FBN1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1684
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- FBN1
- Fields:
- >>TGF-beta signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- FBN1
- Protein Name:
- Fibrillin-1
- Human Gene Id:
- 2200
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P35555
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q61554
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Fibrillin-1. AA range:2811-2860
- Specificity:
- FBN1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of FBN1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- FBN1;FBN;Fibrillin-1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 312kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the fibrillin family of proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate two proteins including the extracellular matrix component fibrillin-1 and the protein hormone asprosin. Fibrillin-1 is an extracellular matrix glycoprotein that serves as a structural component of calcium-binding microfibrils. These microfibrils provide force-bearing structural support in elastic and nonelastic connective tissue throughout the body. Asprosin, secreted by white adipose tissue, has been shown to regulate glucose homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are associated with Marfan syndrome and the related MASS phenotype, as well as ectopia lentis syndrome, Weill-Marchesani syndrome, Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome and neonatal progeroid syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in FBN1 are a cause of isolated ectopia lentis (EL) [MIM:129600]. The symptoms of this autosomal dominant fibrillinopathy overlap with those of Marfan syndrome, with the exclusion of the skeletal and cardiovascular manifestations.,disease:Defects in FBN1 are a cause of Marfan syndrome (MFS) [MIM:154700]. MFS is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects the skeletal, ocular, and cardiovascular systems. A wide variety of skeletal abnormalities occurs with MFS, including scoliosis, chest wall deformity, tall stature, abnormal joint mobility. Ectopia lentis occurs in up to about 80% of MFS patients and is almost always bilateral. The leading cause of premature death in MFS patients is progressive dilation of the aortic root and ascending aorta, causing aortic incompetence and dissection. The majority of the more than 600 mutations in FBN1 currently known are point mutations
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted . Fibrillin-1 and Asprosin chains are still linked together during the secretion from cells, but are subsequently separated by furin (PubMed:24982166). .; [Fibrillin-1]: Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix .; [Asprosin]: Secreted . Secreted by white adipose tissue and circulates in the plasma. .
- Expression:
- Brain,Fibroblast,Liver,Placenta,
Increased RBP4 and Asprosin Are Novel Contributors in Inflammation Process of Periodontitis in Obese Rats INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES Yuwei Zhang WB Rat 1:2000
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
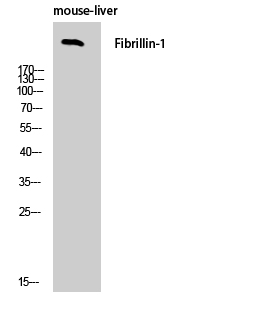
- Western Blot analysis of mouse-liver cells using FBN1 Polyclonal Antibody
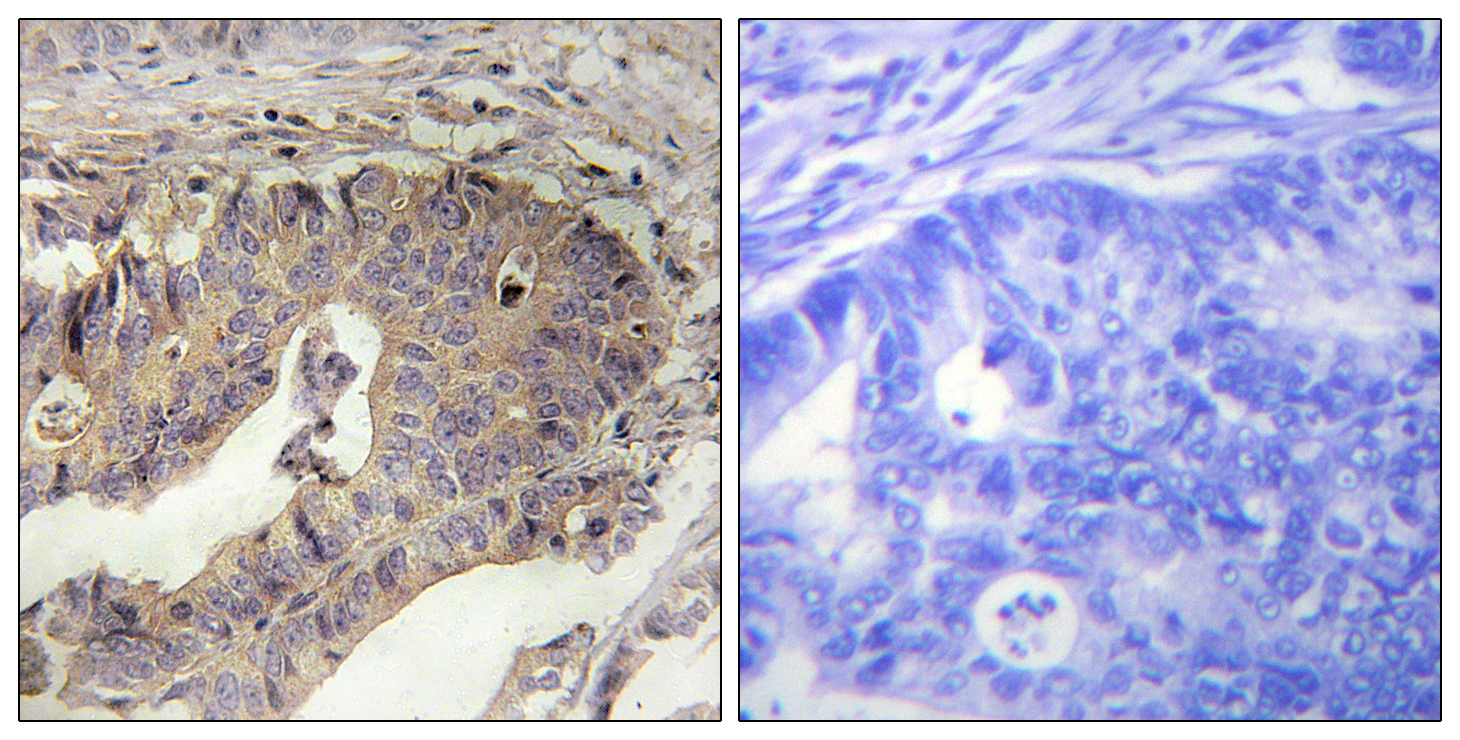
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue, using Fibrillin-1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



