Cystatin B Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1250
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat
- Target:
- Cystatin B
- Gene Name:
- CSTB
- Protein Name:
- Cystatin-B
- Human Gene Id:
- 1476
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P04080
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q62426
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25308
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P01041
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Stefin B. AA range:49-98
- Specificity:
- Cystatin B Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Cystatin B protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CSTB;CST6;STFB;Cystatin-B;CPI-B;Liver thiol proteinase inhibitor;Stefin-B
- Observed Band(KD):
- 11kD
- Background:
- The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and kininogens. This gene encodes a stefin that functions as an intracellular thiol protease inhibitor. The protein is able to form a dimer stabilized by noncovalent forces, inhibiting papain and cathepsins l, h and b. The protein is thought to play a role in protecting against the proteases leaking from lysosomes. Evidence indicates that mutations in this gene are responsible for the primary defects in patients with progressive myoclonic epilepsy (EPM1). One type of mutation responsible for EPM1 is the expansion in the promoter region of this gene of a CCCCGCCCCGCG rep
- Function:
- disease:Defects in CSTB are the cause of progressive myoclonic epilepsy type 1 (EPM1) [MIM:254800]. EPM1 is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe, stimulus-sensitive myoclonus and tonic-clonic seizures. The onset, occurring between 6 and 13 years of age, is characterized by convulsions. Myoclonus begins 1 to 5 years later. The twitchings occur predominantly in the proximal muscles of the extremities and are bilaterally symmetrical, although asynchronous. At first small, they become late in the clinical course so violent that the victim is thrown to the floor. Mental deterioration and eventually dementia develop.,function:This is an intracellular thiol proteinase inhibitor. Tightly binding reversible inhibitor of cathepsins L, H and B.,similarity:Belongs to the cystatin family.,subunit:Able to form dimers stabilized by noncovalent forces.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus .
- Expression:
- Cerebellum,Placenta,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Cystatin B Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
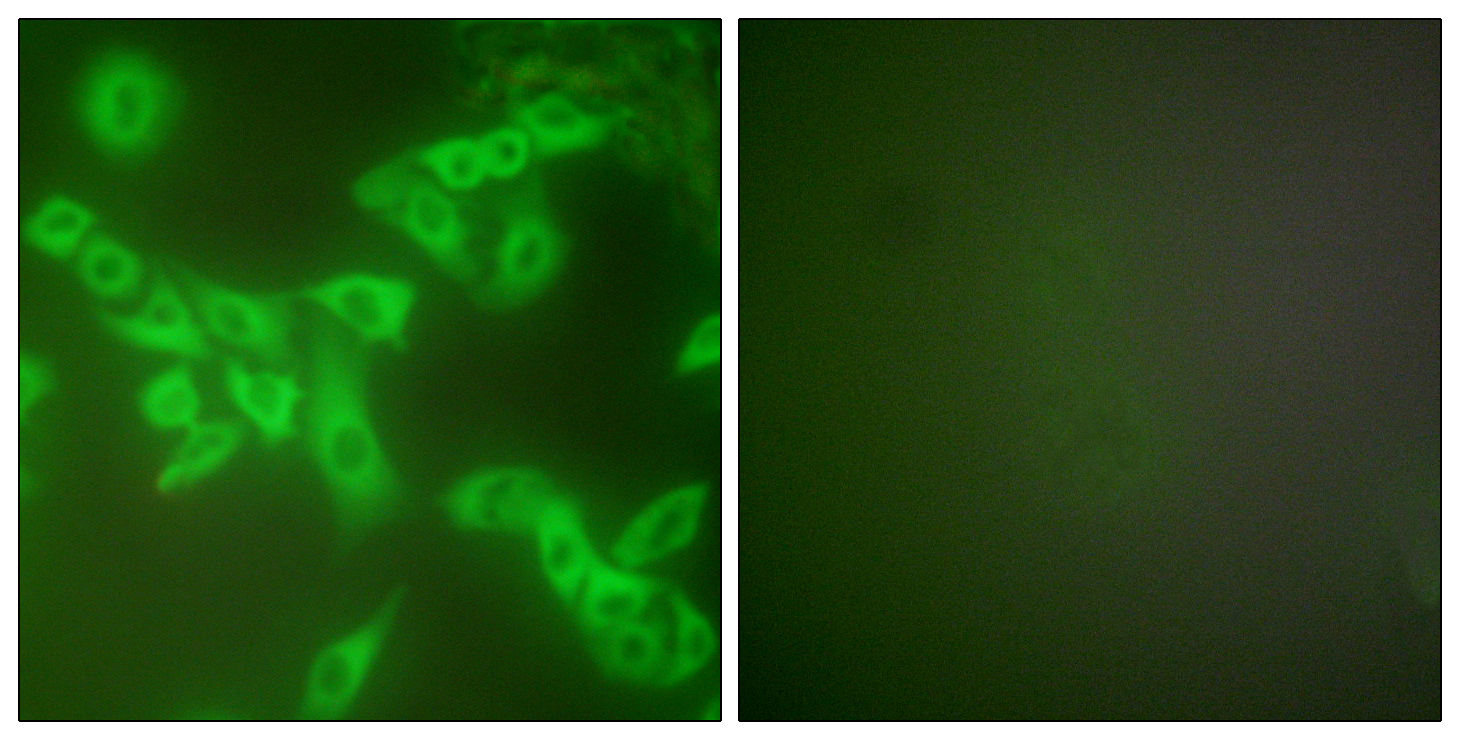
- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using Stefin B Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
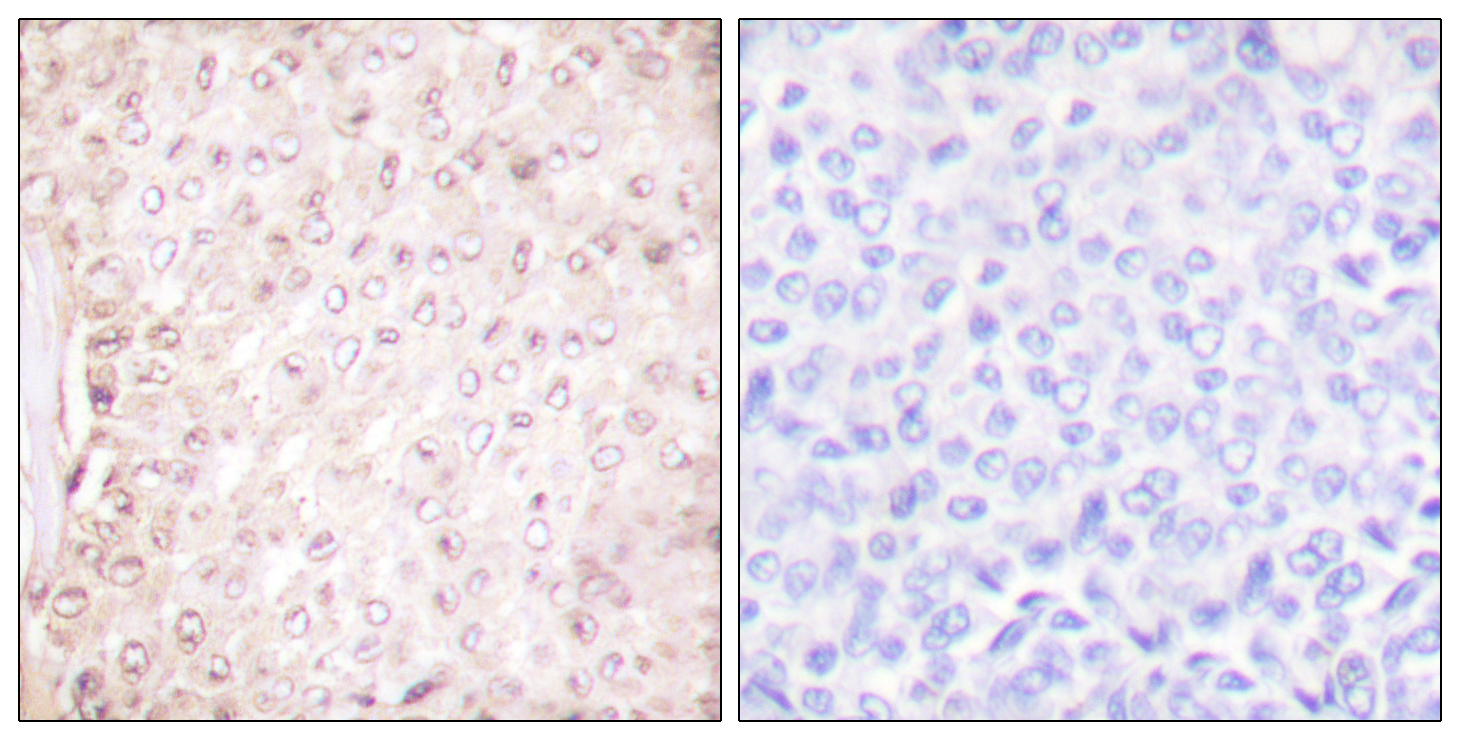
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue, using Stefin B Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
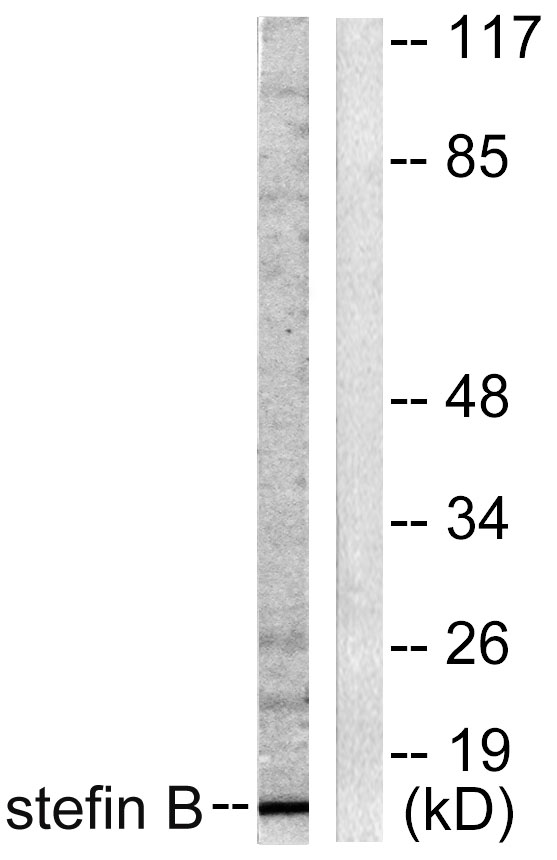

- Western blot analysis of lysates from A549 cells, using Stefin B Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



