Ku-80 (phospho Thr714) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0873
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Monkey
- Target:
- Ku-80
- Fields:
- >>Non-homologous end-joining
- Gene Name:
- XRCC5
- Protein Name:
- X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5
- Human Gene Id:
- 7520
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P13010
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P27641
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Ku80 around the phosphorylation site of Thr714. AA range:683-732
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Ku-80 (T714) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Ku-80 protein only when phosphorylated at T714.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- XRCC5;G22P2;X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5;86 kDa subunit of Ku antigen;ATP-dependent DNA helicase 2 subunit 2;ATP-dependent DNA helicase II 80 kDa subunit;CTC box-binding factor 85 kDa subunit;CTC85;CTCBF;DNA repair pr
- Observed Band(KD):
- 83kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is the 80-kilodalton subunit of the Ku heterodimer protein which is also known as ATP-dependant DNA helicase II or DNA repair protein XRCC5. Ku is the DNA-binding component of the DNA-dependent protein kinase, and it functions together with the DNA ligase IV-XRCC4 complex in the repair of DNA double-strand break by non-homologous end joining and the completion of V(D)J recombination events. This gene functionally complements Chinese hamster xrs-6, a mutant defective in DNA double-strand break repair and in ability to undergo V(D)J recombination. A rare microsatellite polymorphism in this gene is associated with