Connexin-32 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1051
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Connexin-32
- Gene Name:
- GJB1
- Protein Name:
- Gap junction beta-1 protein
- Human Gene Id:
- 2705
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P08034
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14618
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P28230
- Rat Gene Id:
- 29584
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P08033
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Connexin-32. AA range:66-115
- Specificity:
- Connexin-32 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Connexin-32 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:40000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GJB1;CX32;Gap junction beta-1 protein;Connexin-32;Cx32;GAP junction 28 kDa liver protein
- Observed Band(KD):
- 32kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the gap junction protein family. The gap junction proteins are membrane-spanning proteins that assemble to form gap junction channels that facilitate the transfer of ions and small molecules between cells. According to sequence similarities at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, the gap junction proteins are divided into two categories, alpha and beta. Mutations in this gene cause X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, an inherited peripheral neuropathy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in GJB1 are the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease X-linked type 1 (CMTX1) [MIM:302800]; also designated CMT-X. CMTX1 is a form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, the most common inherited disorder of the peripheral nervous system. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies characterized by severely reduced motor nerve conduction velocities (NCVs) (less than 38m/s) and segmental demyelination and remyelination, and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies characterized by normal or mildly reduced NCVs and chronic axonal degeneration and regeneration on nerve biopsy. CMTX1 has both demyelinating and axonal features. Central nervous system involvement may occur.,disease:Defects in GJB1 may contribute to the phenotype of Dejerine-Sottas syndrome (DSS
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction, gap junction.
- Expression:
- Liver,Placenta,Skin,Subthalamic nucleus,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
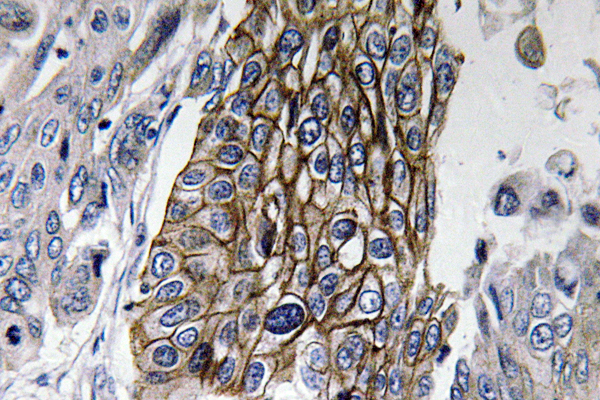
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of Connexin-32 antibody in paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma tissue.

- Western blot analysis of lysate from LOVO cells, using Connexin-32 antibody.



