Bmx (phospho Tyr40) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0899
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- ETK
- Gene Name:
- BMX
- Protein Name:
- Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX
- Human Gene Id:
- 660
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P51813
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 12169
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P97504
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human ETK around the phosphorylation site of Tyr40. AA range:6-55
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Bmx (Y40) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Bmx protein only when phosphorylated at Y40.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:40000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- BMX;Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX;Bone marrow tyrosine kinase gene in chromosome X protein;Epithelial and endothelial tyrosine kinase;ETK;NTK38
- Observed Band(KD):
- 78kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a non-receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the Tec kinase family. The protein contains a PH-like domain, which mediates membrane targeting by binding to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3), and a SH2 domain that binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins and functions in signal transduction. The protein is implicated in several signal transduction pathways including the Stat pathway, and regulates differentiation and tumorigenicity of several types of cancer cells. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,cofactor:Binds 1 zinc ion per subunit.,domain:SH2 domain mediates interaction with RUFY1.,function:Activity is required for interleukin 6 (IL-6) induced differentiation. May play a role in the growth and differentiation of hematopoietic cells. May be involved in signal transduction in endocardial and arterial endothelial cells.,induction:Activated by IL-6 through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) pathway. It is likely that activation occurs through binding of phosphoinositides to the PH domain.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. TEC subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 Btk-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 PH domain.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 1 SH2 domain.,subunit:Interacts with RUFY1 and RUFY2.,tissue sp
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Localizes to the edges of spreading cells when complexed with BCAR1.
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in cells with great migratory potential, including endothelial cells and metastatic carcinoma cell lines.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
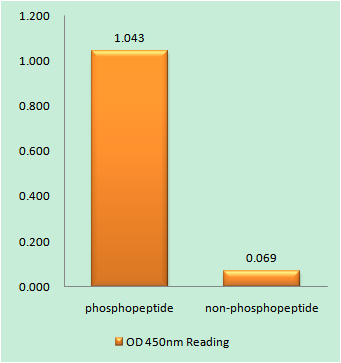
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using ETK (Phospho-Tyr40) Antibody
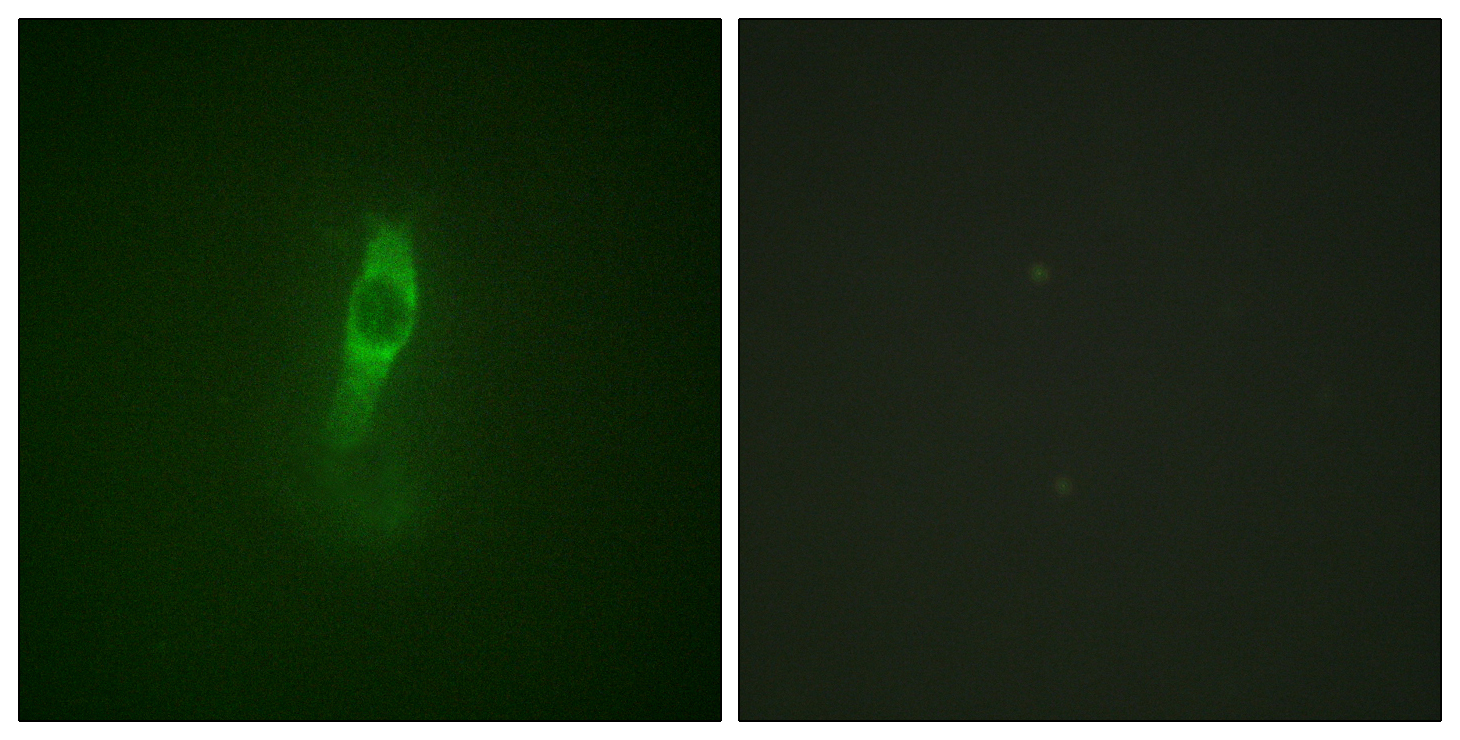
- Immunofluorescence analysis of NIH/3T3 cells, using ETK (Phospho-Tyr40) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.

- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human skin, using ETK (Phospho-Tyr40) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.

- Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2 cells, using ETK (Phospho-Tyr40) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



