Dynein IC2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1430
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;Chicken
- Target:
- Dynein IC2
- Fields:
- >>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Huntington disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases
- Gene Name:
- DNAI2
- Protein Name:
- Dynein intermediate chain 2 axonemal
- Human Gene Id:
- 64446
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9GZS0
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 432611
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- A2AC93
- Rat Gene Id:
- 360654
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q66HC9
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human DNAI2. AA range:71-120
- Specificity:
- Dynein IC2 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Dynein IC2 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- DNAI2;Dynein intermediate chain 2; axonemal;Axonemal dynein intermediate chain 2
- Observed Band(KD):
- 70kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the dynein intermediate chain family, and is part of the dynein complex of respiratory cilia and sperm flagella. Mutations in this gene are associated with primary ciliary dyskinesia type 9. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in DNAI2 are the cause of primary ciliary dyskinesia type 9 (CILD9) [MIM:612444]. CILD is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by axonemal abnormalities of motile cilia. Respiratory infections leading to chronic inflammation and bronchiectasis are recurrent, due to defects in the respiratory cilia; reduced fertility is often observed in male patients due to abnormalities of sperm tails. Half of the patients exhibit situs inversus, due to dysfunction of monocilia at the embryonic node and randomization of left-right body asymmetry. Primary ciliary dyskinesia associated with situs inversus is referred to as Kartagener syndrome.,function:Part of the dynein complex of respiratory cilia.,sequence caution:Intron retention.,similarity:Belongs to the dynein intermediate chain family.,similarity:Contains 5 WD repeats.,subunit:Consists of at least two heavy chains and a nu
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium axoneme . Dynein axonemal particle . Located in the proximal region of respiratory cilia. .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in trachea and testis. Expressed in respiratory ciliated cells (at protein level) (PubMed:33139725).
Ammonia inhalation-mediated mir-202-5p leads to cardiac autophagy through PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. CHEMOSPHERE Chemosphere. 2019 Nov;235:858 WB Chicken 1:1000 heart
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western blot analysis of DNAI2 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the DNAI2 peptide.
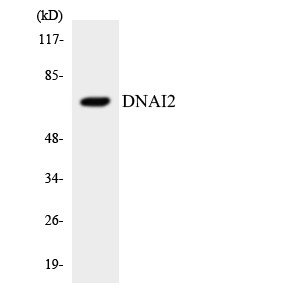
- Western blot analysis of the lysates from RAW264.7cells using DNAI2 antibody.



