HDAC4 (phospho Ser632) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0125
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- HDAC4
- Fields:
- >>Apelin signaling pathway;>>Neutrophil extracellular trap formation;>>Alcoholism;>>Viral carcinogenesis;>>MicroRNAs in cancer
- Gene Name:
- HDAC4
- Protein Name:
- Histone deacetylase 4
- Human Gene Id:
- 9759
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P56524
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 208727
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q6NZM9
- Rat Gene Id:
- 363287
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q99P99
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human HDAC4 around the phosphorylation site of Ser632. AA range:598-647
- Specificity:
- Phospho-HDAC4 (S632) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of HDAC4 protein only when phosphorylated at S632.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- HDAC4;KIAA0288;Histone deacetylase 4;HD4
- Observed Band(KD):
- 119kD
- Background:
- Histones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to class II of the histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. This protein does not bind DNA directly, but through transcription factors MEF2C and MEF2D. It seems to interact in a multiprotein complex with RbAp48 and HDAC3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:Hydrolysis of an N(6)-acetyl-lysine residue of a histone to yield a deacetylated histone.,domain:The nuclear export sequence mediates the shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.,function:Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Involved in muscle maturation via its interaction with the myocyte enhancer factors such as MEF2A, MEF2C and MEF2D.,PTM:Phosphorylated by CaMK4 at Ser-246, Ser-467 and Ser-632. Phosphorylation at other residues is required for the interaction with 14-3-3.,PTM:Sumoylation on Lys-559 is promoted by the E3 SUMO-protein lig
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Upon muscle cells differentiation, it accumulates in the nuclei of myotubes, suggesting a positive role of nuclear HDAC4 in muscle differentiation. The export to cytoplasm depends on the interaction with a 14-3-3 chaperone protein and is due to its phosphorylation at Ser-246, Ser-467 and Ser-632 by CaMK4 and SIK1. The nuclear localization probably depends on sumoylation. Interaction with SIK3 leads to HDAC4 retention in the cytoplasm (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Ubiquitous.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Phospho-HDAC4 (S632) Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
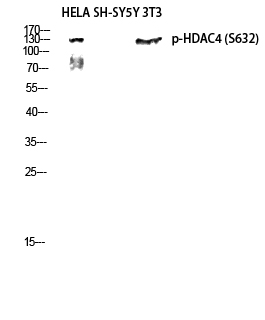
- Western blot analysis of HELA SH-SY5Y 3T3 lysis using Phospho-HDAC4 (S632) antibody. Antibody was diluted at 1:1000
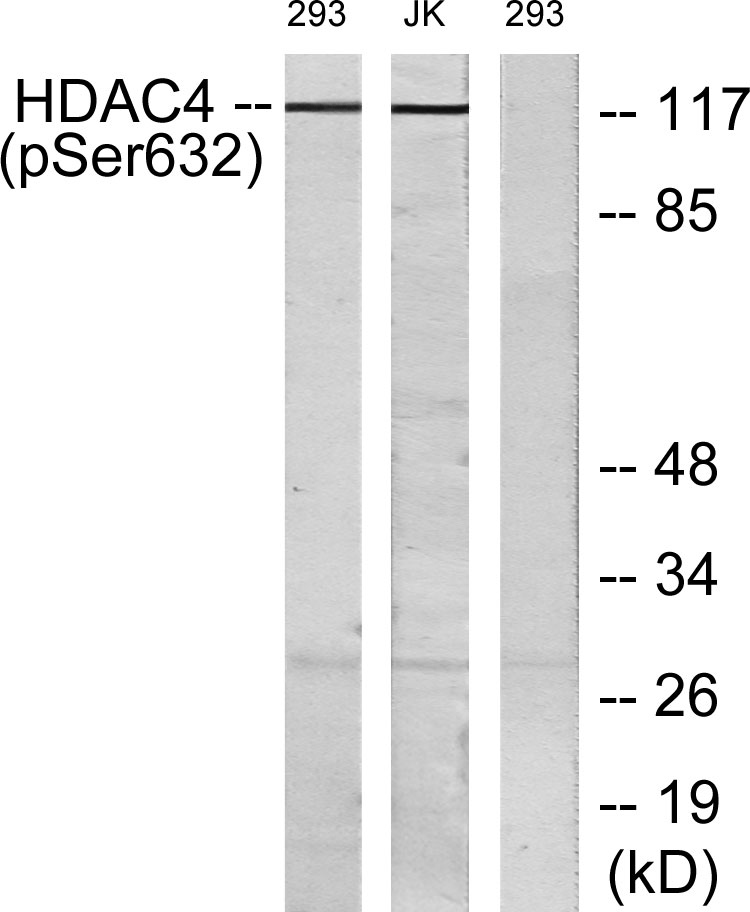
- Western blot analysis of lysates from 293 cells treated with etoposide 25uM 1hour and Jurkat cells treated with etoposide 25uM 24hours, using HDAC4 (Phospho-Ser632) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.



