Dok-7 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1401
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- Dok-7
- Gene Name:
- DOK7
- Protein Name:
- Protein Dok-7
- Human Gene Id:
- 285489
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q18PE1
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 231134
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q18PE0
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human DOK7. AA range:10-59
- Specificity:
- Dok-7 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Dok-7 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- DOK7;C4orf25;Protein Dok-7;Downstream of tyrosine kinase 7
- Observed Band(KD):
- 60kD
- Background:
- docking protein 7(DOK7) Homo sapiens The protein encoded by this gene is essential for neuromuscular synaptogenesis. The protein functions in aneural activation of muscle-specific receptor kinase, which is required for postsynaptic differentiation, and in the subsequent clustering of the acetylcholine receptor in myotubes. This protein can also induce autophosphorylation of muscle-specific receptor kinase. Mutations in this gene are a cause of familial limb-girdle myasthenia autosomal recessive, which is also known as congenital myasthenic syndrome type 1B. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in DOK7 are the cause of familial limb-girdle myasthenia autosomal recessive (LGM) [MIM:254300]; also called congenital myasthenic syndrome type 1B or CMS1B. LGM is a congenital myasthenic syndrome characterized by a typical 'limb girdle' pattern of muscle weakness with small, simplified neuromuscular junctions but normal acetylcholine receptor and acetylcholinesterase function.,function:Probable muscle-intrinsic activator of MUSK that plays an essential role in neuromuscular synaptogenesis. Acts in aneural activation of MUSK and subsequent acetylcholine receptor (AchR) clustering in myotubes. Induces autophosphorylation of MUSK.,similarity:Contains 1 IRS-type PTB domain.,similarity:Contains 1 PH domain.,subcellular location:Accumulates at neuromuscular junctions.,subunit:Interacts with the cytoplasmic part of MUSK.,tissue specificity:Preferentiall eypressed in skeletal m
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein . Cell junction, synapse . Accumulates at neuromuscular junctions. .
- Expression:
- Preferentially expressed in skeletal muscle and heart. Present in thigh muscle, diaphragm and heart but not in the liver or spleen (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
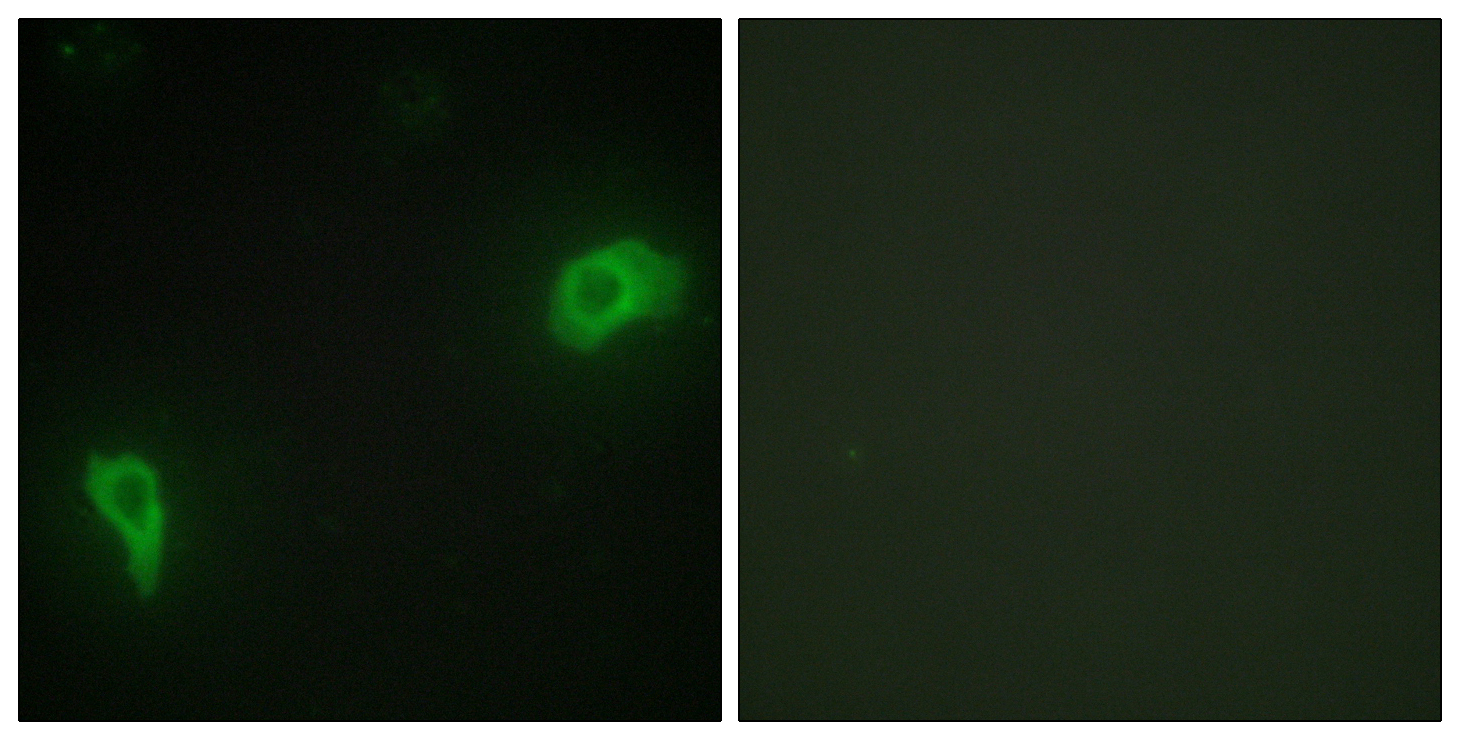
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HepG2 cells, using DOK7 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
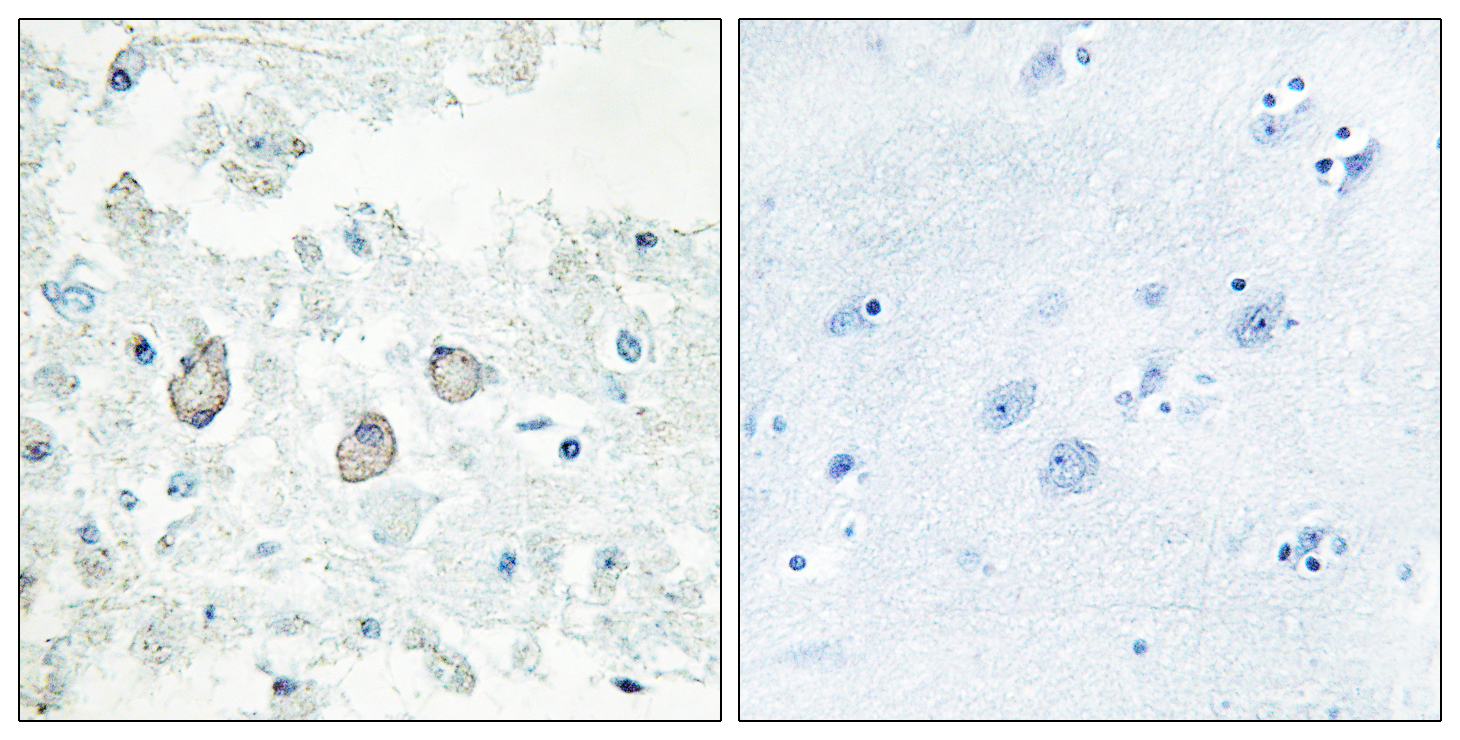
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using DOK7 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
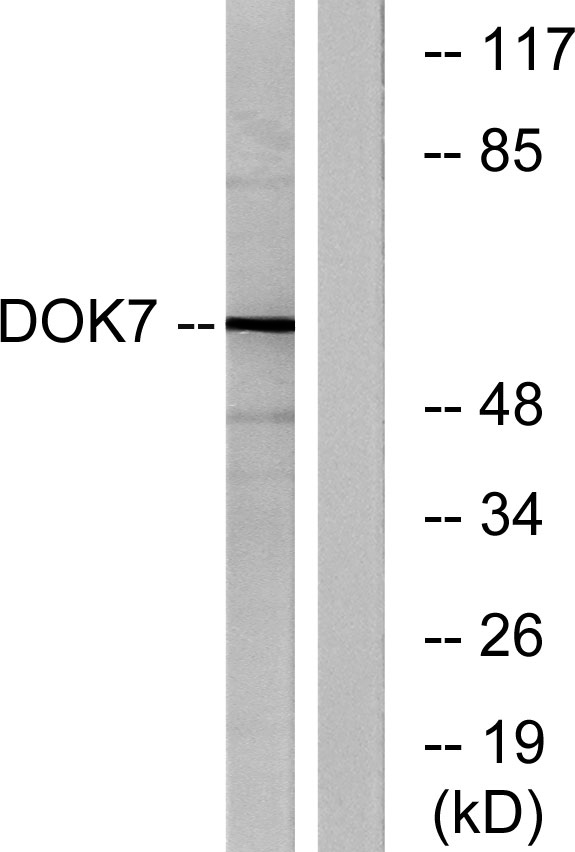
- Western blot analysis of lysates from mouse brain, using DOK7 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



