AASS Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0041
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- AASS
- Fields:
- >>Lysine degradation;>>Metabolic pathways
- Gene Name:
- AASS
- Protein Name:
- Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase mitochondrial
- Human Gene Id:
- 10157
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q9UDR5
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q99K67
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human AASS. AA range:251-300
- Specificity:
- AASS Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of AASS protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- AASS;Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase; mitochondrial;LKR/SDH
- Observed Band(KD):
- 102kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the first two steps in the mammalian lysine degradation pathway. The N-terminal and the C-terminal portions of this enzyme contain lysine-ketoglutarate reductase and saccharopine dehydrogenase activity, respectively, resulting in the conversion of lysine to alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde. Mutations in this gene are associated with familial hyperlysinemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine + NAD(+) + H(2)O = L-glutamate + 2-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde + NADH.,catalytic activity:N(6)-(L-1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-L-lysine + NADP(+) + H(2)O = L-lysine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH.,disease:Defects in AASS are the cause of hyperlysinemia [MIM:238700]. Hyperlysinemia is an autosomal recessive condition characterized by hyperlysinemia lysinuria and variable saccharopinuria.,function:Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the first two steps in lysine degradation. The N-terminal and the C-terminal contain lysine-ketoglutarate reductase and saccharopine dehydrogenase activity, respectively.,induction:Induced by starvation.,pathway:Amino-acid degradation; L-lysine degradation via saccharopine pathway; glutaryl-CoA from L-lysine: step 1/6.,pathway:Amino-acid degradation; L-lysine degradation via saccharopine pathway; glutaryl-CoA from L-lys
- Subcellular Location:
- Mitochondrion .
- Expression:
- Expressed in all 16 tissues examined with highest expression in the liver.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
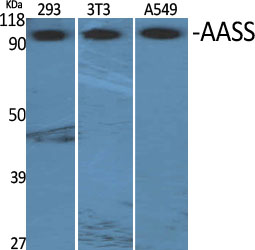
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using AASS Polyclonal Antibody
.jpg)
- Western Blot analysis of HeLa cells using AASS Polyclonal Antibody
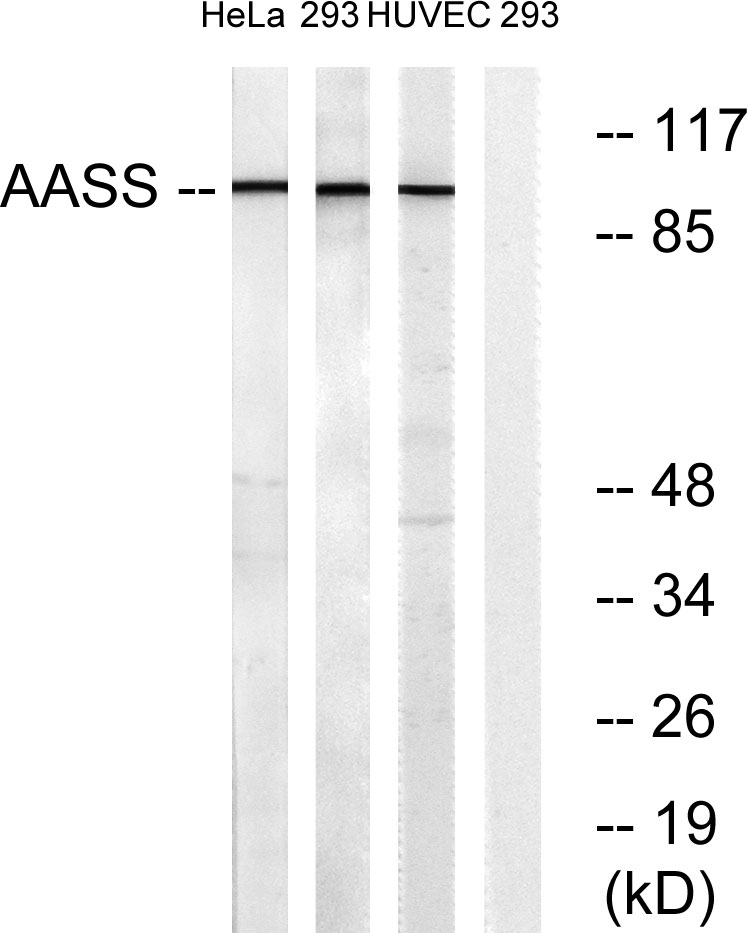
- Western blot analysis of lysates from 293, HUVEC, and HeLa cells, using AASS Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
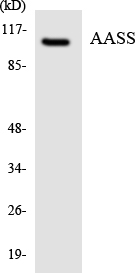
- Western blot analysis of the lysates from COLO205 cells using AASS antibody.



