CLIC4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0965
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- CLIC4
- Gene Name:
- CLIC4
- Protein Name:
- Chloride intracellular channel protein 4
- Human Gene Id:
- 25932
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9Y696
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 29876
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9QYB1
- Rat Gene Id:
- 83718
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9Z0W7
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human CLIC4. AA range:1-50
- Specificity:
- CLIC4 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of CLIC4 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:40000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CLIC4;Chloride intracellular channel protein 4;Intracellular chloride ion channel protein p64H1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 29kD
- Background:
- chloride intracellular channel 4(CLIC4) Homo sapiens Chloride channels are a diverse group of proteins that regulate fundamental cellular processes including stabilization of cell membrane potential, transepithelial transport, maintenance of intracellular pH, and regulation of cell volume. Chloride intracellular channel 4 (CLIC4) protein, encoded by the CLIC4 gene, is a member of the p64 family; the gene is expressed in many tissues and exhibits a intracellular vesicular pattern in Panc-1 cells (pancreatic cancer cells). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:Members of this family may change from a globular, soluble state to a state where the N-terminal domain is inserted into the membrane and functions as chloride channel. A conformation change of the N-terminal domain is thought to expose hydrophobic surfaces that trigger membrane insertion.,function:Can insert into membranes and form poorly selective ion channels that may also transport