CEP55 (phospho Ser425) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP1087
- Applications:IHC;IF;WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- CEP55
- Gene Name:
- CEP55
- Protein Name:
- Centrosomal protein of 55 kDa
- Human Gene Id:
- 55165
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q53EZ4
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8BT07
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized phospho-peptide around the phosphorylation site of human CEP55 (phospho Ser425)
- Specificity:
- Phospho-CEP55 (S425) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of CEP55 protein only when phosphorylated at S425.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:20000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CEP55;C10orf3;URCC6;Centrosomal protein of 55 kDa;Cep55;Up-regulated in colon cancer 6
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 54kD
- Background:
- function:Plays a role in mitotic exit and cytokinesis. Not required for microtubule nucleation. Recruits PDCD6IP and TSG101 to midbody during cytokinesis.,PTM:There is a hierachy of phosphorylation, where both Ser-425 and Ser-428 are phosphorylated at the onset of mitosis, prior to Ser-436. Phosphorylation at Ser-425 and Ser-428 is required for dissociation from the centrosome at the G2/M boundary. Phosphorylation at the 3 sites, Ser-425, Ser-428 and Ser-436, is required for protein function at the final stages of cell division to complete cytokinesis successfully.,subcellular location:Present at the centrosomes at interphase. A small portion is associated preferentially with the mother centriole, whereas the majority localizes to the pericentriolar material. During mitosis, loss of affinity for the centrosome at the onset of prophase and diffusion throughout the cell. This dissociation from the centrosome is phosphorylation-dependent. May remain localized at the centrosome during mitosis in certain cell types. Appears at the cleavage furrow in late anaphase and in the midbody in cytokinesis.,subunit:Homodimer. Interacts (phosphorylated on Ser-425 and Ser-428) with PLK1. Interacts with AKAP9; the interaction occurs in interphase and is lost upon mitotic entry. Interacts with PCNT; the interaction occurs in interphase and is lost upon mitotic entry. Interacts with PDCD6IP; the interaction is direct; CEP55 binds PDCD6IP in a 2:1 stoechiometry; PDCD6IP competes with TSG101 for the same binding site. Interacts with TSG101; TSG101 competes with PDCD6IP for the same binding site; interaction is required for cytokinesis but not for viral budding. Interacts with FAM125A, VPS37B, VPS37C and VPS28.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed, mostly in proliferative tissues. Highly expressed in testis. Intermediate levels in adult and fetal thymus, as well as in various cancer cell lines. Low levels in different parts of the digestive tract, bone marrow, lymph nodes, placenta, fetal heart and fetal spleen. Hardly detected in brain.,
- Function:
- function:Plays a role in mitotic exit and cytokinesis. Not required for microtubule nucleation. Recruits PDCD6IP and TSG101 to midbody during cytokinesis.,PTM:There is a hierachy of phosphorylation, where both Ser-425 and Ser-428 are phosphorylated at the onset of mitosis, prior to Ser-436. Phosphorylation at Ser-425 and Ser-428 is required for dissociation from the centrosome at the G2/M boundary. Phosphorylation at the 3 sites, Ser-425, Ser-428 and Ser-436, is required for protein function at the final stages of cell division to complete cytokinesis successfully.,subcellular location:Present at the centrosomes at interphase. A small portion is associated preferentially with the mother centriole, whereas the majority localizes to the pericentriolar material. During mitosis, loss of affinity for the centrosome at the onset of prophase and diffusion throughout the cell. This dissociation
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Cleavage furrow . Midbody, Midbody ring . Present at the centrosomes at interphase. A small portion is associated preferentially with the mother centriole, whereas the majority localizes to the pericentriolar material. During mitosis, loses affinity for the centrosome at the onset of prophase and diffuses throughout the cell. This dissociation from the centrosome is phosphorylation-dependent. May remain localized at the centrosome during mitosis in certain cell types. Appears at the cleavage furrow in late anaphase and in the midbody in cytokinesis. .
- Expression:
- Expressed in embryonic brain (PubMed:28264986). Expressed in fetal brain ganglionic eminence, kidney tubules and multinucleate neurons in the temporal cortex (PubMed:28264986). Expressed in adult brain, cerebellum, kidney tubules, intestine and muscles (at protein level) (PubMed:28295209, PubMed:28264986). Widely expressed, mostly in proliferative tissues. Highly expressed in testis. Intermediate levels in adult and fetal thymus, as well as in various cancer cell lines. Low levels in different parts of the digestive tract, bone marrow, lymph nodes, placenta, fetal heart and fetal spleen. Hardly detected in brain.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
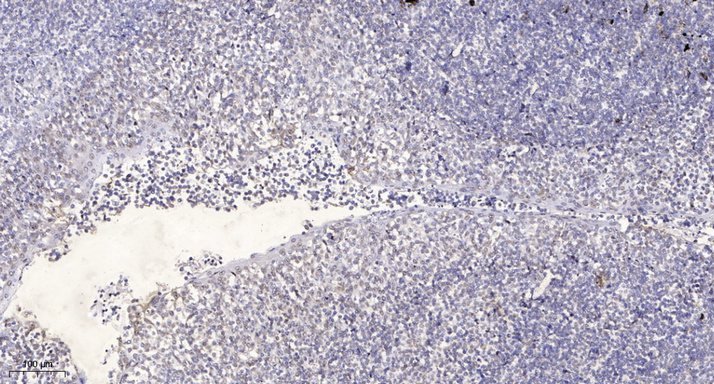
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 30min).
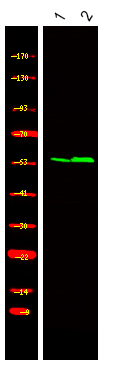
- Western Blot analysis of 1 HEK-293 cell, 2, LPS 100ng/mL 30min treated ,using primary antibody at 1:1000 dilution. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS23920) was diluted at 1:10000



