FH Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YN5599
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- FH
- Fields:
- >>Citrate cycle (TCA cycle);>>Pyruvate metabolism;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Carbon metabolism;>>Cushing syndrome;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Renal cell carcinoma
- Gene Name:
- FH
- Protein Name:
- Fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial
- Human Gene Id:
- 2271
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P07954
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 14194
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P97807
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P14408
- Immunogen:
- Recombinant Protein of Fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial
- Specificity:
- The antibody detects endogenous fumarase proteins.
- Formulation:
- PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.5%BSA, 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:1000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial (Fumarase) (EC 4.2.1.2)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 50kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is an enzymatic component of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, or Krebs cycle, and catalyzes the formation of L-malate from fumarate. It exists in both a cytosolic form and an N-terminal extended form, differing only in the translation start site used. The N-terminal extended form is targeted to the mitochondrion, where the removal of the extension generates the same form as in the cytoplasm. It is similar to some thermostable class II fumarases and functions as a homotetramer. Mutations in this gene can cause fumarase deficiency and lead to progressive encephalopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:(S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O.,disease:Defects in FH are the cause of fumarase deficiency (FD) [MIM:606812]; also known as fumaricaciduria. FD is characterized by progressive encephalopathy, developmental delay, hypotonia, cerebral atrophy and lactic and pyruvic acidemia.,disease:Defects in FH are the cause of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC) [MIM:605839].,disease:Defects in FH are the cause of multiple cutaneous and uterine leiomyomata (MCUL1) [MIM:150800]. MCUL1 is an autosomal dominant condition in which affected individuals develop benign smooth muscle tumors (leiomyomata) of the skin. Affected females also usually develop leiomyomata of the uterus (fibroids).,function:Also acts as a tumor suppressor.,miscellaneous:There are 2 substrate binding sites: the catalytic A site, and the non-catalytic B site that may play a role in the transfer of s
- Subcellular Location:
- [Isoform Mitochondrial]: Mitochondrion .; [Isoform Cytoplasmic]: Cytoplasm, cytosol . Nucleus . Chromosome . Translocates to the nucleus in response to DNA damage: localizes to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) following phosphorylation by PRKDC. .
- Expression:
- Expressed in red blood cells; underexpressed in red blood cells (cytoplasm) of patients with hereditary non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia of unknown etiology.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
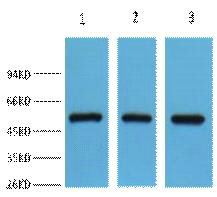
- Western blot analysis of 1) Hela, 2) Mouse Brain, 3) HepG2, diluted at 1:2000. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000



