COX15 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1070
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- COX15
- Fields:
- >>Oxidative phosphorylation;>>Porphyrin metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Biosynthesis of cofactors;>>Thermogenesis
- Gene Name:
- COX15
- Protein Name:
- Cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein COX15 homolog
- Human Gene Id:
- 1355
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q7KZN9
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 226139
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8BJ03
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human COX15. AA range:181-230
- Specificity:
- COX15 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of COX15 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:5000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- COX15;Cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein COX15 homolog
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 46kD
- Background:
- Cytochrome c oxidase (COX), the terminal component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, catalyzes the electron transfer from reduced cytochrome c to oxygen. This component is a heteromeric complex consisting of 3 catalytic subunits encoded by mitochondrial genes and multiple structural subunits encoded by nuclear genes. The mitochondrially-encoded subunits function in electron transfer, and the nuclear-encoded subunits may function in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This nuclear gene encodes a protein which is not a structural subunit, but may be essential for the biogenesis of COX formation and may function in the hydroxylation of heme O, according to the yeast mutant studies. This protein is predicted to contain 5 transmembrane domains localized in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Alternative splicing of this gene generates two transcript variants diverging
- Function:
- disease:Defects in COX15 are a cause of cytochrome c oxidase deficiency (COX deficiency) [MIM:220110]. COX deficiency is a clinically heterogeneous disorder. The clinical features range from isolated myopathy to severe multisystem disease with onset from infancy to adulthood.,disease:Defects in COX15 are a cause of Leigh syndrome [MIM:256000]. Leigh syndrome is an early-onset progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by delayed onset of symptoms, hypotonia, feeding difficulties, failure to thrive, motor regression and brainstem signs. Diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of focal, bilateral lesions in one or more areas of the central nervous system including the brainstem, thalamus, basal ganglia, cerebellum and spinal cord.,function:May be involved in the biosynthesis of heme A.,pathway:Porphyrin metabolism; heme A biosynthesis; heme A from heme O: step 1/1.,similarity:Belo
- Subcellular Location:
- Mitochondrion membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Predominantly found in tissues characterized by high rates of oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos), including muscle, heart, and brain.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
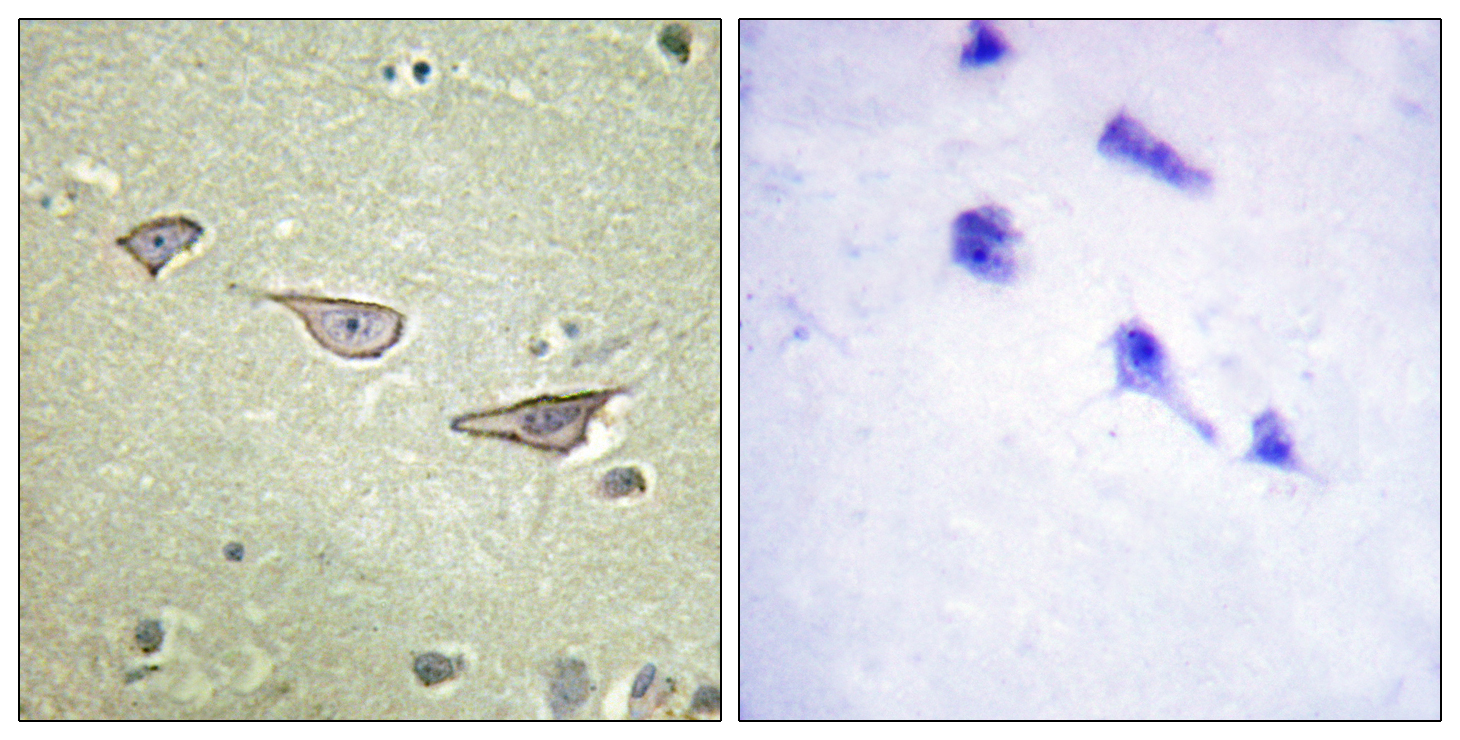
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using COX15 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



