Dok-4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1398
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- Dok-4
- Gene Name:
- DOK4
- Protein Name:
- Docking protein 4
- Human Gene Id:
- 55715
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8TEW6
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 114255
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q99KE3
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human DOK4. AA range:11-60
- Specificity:
- Dok-4 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Dok-4 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- DOK4;Docking protein 4;Downstream of tyrosine kinase 4;Insulin receptor substrate 5;IRS-5;IRS5
- Observed Band(KD):
- 37kD
- Background:
- domain:PTB domain mediates receptor interaction.,function:DOK proteins are enzymatically inert adaptor or scaffolding proteins. They provide a docking platform for the assembly of multimolecular signaling complexes. DOK4 functions in RET-mediated neurite outgrowth and plays a positive role in activation of the MAP kinase pathway (By similarity). Putative link with downstream effectors of RET in neuronal differentiation. May be involved in the regulation of the immune response induced by T-cells.,PTM:Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues in response to insulin, IGF1 or RET stimulation.,similarity:Belongs to the DOK family. Type B subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 IRS-type PTB domain.,similarity:Contains 1 PH domain.,subunit:Interacts with RET and TEK/TIE2. Interaction with RET is mediated through the PTB domain and requires phosphorylation of RET 'Tyr-1062'.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed. High expression in skeletal muscle, heart, kidney and liver. Weaker expression in spleen, lung and small intestine, brain, heart and. Expressed in both resting and activated peripheral blood T-cells.,
- Function:
- domain:PTB domain mediates receptor interaction.,function:DOK proteins are enzymatically inert adaptor or scaffolding proteins. They provide a docking platform for the assembly of multimolecular signaling complexes. DOK4 functions in RET-mediated neurite outgrowth and plays a positive role in activation of the MAP kinase pathway (By similarity). Putative link with downstream effectors of RET in neuronal differentiation. May be involved in the regulation of the immune response induced by T-cells.,PTM:Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues in response to insulin, IGF1 or RET stimulation.,similarity:Belongs to the DOK family. Type B subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 IRS-type PTB domain.,similarity:Contains 1 PH domain.,subunit:Interacts with RET and TEK/TIE2. Interaction with RET is mediated through the PTB domain and requires phosphorylation of RET 'Tyr-1062'.,tissue specificity:Widely express
- Subcellular Location:
- intracellular,
- Expression:
- Widely expressed. High expression in skeletal muscle, heart, kidney and liver. Weaker expression in spleen, lung and small intestine, brain, heart and. Expressed in both resting and activated peripheral blood T-cells.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
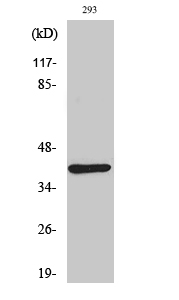
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Dok-4 Polyclonal Antibody
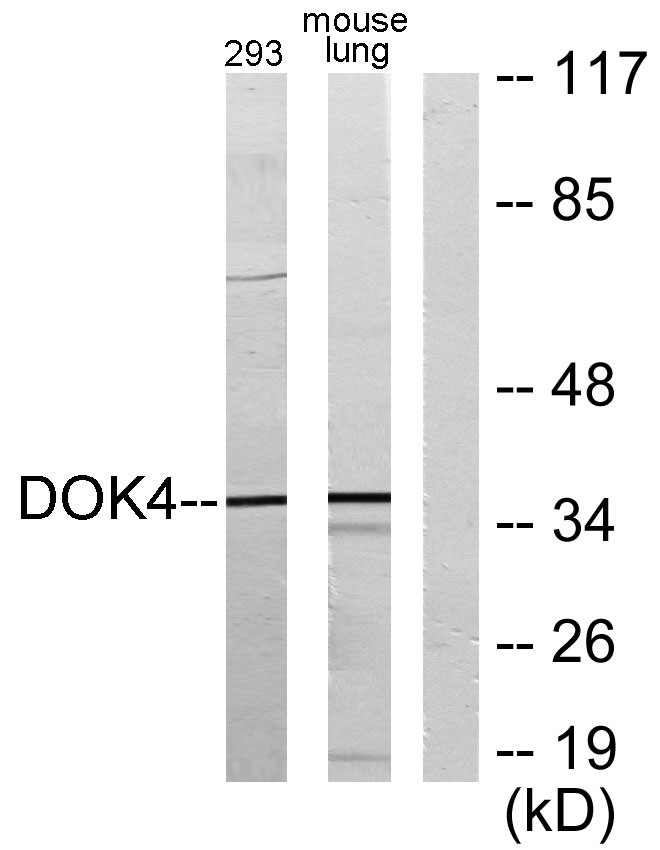
- Western blot analysis of lysates from 293 and mouse lung, using DOK4 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
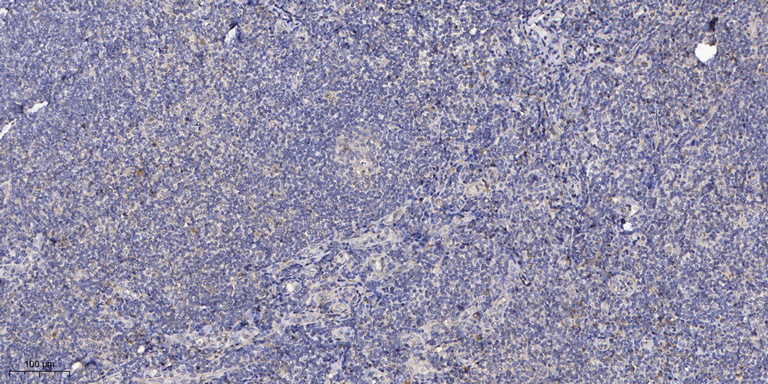
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 30min).



