GAD67 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1831
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- GAD67
- Fields:
- >>Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism;>>beta-Alanine metabolism;>>Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism;>>Butanoate metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>GABAergic synapse;>>Type I diabetes mellitus
- Gene Name:
- GAD1
- Protein Name:
- Glutamate decarboxylase 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 2571
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q99259
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14415
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P48318
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24379
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P18088
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human GAD1. AA range:471-520
- Specificity:
- GAD67 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of GAD67 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GAD1;GAD;GAD67;Glutamate decarboxylase 1;67 kDa glutamic acid decarboxylase;GAD-67;Glutamate decarboxylase 67 kDa isoform
- Observed Band(KD):
- 67kD
- Background:
- glutamate decarboxylase 1(GAD1) Homo sapiens This gene encodes one of several forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase, identified as a major autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes. The enzyme encoded is responsible for catalyzing the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid from L-glutamic acid. A pathogenic role for this enzyme has been identified in the human pancreas since it has been identified as an autoantigen and an autoreactive T cell target in insulin-dependent diabetes. This gene may also play a role in the stiff man syndrome. Deficiency in this enzyme has been shown to lead to pyridoxine dependency with seizures. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two products, the predominant 67-kD form and a less-frequent 25-kD form. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:L-glutamate = 4-aminobutanoate + CO(2).,cofactor:Pyridoxal phosphate.,disease:Defects in GAD1 are the cause of autosomal recessive symmetric spastic cerebral palsy (SCP) [MIM:603513]. Cerebral palsy (CP) is an heterogeneous group of neurological disorders of movement and/or posture, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 250 to 1'000 live births, making CP one the commonest congenital disabilities. Non-progressive forms of symmetrical, spastic CP have been identified, which show a Mendelian autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. Patients present developmental delay, mental retardation and sometimes epilepsy as part of the phenotype.,function:Catalyzes the production of GABA.,online information:Glutamate decarboxylase entry,similarity:Belongs to the group II decarboxylase family.,subunit:Homodimer.,tissue specificity:Isoform 3 is expressed in pancreatic islets, testis
- Subcellular Location:
- intracellular,plasma membrane,vesicle membrane,presynaptic active zone,clathrin-sculpted gamma-aminobutyric acid transport vesicle membrane,
- Expression:
- [Isoform 1]: Expressed in brain. ; [Isoform 3]: Expressed in pancreatic islets, testis, adrenal cortex, and perhaps other endocrine tissues, but not in brain.
Study on the neuroprotective and sedative effects of the combination of jujuboside B and spinosin from Ziziphi Spinosae Semen Journal of Functional Foods Juntao Wang IHC Mouse hippocampus tissue
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
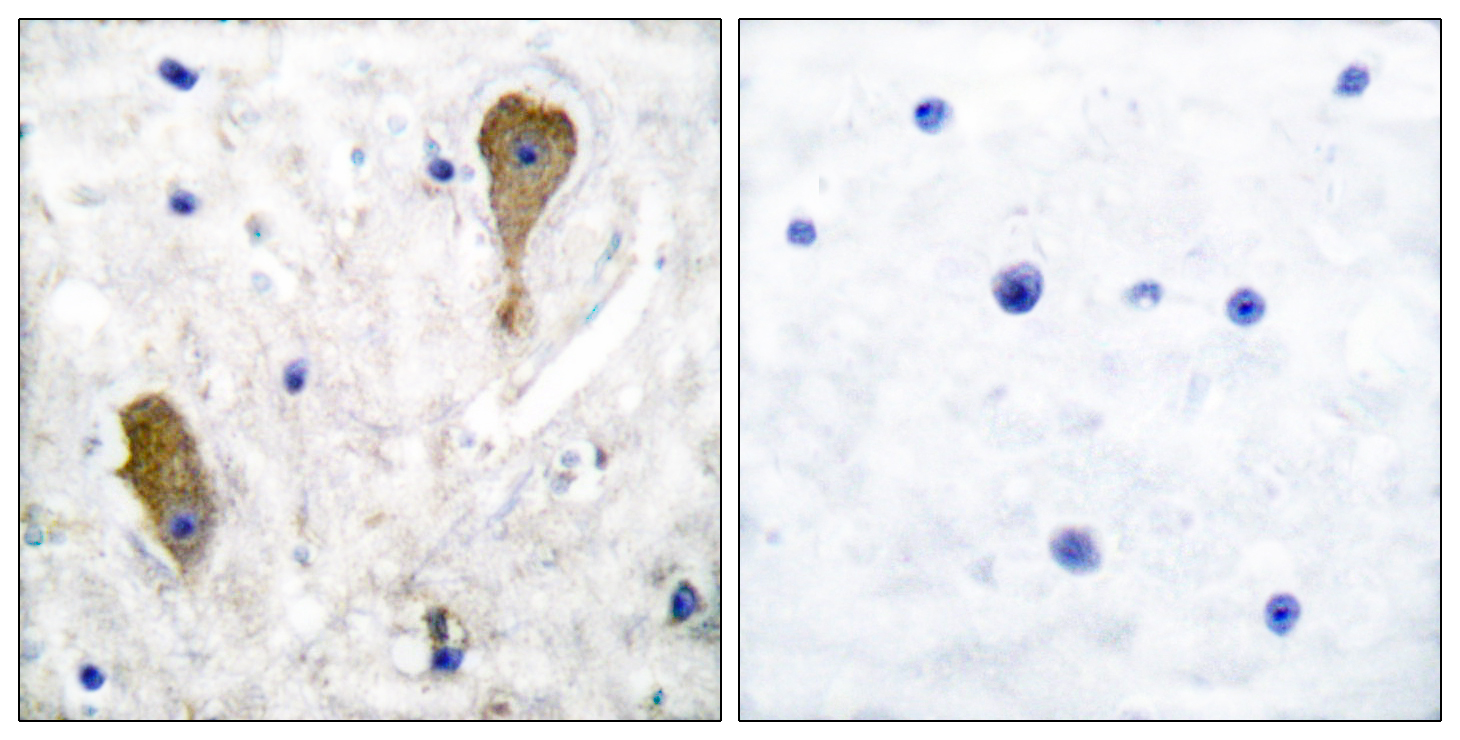
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using GAD1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
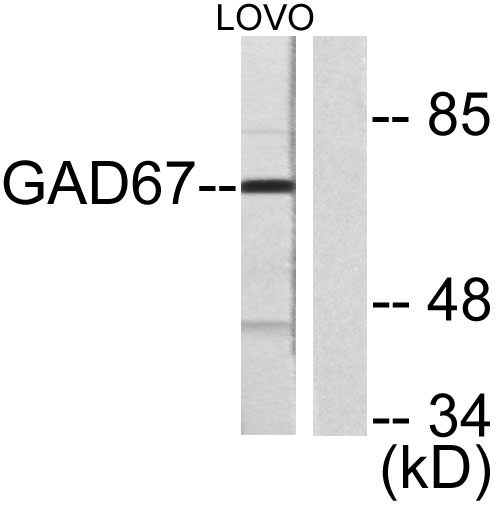
- Western blot analysis of lysates from LOVO cells, using GAD1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