chloride ions. Channel activity depends on the pH. Membrane insertion seems to be redox-regulated and may occur only under oxydizing conditions. Promotes cell-surface expression of HRH3. May play a role in angiogenesis.,induction:Up-regulated by calcium ions in differentiating keratinocytes.,similarity:Belongs to the chloride channel CLIC family.,similarity:Contains 1 GST C-terminal domain.,subcellular location:Exists both as soluble cytoplasmic protein and as membrane protein with probably a single
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane ; Single-pass membrane protein . Nucleus matrix. Cell membrane ; Single-pass membrane protein . Mitochondrion. Cell junction. Colocalized with AKAP9 at the centrosome and midbody. Exists both as soluble cytoplasmic protein and as membrane protein with probably a single transmembrane domain. Present in an intracellular vesicular compartment that likely represent trans-Golgi network vesicles.
- Expression:
- Detected in epithelial cells from colon, esophagus and kidney (at protein level). Expression is prominent in heart, kidney, placenta and skeletal muscle.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
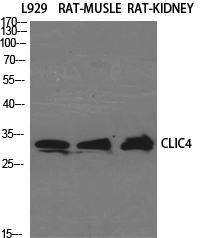
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using CLIC4 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of HT29 cells using CLIC4 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
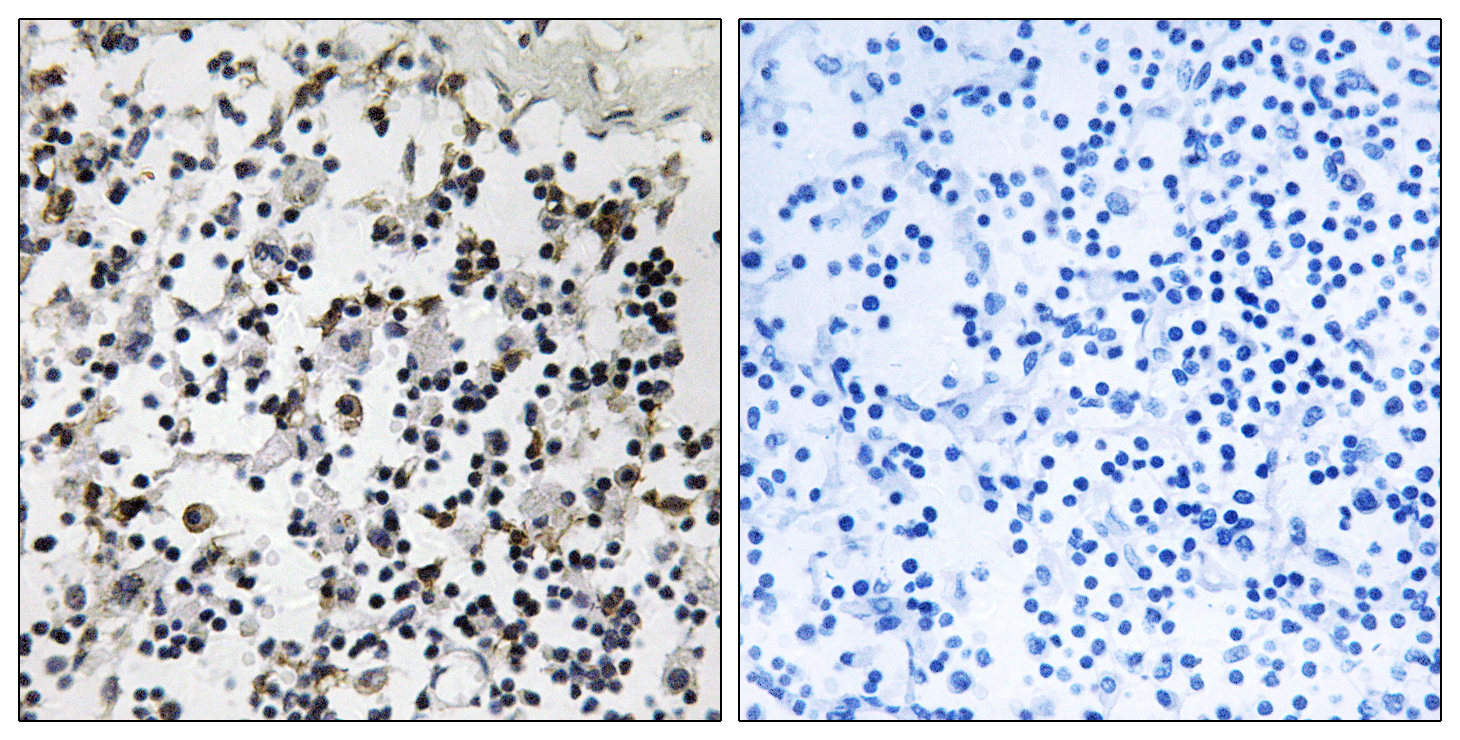
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human lymph node tissue, using CLIC4 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
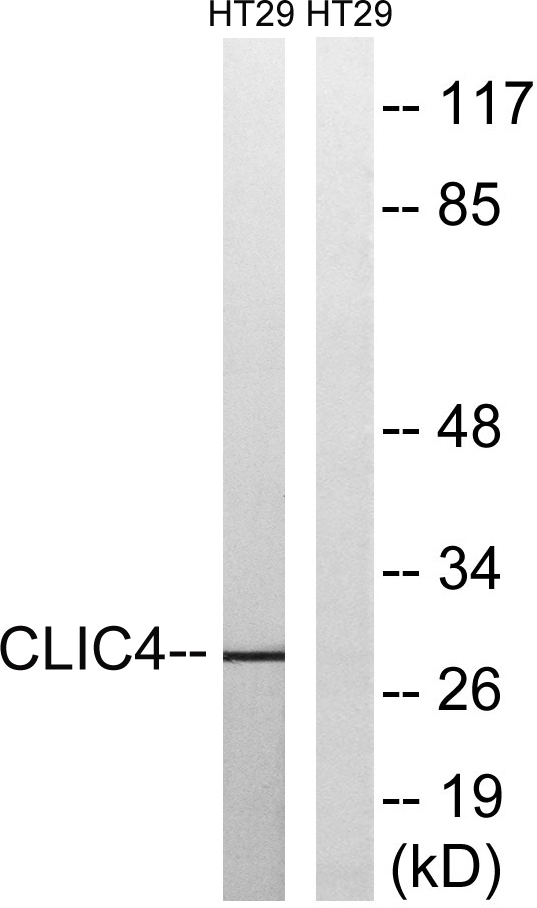
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HT-29 cells, using CLIC4 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
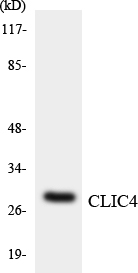
- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HeLa cells using CLIC4 antibody.



