Lamin A/C (phospho Ser392) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0882
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Lamin A/C
- Fields:
- >>Apoptosis;>>Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;>>Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy;>>Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Gene Name:
- LMNA
- Protein Name:
- Prelamin-A/C
- Human Gene Id:
- 4000
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P02545
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 16905
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P48678
- Rat Gene Id:
- 60374
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P48679
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Lamin A/C around the phosphorylation site of Ser392. AA range:361-410
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Lamin A/C (S392) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Lamin A/C protein only when phosphorylated at S392.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- LMNA;LMN1;Prelamin-A/C
- Observed Band(KD):
- 74kD
- Background:
- lamin A/C(LMNA) Homo sapiens The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins located next to the inner nuclear membrane. The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. During mitosis, the lamina matrix is reversibly disassembled as the lamin proteins are phosphorylated. Lamin proteins are thought to be involved in nuclear stability, chromatin structure and gene expression. Vertebrate lamins consist of two types, A and B. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Mutations in this gene lead to several diseases: Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, familial partial lipodystrophy, limb girdle muscular dystrophy, dilated cardiomyopathy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in LMNA are a cause of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy type 2 (EDMD2) [MIM:181350]. EDMD2 is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by slowly progressive muscle wasting and weakness, early contractures of the elbows Achilles tendons and spine, and cardiomyopathy associated with cardiac conduction defects.,disease:Defects in LMNA are a cause of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy type 3 (EDMD3) [MIM:604929]. EDMD3 is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by early contractures, muscle wasting and weakness and cardiomyopathy.,disease:Defects in LMNA are a cause of familial partial lipodystrophy type 2 (FPLD2) [MIM:151660]; also known as familial partial lipodystrophy Dunnigan type. FPLD2 is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue from the extremities and trunk but by excess fat deposition in the head and neck.
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Nucleus envelope . Nucleus lamina. