DNA pol θ Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1376
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- POLQ
- Gene Name:
- POLQ
- Protein Name:
- DNA polymerase theta
- Human Gene Id:
- 10721
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O75417
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human POLQ. AA range:181-230
- Specificity:
- DNA pol θ Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of DNA pol θ protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- POLQ;POLH;DNA polymerase theta;DNA polymerase eta
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 198kD
- Background:
- POLQ (Polymerase (DNA) Theta) is a Protein Coding gene. Among its related pathways are Platinum Pathway, Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics and DNA Double-Strand Break Repair. GO annotations related to this gene include nucleic acid binding and damaged DNA binding. An important paralog of this gene is SNRNP200. NA polymerase that promotes microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ), an alternative non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) machinery triggered in response to double-strand breaks in DNA (PubMed: 25642963, PubMed: 25643323). MMEJ is an error-prone repair pathway that produces deletions of sequences from the strand being repaired and promotes genomic rearrangements, such as telomere fusions, some of them leading to cellular transformation (PubMed: 25642963, PubMed: 25643323). POLQ acts as an inhibitor of homology-recombination repair (HR) pathway by limiting RAD51 accumulation at resected ends (PubMed: 25642963). POLQ-mediated MMEJ may be required to promote the survival of cells with a compromised HR repair pathway, thereby preventing genomic havoc by resolving unrepaired lesions (By similarity). The polymerase acts by binding directly the 2 ends of resected double-strand breaks, allowing microhomologous sequences in the overhangs to form base pairs. It then extends each strand from the base-paired region using the opposing overhang as a template. Requires partially resected DNA containing 2 to 6 base pairs of microhomology to perform MMEJ (PubMed: 25643323). The polymerase activity is highly promiscuous: unlike most polymerases, promotes extension of ssDNA and partial ssDNA (pssDNA) substrates (PubMed: 18503084, PubMed: 21050863, PubMed: 22135286). Also exhibits low-fidelity DNA synthesis, translesion synthesis and lyase activity, and it is implicated in interstrand-cross-link repair, base excision repair and DNA end-joining (PubMed: 14576298, PubMed: 18503084, PubMed: 19188258, PubMed: 24648516). Involved in somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes, a process that requires the activity of DNA polymerases to ultimately introduce mutations at both A/T and C/G base pairs (By similarity).
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Chromosome . Enriched in chromatin in response to ultaviolet (UV) light (PubMed:25642963). Binds to chromatin during early G1 (PubMed:24989122). .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in testis.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
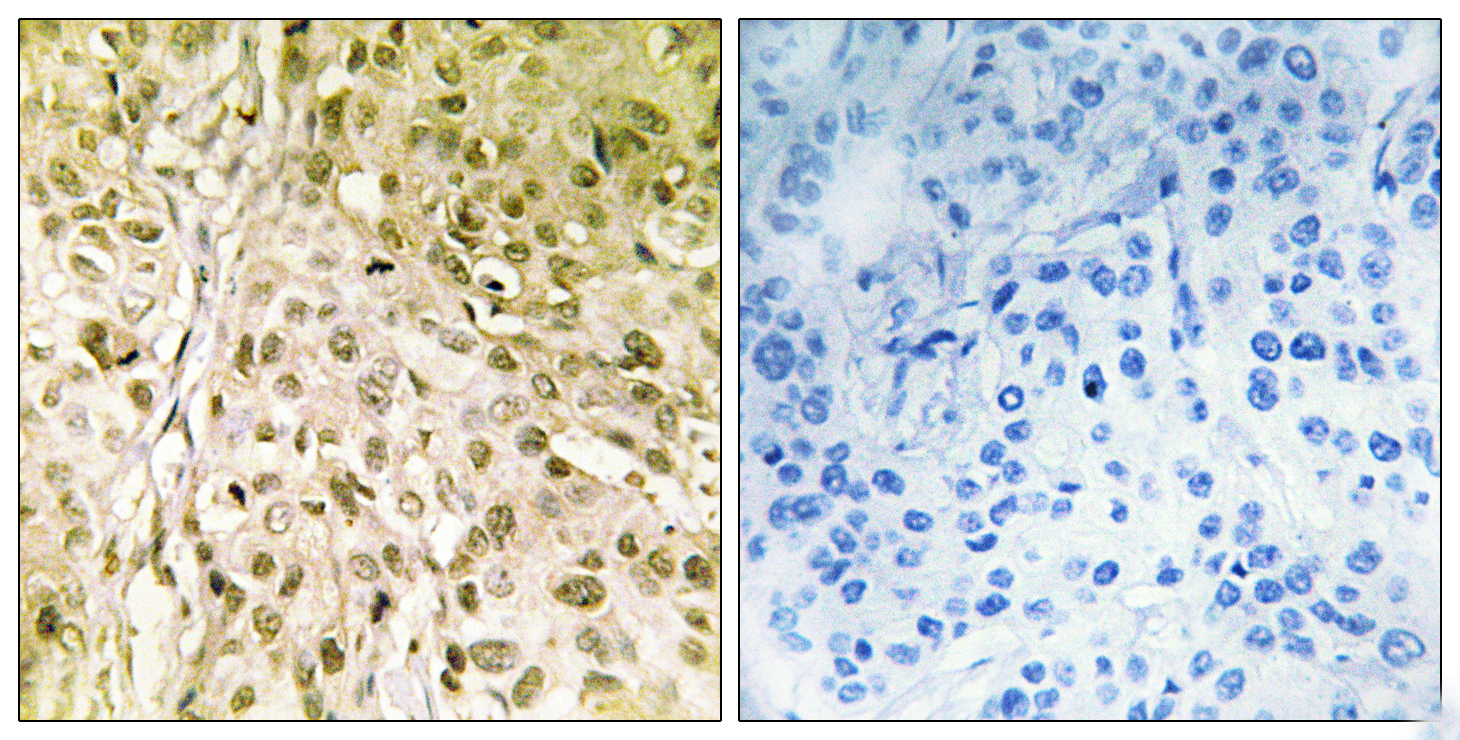
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma, using DNA Polymerase thet Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



