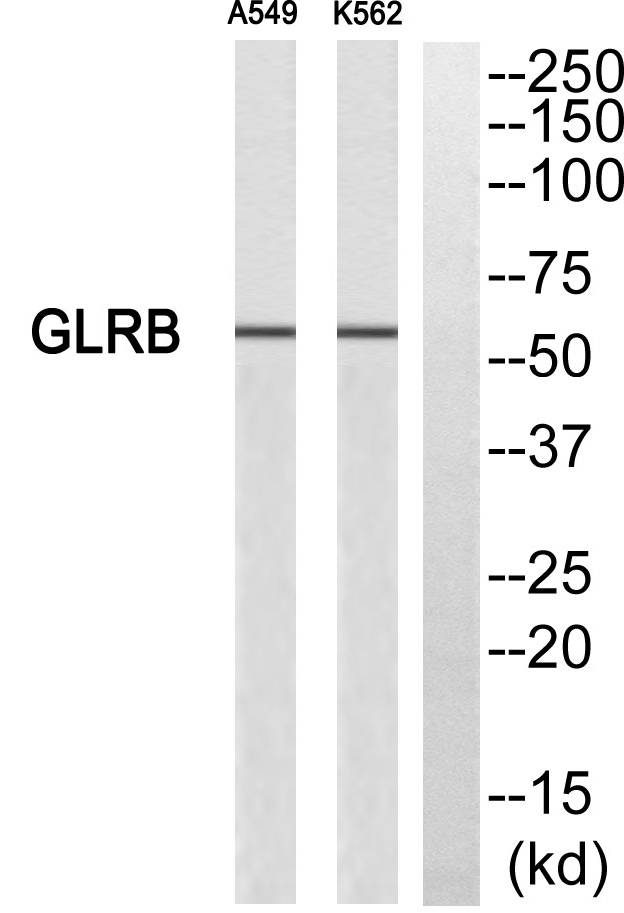
- Western blot analysis of GLRB Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the GLRB peptide.

- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HUVECcells using GLRB antibody.



