ATP5G2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0404
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- ATP5G2
- Fields:
- >>Oxidative phosphorylation;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Thermogenesis;>>Alzheimer disease;>>Parkinson disease;>>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Huntington disease;>>Prion disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases;>>Chemical carcinogenesis - reactive oxygen species;>>Diabetic cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- ATP5G2
- Protein Name:
- ATP synthase lipid-binding protein mitochondrial
- Human Gene Id:
- 517
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q06055
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P56383
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human ATP5G2. AA range:1-50
- Specificity:
- ATP5G2 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of ATP5G2 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:40000. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ATP5G2;PSEC0033;ATP synthase lipid-binding protein; mitochondrial;ATP synthase proteolipid P2;ATPase protein 9;ATPase subunit c
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 20kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and single representatives of the gamma, delta, and epsilon subunits. The proton channel likely has nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). There are three separate genes which encode subunit c of the proton channel and they specify precursors with different import sequences but iden
- Function:
- disease:This protein is the major protein stored in the storage bodies of animals or humans affected with ceroid lipofuscinosis (Batten disease).,function:Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(0) domain. A homomeric c-ring of probably 10 subunits is part of the complex rotary element.,miscellaneous:There are three gene
- Subcellular Location:
- Mitochondrion membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
- Expression:
- Liver,Lung,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
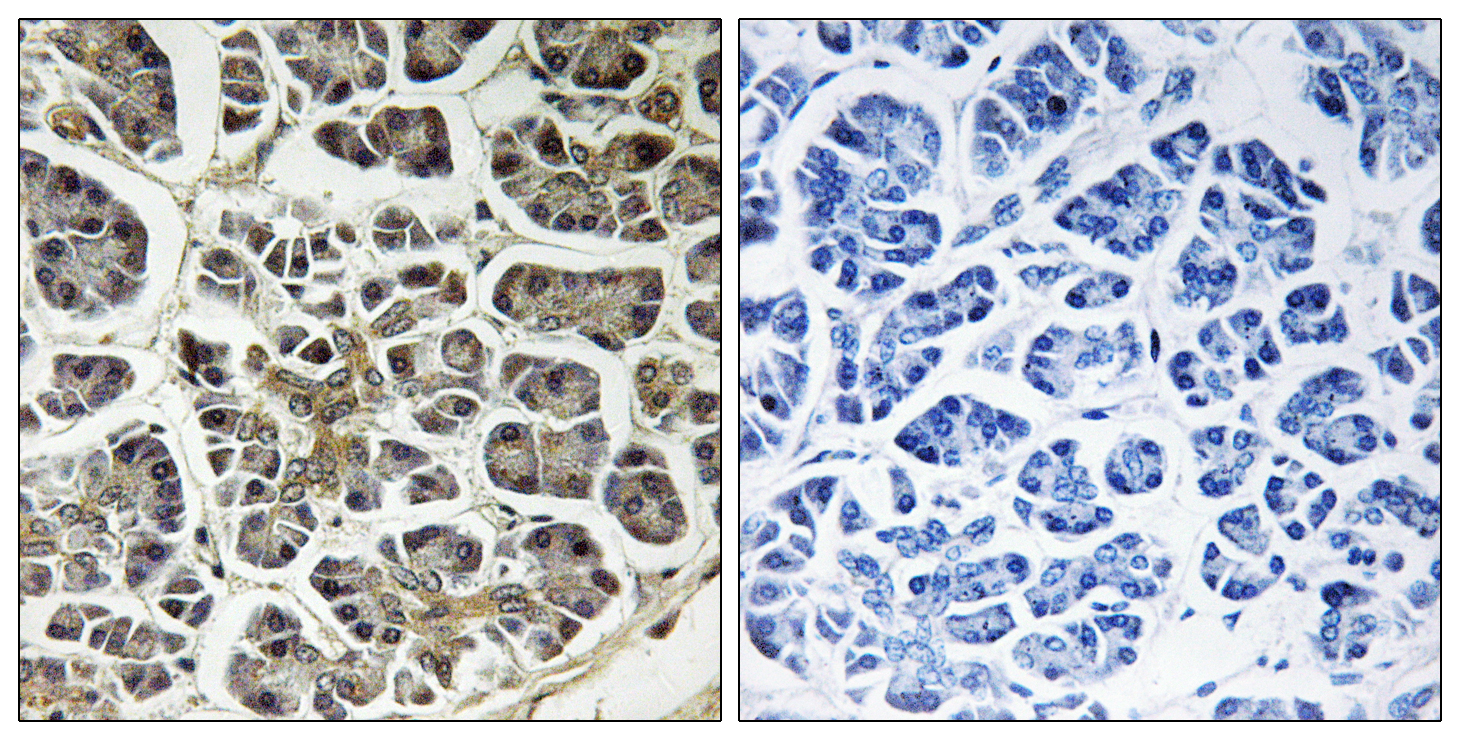
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human pancreas, using ATP5G2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