cancer in patients of varying radiosensitivity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- developmental stage:Expression increases during promyelocyte differentiation.,disease:Individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and related disorders produce extremely large amounts of autoantibodies to p70 and p86.,domain:The EEXXXDDL motif is required for the interaction with catalytic subunit PRKDC and its recruitment to sites of DNA damage.,function:Single stranded DNA-dependent ATP-dependent helicase. Has a role in chromosome translocation. The DNA helicase II complex binds preferentially to fork-like ends of double-stranded DNA in a cell cycle-dependent manner. It works in the 3'-5' direction. Binding to DNA may be mediated by p70. Involved in DNA nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) required for double-strand break repair and V(D)J recombination. The Ku p70/p86 dimer acts as regulatory subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase complex DNA-PK by increasing the affinity of t
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus . Nucleus, nucleolus . Chromosome .
- Expression:
- Cervix carcinoma,Coronary artery,Heart,Neuroblastoma,Osteoblast,Thy
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells, using Ku80 (Phospho-Thr714) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
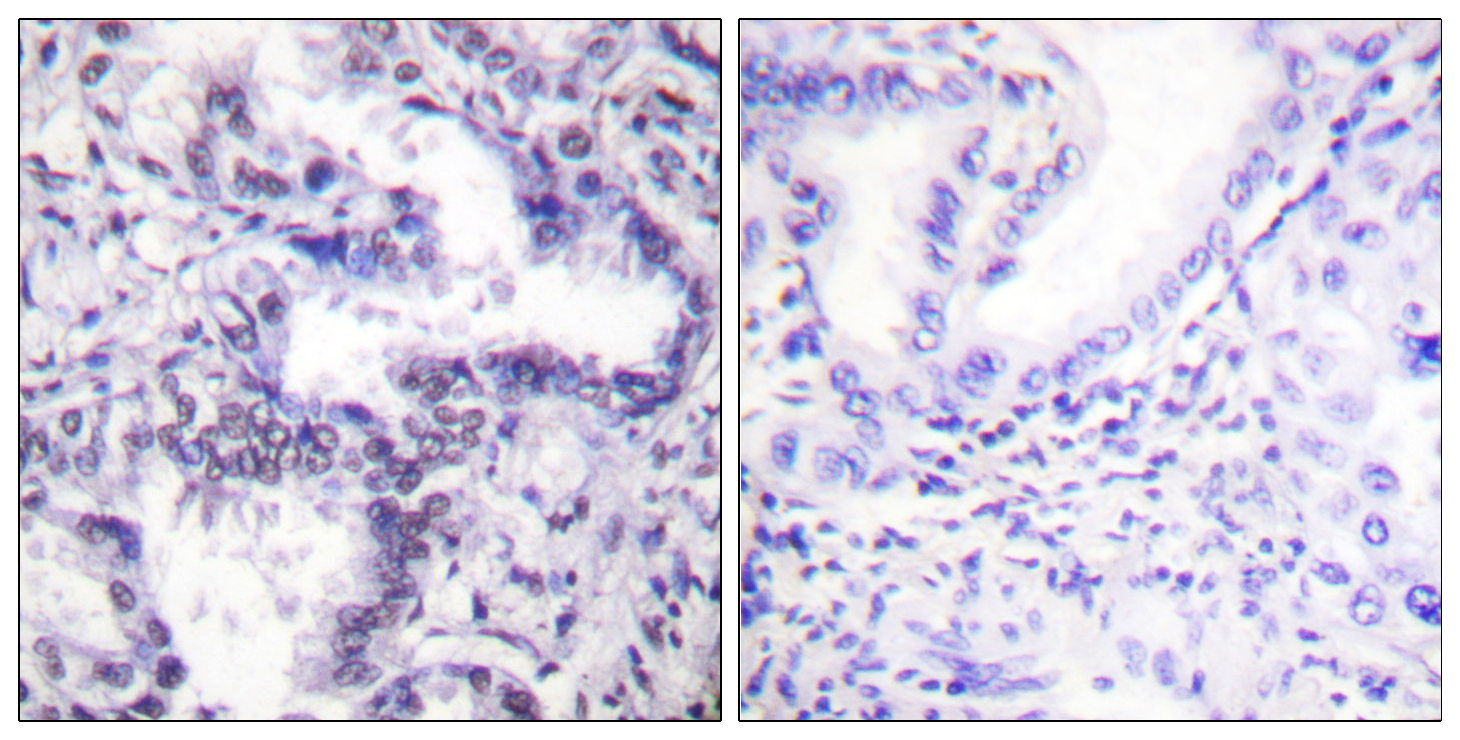
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma, using Ku80 (Phospho-Thr714) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
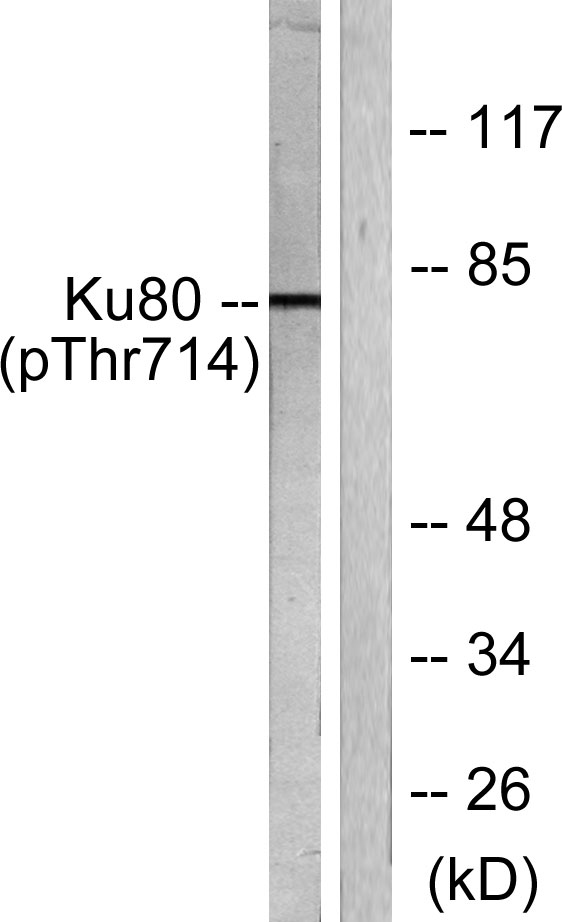

- Western blot analysis of lysates from COS7 cells, using Ku80 (Phospho-Thr714) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



