ATRX Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0420
- Applications:IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- ATRX
- Gene Name:
- ATRX
- Protein Name:
- Transcriptional regulator ATRX
- Human Gene Id:
- 546
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P46100
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22589
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q61687
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human ATRX. AA range:111-160
- Specificity:
- ATRX Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of ATRX protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ATRX;RAD54L;XH2;Transcriptional regulator ATRX;ATP-dependent helicase ATRX;X-linked helicase II;X-linked nuclear protein;XNP;Znf-HX
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 283kD
- Background:
- ATRX, chromatin remodeler(ATRX) Homo sapiens The protein encoded by this gene contains an ATPase/helicase domain, and thus it belongs to the SWI/SNF family of chromatin remodeling proteins. This protein is found to undergo cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation, which regulates its nuclear matrix and chromatin association, and suggests its involvement in the gene regulation at interphase and chromosomal segregation in mitosis. Mutations in this gene are associated with an X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) syndrome most often accompanied by alpha-thalassemia (ATRX) syndrome. These mutations have been shown to cause diverse changes in the pattern of DNA methylation, which may provide a link between chromatin remodeling, DNA methylation, and gene expression in developmental processes. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in ATRX are a cause of alpha-thalassemia myelodysplasia syndrome (ATMDS) [MIM:300448]. In this disorder, alpha-thalassemia occurs as an acquired abnormality in association with a multilineage myelodysplasia.,disease:Defects in ATRX are the cause of mental retardation syndromic X-linked with hypotonic facies syndrome type 1 (MRXSHF1) [MIM:309580]; also called Carpenter-Waziri syndrome (CWS), Juberg-Marsidi syndrome (JMS), Smith-Fineman-Myers syndrome type 1 (SFM1). Clinical features include severe mental retardation, dysmorphic facies, and a highly skewed X-inactivation pattern in carrier women. Other more variable features include hypogonadism, deafness, renal anomalies, and mild skeletal defects.,disease:Defects in ATRX are the cause of X-linked alpha-thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome (ATR-X) [MIM:301040]. ATR-X is an X-linked disorder comprising severe psychomotor
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Chromosome, telomere. Nucleus, PML body. Associated with pericentromeric heterochromatin during interphase and mitosis, probably by interacting with CBX5/HP1 alpha. Colocalizes with histone H3.3, DAXX, HIRA and ASF1A at PML-nuclear bodies. Colocalizes with cohesin (SMC1 and SMC3) and MECP2 at the maternal H19 ICR (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Ubiquitous.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
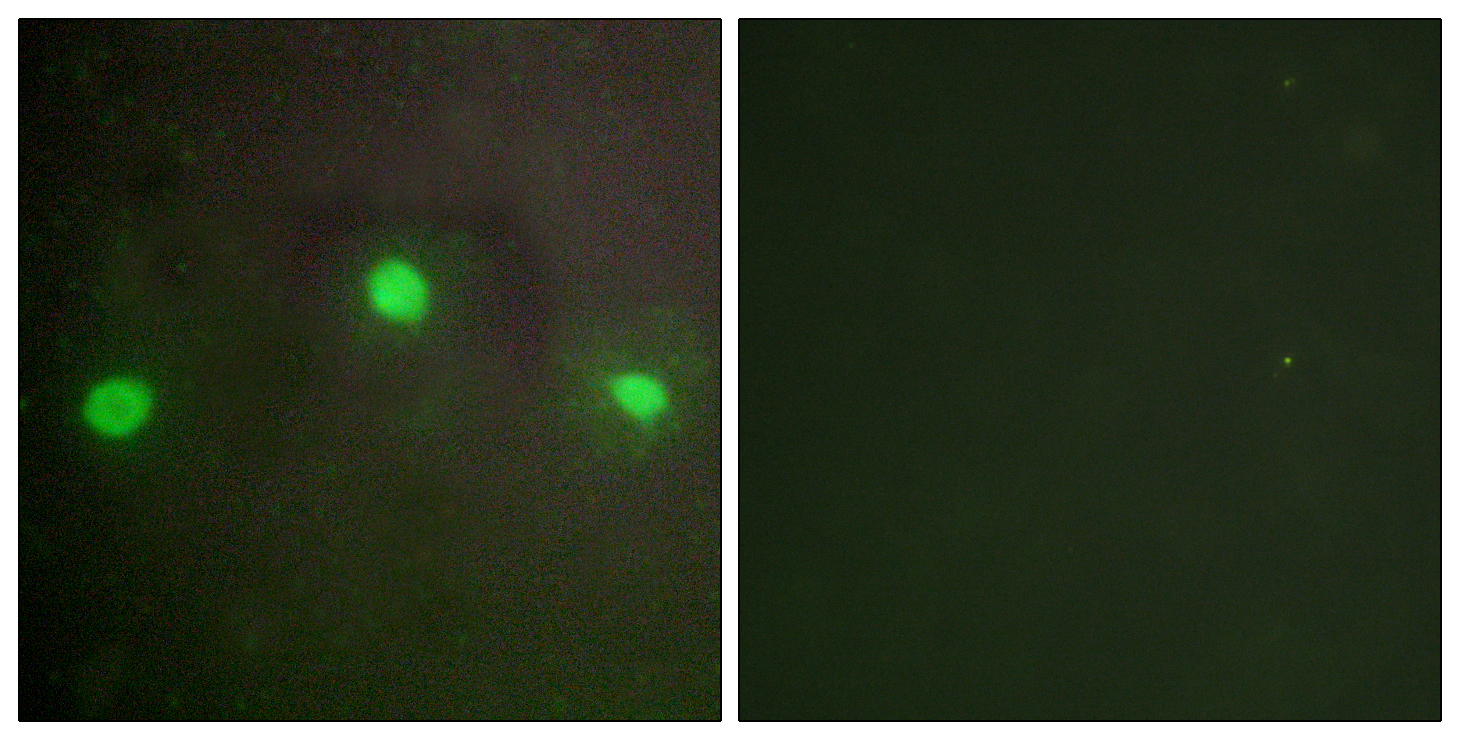
- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using ATRX Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



