Caldesmon (phospho Ser759) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP1084
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Caldesmon
- Fields:
- >>Vascular smooth muscle contraction
- Gene Name:
- CALD1
- Protein Name:
- Caldesmon
- Human Gene Id:
- 800
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q05682
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25687
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q62736
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Caldesmon around the phosphorylation site of Ser759. AA range:725-774
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Caldesmon (S759) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Caldesmon protein only when phosphorylated at S759.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- CALD1;CAD;CDM;Caldesmon;CDM
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- high molecular weight (predominantly in smooth muscles) (120-150 KD) and a low molecular weight (60-90KD)
- Background:
- This gene encodes a calmodulin- and actin-binding protein that plays an essential role in the regulation of smooth muscle and nonmuscle contraction. The conserved domain of this protein possesses the binding activities to Ca(2+)-calmodulin, actin, tropomyosin, myosin, and phospholipids. This protein is a potent inhibitor of the actin-tropomyosin activated myosin MgATPase, and serves as a mediating factor for Ca(2+)-dependent inhibition of smooth muscle contraction. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- domain:The N-terminal part seems to be a myosin/calmodulin-binding domain, and the C-terminal a tropomyosin/actin/calmodulin-binding domain. These two domains are separated by a central helical region in the smooth-muscle form.,function:Actin- and myosin-binding protein implicated in the regulation of actomyosin interactions in smooth muscle and nonmuscle cells (could act as a bridge between myosin and actin filaments). Stimulates actin binding of tropomyosin which increases the stabilization of actin filament structure. In muscle tissues, inhibits the actomyosin ATPase by binding to F-actin. This inhibition is attenuated by calcium-calmodulin and is potentiated by tropomyosin. Interacts with actin, myosin, two molecules of tropomyosin and with calmodulin. Also play an essential role during cellular mitosis and receptor capping.,PTM:In non-muscle cells, phosphorylation by CDC2 during mit
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Cytoplasm, myofibril . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, stress fiber . On thin filaments in smooth muscle and on stress fibers in fibroblasts (nonmuscle). .
- Expression:
- High-molecular-weight caldesmon (isoform 1) is predominantly expressed in smooth muscles, whereas low-molecular-weight caldesmon (isoforms 2, 3, 4 and 5) are widely distributed in non-muscle tissues and cells. Not expressed in skeletal muscle or heart.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
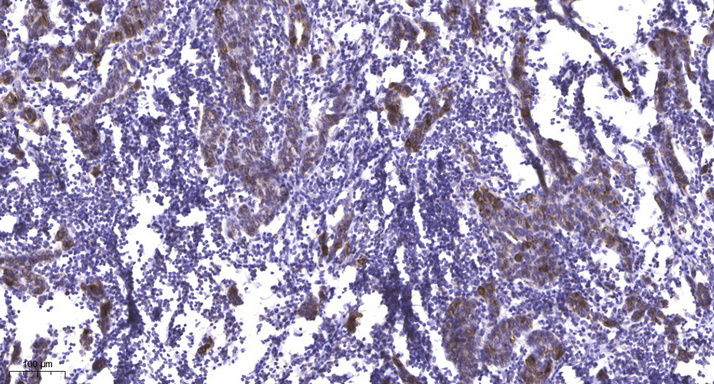
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human Breast cancer. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).



