Histamine H1 Receptor (phospho Ser398) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP1187
- Applications:IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Histamine H1 Receptor
- Fields:
- >>Calcium signaling pathway;>>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction;>>Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels
- Gene Name:
- HRH1
- Protein Name:
- Histamine H1 receptor
- Human Gene Id:
- 3269
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P35367
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 15465
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P70174
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24448
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P31390
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Histamine H1 Receptor around the phosphorylation site of Ser398. AA range:364-413
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Histamine H1 Receptor (S398) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Histamine H1 Receptor protein only when phosphorylated at S398.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- HRH1;Histamine H1 receptor;H1R;HH1R
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 56kD
- Background:
- Histamine is a ubiquitous messenger molecule released from mast cells, enterochromaffin-like cells, and neurons. Its various actions are mediated by histamine receptors H1, H2, H3 and H4. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. It mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, the increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, the release of catecholamine from adrenal medulla, and neurotransmission in the central nervous system. It has been associated with multiple processes, including memory and learning, circadian rhythm, and thermoregulation. It is also known to contribute to the pathophysiology of allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, anaphylaxis and allergic rhinitis. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by Ref
- Function:
- function:In peripheral tissues, the H1 subclass of histamine receptors mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, and catecholamine release from adrenal medulla, as well as mediating neurotransmission in the central nervous system.,PTM:Potential sites of phosphorylation in the third cytoplasmic loop may play an important role in regulating signal transduction through the receptor molecule.,similarity:Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
- Expression:
- Lens epithelium,Lung,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
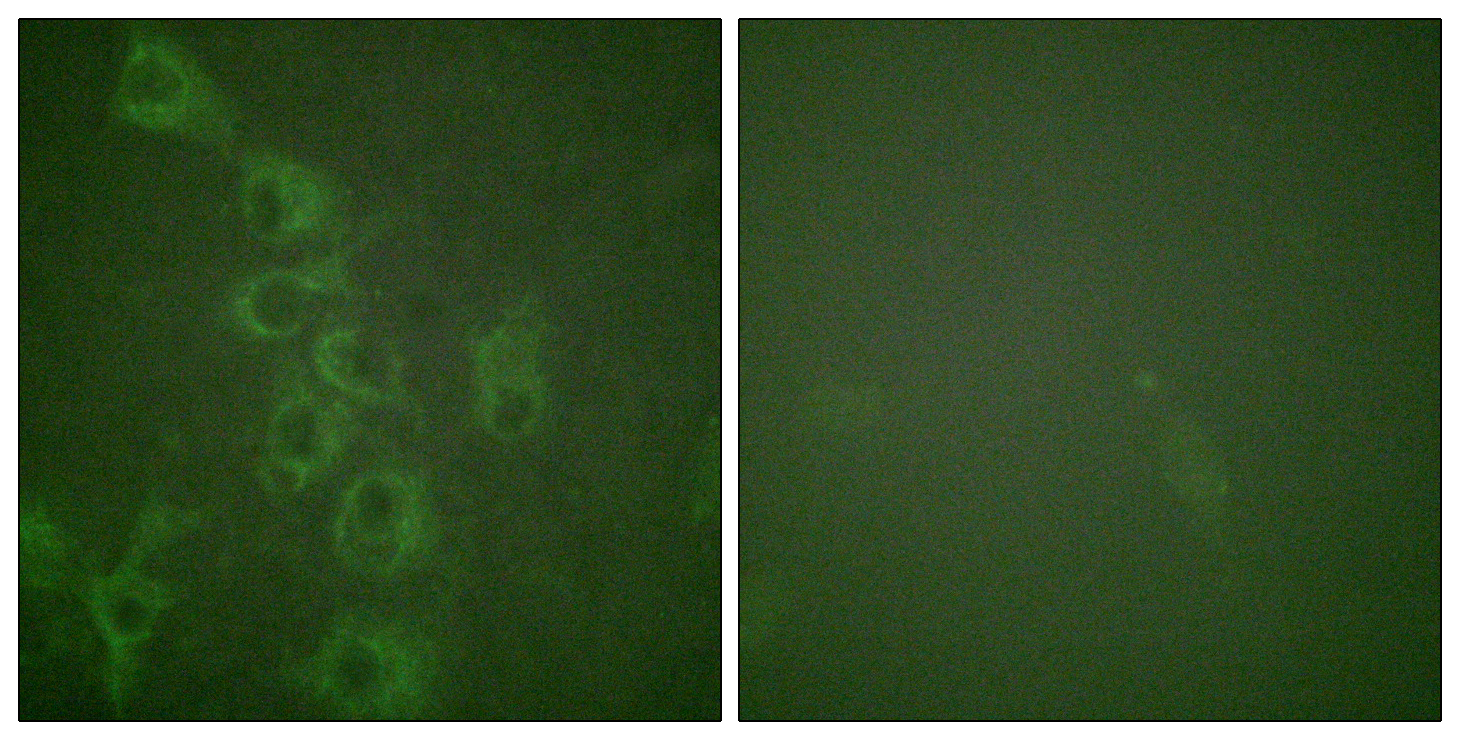
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HUVEC cells, using Histamine H1 Receptor (Phospho-Ser398) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