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus matrix . Farnesylation of prelamin-A/C facilitates nuclear envelope targeting and subsequent cleavage by ZMPSTE24/FACE1 to remove the farnesyl group produces mature lamin-A/C, which can then be inserted into the nuclear lamina. EMD is required for proper localization of non-farnesylated prelamin-A/C.; [Isoform C]: Nucleus speckle .
- Expression:
- In the arteries, prelamin-A/C accumulation is not observed in young healthy vessels but is prevalent in medial vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) from aged individuals and in atherosclerotic lesions, where it often colocalizes with senescent and degenerate VSMCs. Prelamin-A/C expression increases with age and disease. In normal aging, the accumulation of prelamin-A/C is caused in part by the down-regulation of ZMPSTE24/FACE1 in response to oxidative stress.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
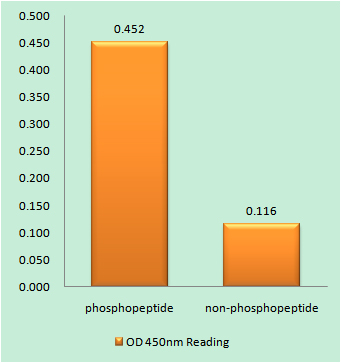
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using Lamin A/C (Phospho-Ser392) Antibody
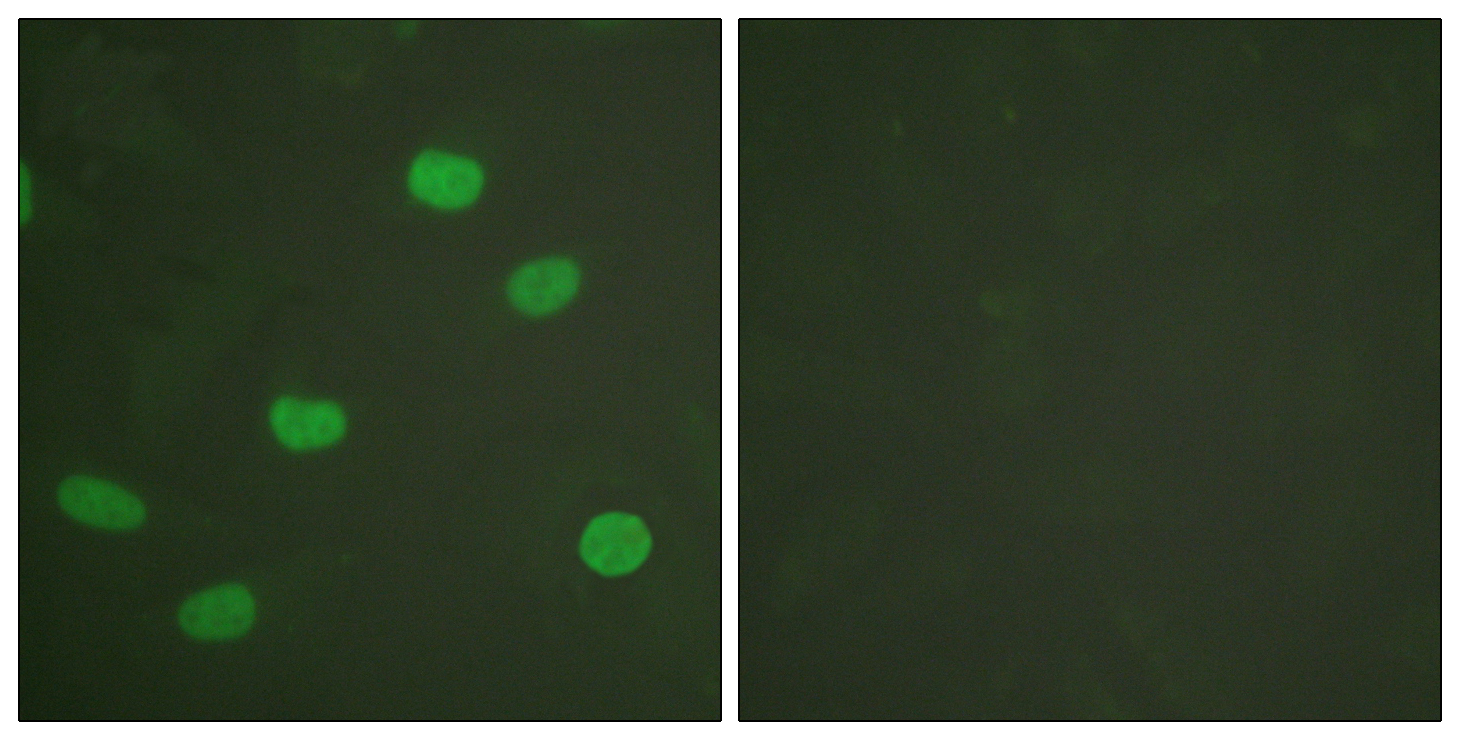
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells, using Lamin A/C (Phospho-Ser392) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
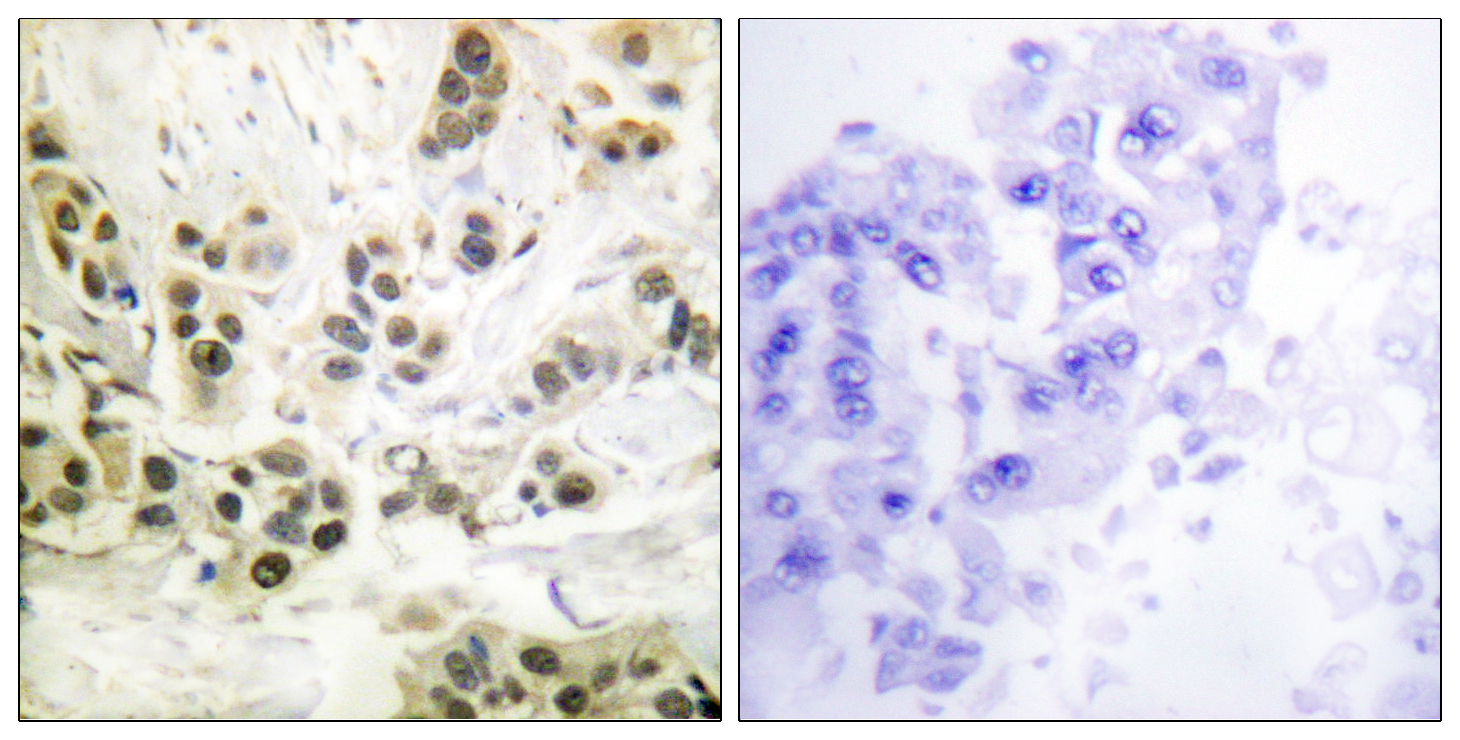
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma, using Lamin A/C (Phospho-Ser392) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
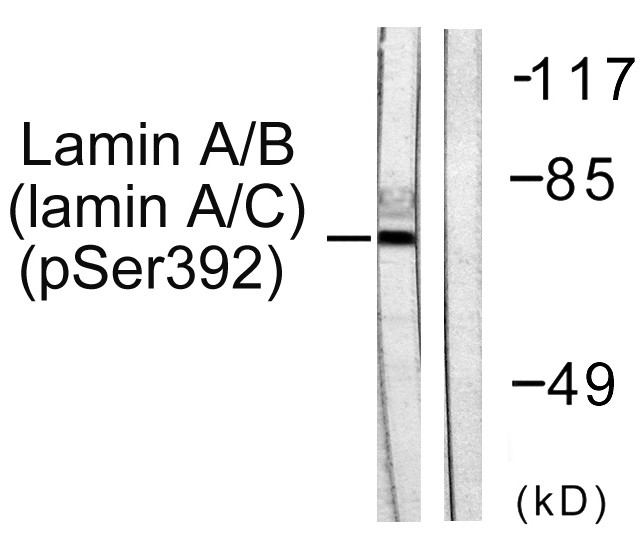
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa cells, using Lamin A/C (Phospho-Ser392) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



