Actin α1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0097
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Actin α1
- Gene Name:
- ACTA1
- Protein Name:
- Actin alpha skeletal muscle
- Human Gene Id:
- 58
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P68133
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 11459
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P68134
- Rat Gene Id:
- 29437
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P68136
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Actin-alpha-1. AA range:1-50
- Specificity:
- Actin α1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Actin α1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ACTA1;ACTA;Actin; alpha skeletal muscle;Alpha-actin-1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 45kD
- Background:
- The product encoded by this gene belongs to the actin family of proteins, which are highly conserved proteins that play a role in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha, beta and gamma actin isoforms have been identified, with alpha actins being a major constituent of the contractile apparatus, while beta and gamma actins are involved in the regulation of cell motility. This actin is an alpha actin that is found in skeletal muscle. Mutations in this gene cause nemaline myopathy type 3, congenital myopathy with excess of thin myofilaments, congenital myopathy with cores, and congenital myopathy with fiber-type disproportion, diseases that lead to muscle fiber defects. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in ACTA1 are a cause of congenital myopathy with excess of thin myofilaments (CM) [MIM:102610].,disease:Defects in ACTA1 are a cause of congenital myopathy with fiber-type disproportion (CFTD) [MIM:255310]; also known as congenital fiber-type disproportion myopathy (CFTDM). CFTD is a genetically heterogeneous disorder in which there is relative hypotrophy of type 1 muscle fibers compared to type 2 fibers on skeletal muscle biopsy. However, these findings are not specific and can be found in many different myopathic and neuropathic conditions.,disease:Defects in ACTA1 are the cause of nemaline myopathy type 3 (NEM3) [MIM:161800]. Nemaline myopathy (NEM) is a form of congenital myopathy characterized by abnormal thread- or rod-like structures in muscle fibers on histologic examination. The clinical phenotype is highly variable, with differing age at onset and severity.,func
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
- Expression:
- Epithelium,Skeletal muscle,
Direct-writing Process and in vivo Evaluation of Prevascularized Composite Constructs for Muscle Tissue Engineering Application. Journal of Bionic Engineering J Bionic Eng. 2020 May;17(3):457-468 IHC Human,Mouse C2C12 cell,HUVECs
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
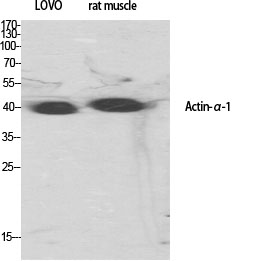
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Actin α1 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of HEPG2-UV cells using Actin α1 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
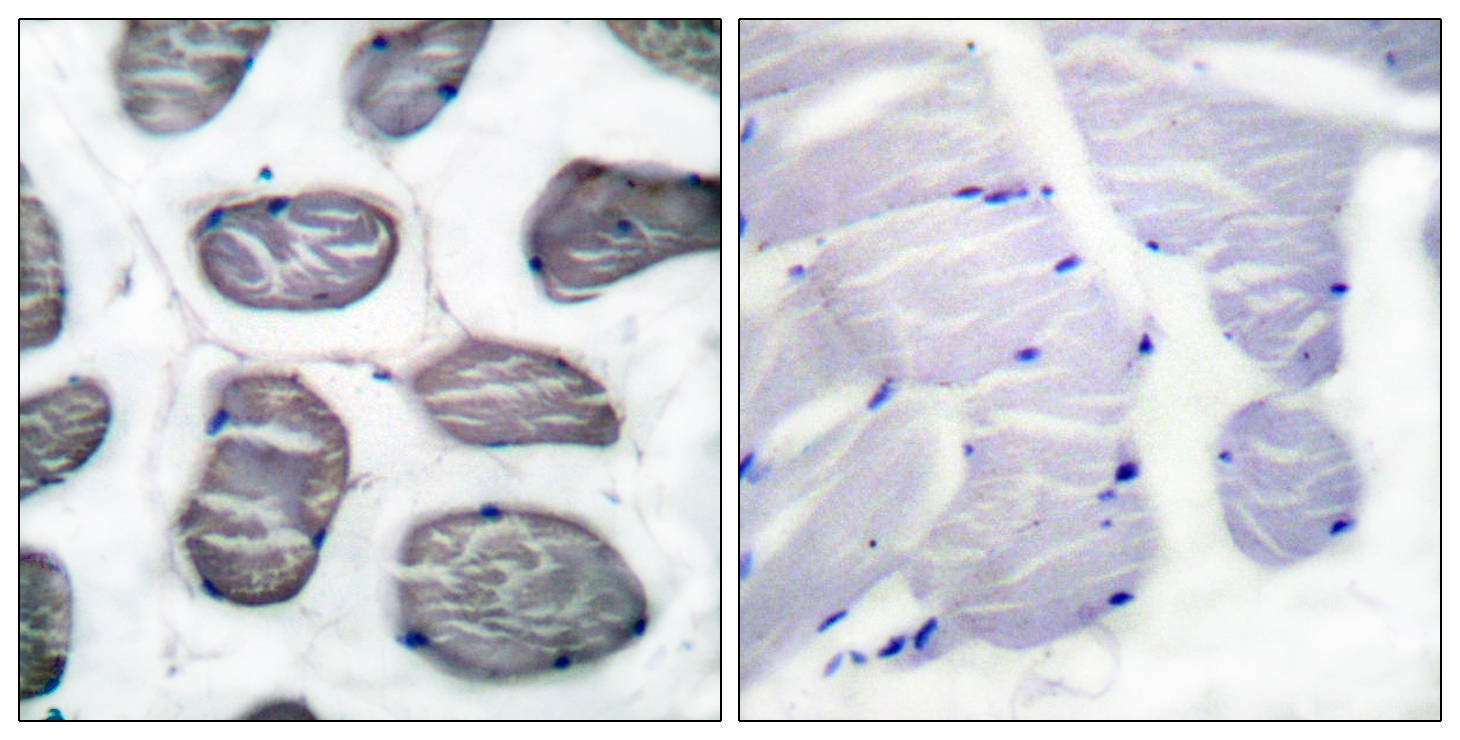
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human muscle tissue, using Actin-alpha-1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
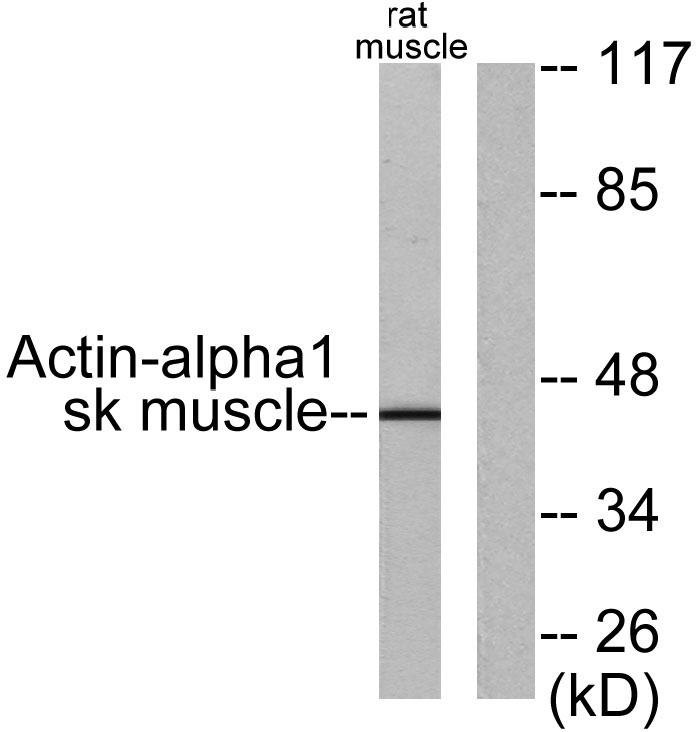
- Western blot analysis of lysates from rat muscle cells, using Actin-alpha-1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



