ELOVL4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1538
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- ELOVL4
- Fields:
- >>Fatty acid elongation;>>Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Fatty acid metabolism
- Gene Name:
- ELOVL4
- Protein Name:
- Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 4
- Human Gene Id:
- 6785
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9GZR5
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 83603
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9EQC4
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human ELOVL4. AA range:41-90
- Specificity:
- ELOVL4 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of ELOVL4 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:40000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ELOVL4;Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 4;3-keto acyl-CoA synthase ELOVL4;ELOVL fatty acid elongase 4;ELOVL FA elongase 4
- Observed Band(KD):
- 37kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a membrane-bound protein which is a member of the ELO family, proteins which participate in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Consistent with the expression of the encoded protein in photoreceptor cells of the retina, mutations and small deletions in this gene are associated with Stargardt-like macular dystrophy (STGD3) and autosomal dominant Stargardt-like macular dystrophy (ADMD), also referred to as autosomal dominant atrophic macular degeneration. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in ELOVL4 are the cause of macular dystrophy autosomal dominant chromosome 6-linked (ADMD) [MIM:600110]. A form of macular degeneration characterized by decreased visual acuity, macular atrophy and extensive fundus flecks.,disease:Defects in ELOVL4 are the cause of Stargardt disease type 3 (STGD3) [MIM:600110]. STGD is one of the most frequent causes of macular degeneration in childhood. It is characterized by macular dystrophy with juvenile-onset, rapidly progressive course, alterations of the peripheral retina, and subretinal deposition of lipofuscin-like material. STGD3 inheritance is autosomal dominant.,domain:The di-lysine motif confers endoplasmic reticulum localization for type I membrane proteins.,function:Involved in the biosynthesis of very long chain fatty acids. Seems to represent a photoreceptor-specific component of the fatty acid elongation system residing
- Subcellular Location:
- Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Expressed in the retina and at much lower level in the brain. Ubiquitous, highest expression in thymus, followed by testis, small intestine, ovary, and prostate. Little or no expression in heart, lung, liver, or leukocates.
The tibetan medicine Zuozhu-Daxi can prevent Helicobacter pylori induced-gastric mucosa inflammation by inhibiting lipid metabolism
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
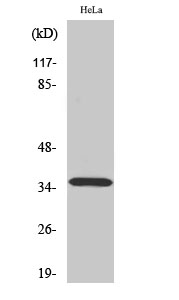
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using ELOVL4 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
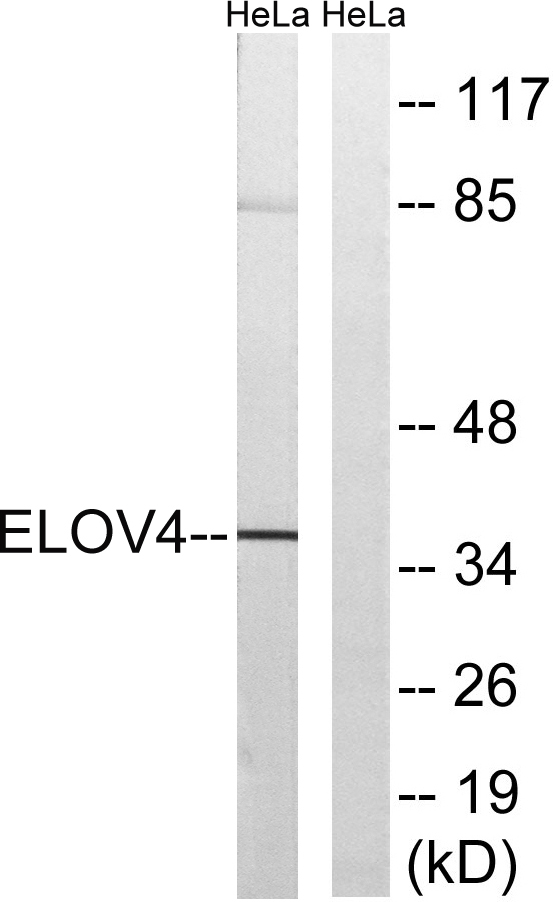
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa cells, using ELOVL4 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



