TLR4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YN5450
- Applications:IHC;IF
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- TLR4
- Fields:
- >>NF-kappa B signaling pathway;>>HIF-1 signaling pathway;>>Phagosome;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>Necroptosis;>>Neutrophil extracellular trap formation;>>Toll-like receptor signaling pathway;>>NOD-like receptor signaling pathway;>>Alcoholic liver disease;>>Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection;>>Shigellosis;>>Salmonella infection;>>Pertussis;>>Legionellosis;>>Yersinia infection;>>Leishmaniasis;>>Chagas disease;>>Malaria;>>Toxoplasmosis;>>Amoebiasis;>>Tuberculosis;>>Hepatitis B;>>Measles;>>Influenza A;>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection;>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19;>>Proteoglycans in cancer;>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer;>>Inflammatory bowel disease;>>Rheumatoid arthritis;>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- TLR4
- Protein Name:
- Toll-like receptor 4
- Human Gene Id:
- 7099
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O00206
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9QUK6
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9QX05
- Immunogen:
- Recombinant Protein of TLR4
- Specificity:
- The antibody detects endogenous TLR4 protein.
- Formulation:
- PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.5%BSA, 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200-500. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- TLR4;Toll-like receptor 4;hToll;CD284
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This receptor has been implicated in signal transduction events induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) found in most gram-negative bacteria. Mutations in this gene have been associated with differences in LPS responsiveness. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012],
- Function:
- disease:Genetic variation in TLR4 is associated with age-related macular degeneration type 10 (ARMD10) [MIM:611488]. ARMD is a multifactorial eye disease and the most common cause of irreversible vision loss in the developed world. In most patients, the disease is manifest as ophthalmoscopically visible yellowish accumulations of protein and lipid that lie beneath the retinal pigment epithelium and within an elastin-containing structure known as Bruch membrane.,domain:The TIR domain mediates interaction with NOX4.,function:Cooperates with LY96 and CD14 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Acts via MYD88, TIRAP and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response.,polymorphism:Allele TLR4*B (Gly-299, Ile-399) is associated with a blunted response to inhaled LPS.,PTM:N-glycosylated. Glycosylation of Asn-526 an
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Early endosome . Cell projection, ruffle . Upon complex formation with CD36 and TLR6, internalized through dynamin-dependent endocytosis (PubMed:20037584). Colocalizes with RFTN1 at cell membrane and then together with RFTN1 moves to endosomes, upon lipopolysaccharide stimulation. .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in placenta, spleen and peripheral blood leukocytes (PubMed:9435236, PubMed:9237759). Detected in monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and several types of T-cells (PubMed:9237759, PubMed:27022195).
Selected lactobacilli strains inhibit inflammation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing the TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPKs activation Food Sci Tech-Brazil. 2022 Mar;42:. WB Mouse 1:500
Dibromoacetic Acid Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice through Oxidative Stress and Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathway Activation. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5637235 WB Mouse Liver
Knockdown of PLCε inhibits inflammatory cytokine release via STAT3 phosphorylation in human bladder cancer cells. TUMOR BIOLOGY Tumor Biol. 2015 Dec;36(12):9723-9732 WB Human 1:1000 T24 cell, BIU-87 cell
Ambient fine particulate matter induces inflammatory responses of vascular endothelial cells through activating TLR-mediated pathway:. TOXICOLOGY AND INDUSTRIAL HEALTH Toxicol Ind Health. 2019;35(10):670-678 WB Mouse,Human aortas HUVECs
The elevated expression of TLR4 and MMP9 in human abdominal aortic aneurysm tissues and its implication. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders Bmc Cardiovasc Disor. 2021 Dec;21(1):1-11 IHC Human 1:300 Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA),non-aneurysmal contro tissues
Chlamydia psittaci plasmid-encoded CPSIT_P7 induces macrophage polarization to enhance the antibacterial response through TLR4-mediated MAPK and NF-κB pathways BIOCHIMICA ET BIOPHYSICA ACTA-MOLECULAR CELL RESEARCH Chaoqun Chen WB Mouse
Disturbance of neuron–microglia crosstalk mediated by GRP78 in Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus mice. Ling Qin IF Mouse 1:400 BV2 cell
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
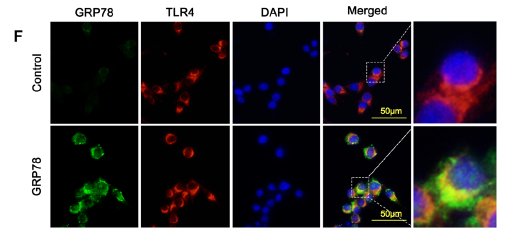
- Disturbance of neuron–microglia crosstalk mediated by GRP78 in Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus mice. Ling Qin IHC,IF Mouse 1:200 brain tissue BV2 cell
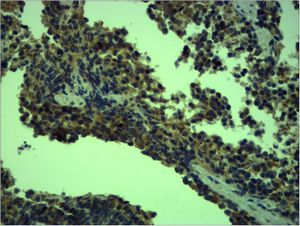
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded Mouse Spleen Tissue using TLR4 Polyclonal Antibody.



