FGF-23 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1699
- Applications:WB;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- FGF-23
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Ras signaling pathway;>>Rap1 signaling pathway;>>Calcium signaling pathway;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>Regulation of actin cytoskeleton;>>Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Melanoma;>>Breast cancer;>>Gastric cancer
- Gene Name:
- FGF23
- Protein Name:
- Fibroblast growth factor 23
- Human Gene Id:
- 8074
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9GZV9
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 64654
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9EPC2
- Rat Gene Id:
- 170583
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q8VI82
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human FGF23. AA range:151-200
- Specificity:
- FGF-23 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of FGF-23 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:20000. IF 1:100-300 Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- FGF23;HYPF;Fibroblast growth factor 23;FGF-23;Phosphatonin;Tumor-derived hypophosphatemia-inducing factor
- Observed Band(KD):
- 27kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the fibroblast growth factor family of proteins, which possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities and are involved in a variety of biological processes. The product of this gene regulates phosphate homeostasis and transport in the kidney. The full-length, functional protein may be deactivated via cleavage into N-terminal and C-terminal chains. Mutation of this cleavage site causes autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets (ADHR). Mutations in this gene are also associated with hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC). [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2013],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in FGF23 are a cause of hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC) [MIM:211900]. HFTC is a severe autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that manifests with hyperphosphatemia and massive calcium deposits in the skin and subcutaneous tissues.,disease:Defects in FGF23 are the cause of autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets (ADHR) [MIM:193100]. ADHR is characterized by low serum phosphorus concentrations, rickets, osteomalacia, leg deformities, short stature, bone pain and dental abscesses.,PTM:After secretion it is processed into a N-terminal fragment and a C-terminal fragment. The processing is effected by the proprotein convertases.,similarity:Belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted . Secretion is dependent on O-glycosylation.
- Expression:
- Expressed in osteogenic cells particularly during phases of active bone remodeling. In adult trabecular bone, expressed in osteocytes and flattened bone-lining cells (inactive osteoblasts).
Effects of selenium-cadmium co-enriched Cardamine hupingshanensis on bone damage in mice ECOTOXICOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY Lin Zhang WB Mouse 1:1000 kidney tissue
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
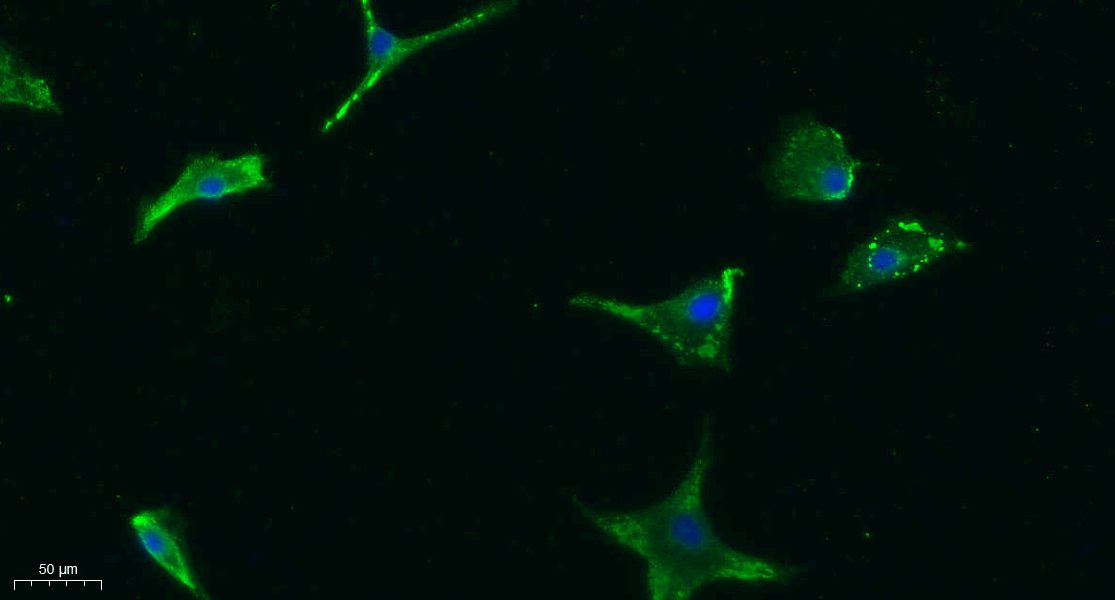
- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549. 1,primary Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4°C overnight). 2, Goat Anti Rabbit IgG (H&L) - Alexa Fluor 488 Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:1000(room temperature, 50min).3, Picture B: DAPI(blue) 10min.

- Western blot analysis of lysates from Jurkat cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night



