AChRβ1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0084
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- AChRβ1
- Fields:
- >>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB1
- Protein Name:
- Acetylcholine receptor subunit beta
- Human Gene Id:
- 1140
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P11230
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 11443
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P09690
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24261
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P25109
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human CHRNB1. AA range:41-90
- Specificity:
- AChRβ1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of AChRβ1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:5000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CHRNB1;ACHRB;CHRNB;Acetylcholine receptor subunit beta
- Observed Band(KD):
- 55kD
- Background:
- The muscle acetylcholine receptor is composed of five subunits: two alpha subunits and one beta, one gamma, and one delta subunit. This gene encodes the beta subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. The acetylcholine receptor changes conformation upon acetylcholine binding leading to the opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. Mutations in this gene are associated with slow-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in CHRNB1 are a cause of congenital myasthenic syndrome slow-channel type (SCCMS) [MIM:601462]. SCCMS is the most common congenital myasthenic syndrome. Congenital myasthenic syndromes are characterized by muscle weakness affecting the axial and limb muscles (with hypotonia in early-onset forms), the ocular muscles (leading to ptosis and ophthalmoplegia), and the facial and bulbar musculature (affecting sucking and swallowing, and leading to dysphonia). The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. SCCMS is caused by kinetic abnormalities of the AChR, resulting in prolonged endplate currents and prolonged AChR channel opening episodes.,disease:Defects in CHRNB1 are a cause of congenital myasthenic syndrome with acetylcholine receptor deficiency (ACHRDCMS) [MIM:608931]. ACHRDCMS is a post-synaptic congenital myasthenic syndrome. Mutations underlying AChR deficien
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
- Expression:
- Eye,Muscle,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
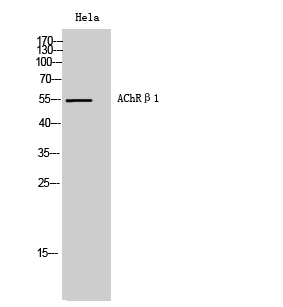
- Western Blot analysis of Hela cells using AChRβ1 Polyclonal Antibody



