Filamin A (PT0388R) PT® Rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8238
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;IP;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human; Mouse; Rat;
- Target:
- Filamin 1
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Focal adhesion;>>Salmonella infection;>>Proteoglycans in cancer
- Gene Name:
- FLNA
- Protein Name:
- Filamin-A
- Human Gene Id:
- 2316
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P21333
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 192176
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8BTM8
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal, rabbit, IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:4000-1:10000,WB 1:1000-1:5000,IF 1:200-1:1000,ELISA 1:5000-1:20000,IP 1:50-1:200,
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- FLNA;FLN;FLN1;Filamin-A;FLN-A;Actin-binding protein 280;ABP-280;Alpha-filamin;Endothelial actin-binding protein;Filamin-1;Non-muscle filamin
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 281kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 281kD
- Background:
- filamin A(FLNA) Homo sapiens The protein encoded by this gene is an actin-binding protein that crosslinks actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. The encoded protein is involved in remodeling the cytoskeleton to effect changes in cell shape and migration. This protein interacts with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes, and second messengers. Defects in this gene are a cause of several syndromes, including periventricular nodular heterotopias (PVNH1, PVNH4), otopalatodigital syndromes (OPD1, OPD2), frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD), Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS), and X-linked congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction (CIIPX). Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in FLNA are associated with cerebrofrontofacial syndrome [MIM:608578]. This syndrome consists of a phenotype of male PVNH, with relatively normal development, no epilepsy or other neurological abnormality, severe constipation, and facial dysmorphism and without a discernible skeletal phenotype.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD) [MIM:305620]. FMD is a congenital bone disease characterized by supraorbital hyperostosis, deafness and digital anomalies.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS) [MIM:309350]. MNS is a severe congenital bone disorder characterized by typical facies (exophthalmos, full cheeks, micrognathia and malalignment of teeth), flaring of the metaphyses of long bones, s-like curvature of bones of legs, irregular constrictions in the ribs, and sclerosis of base of skull.,disease:Defects i
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm
- Expression:
- Ubiquitous.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
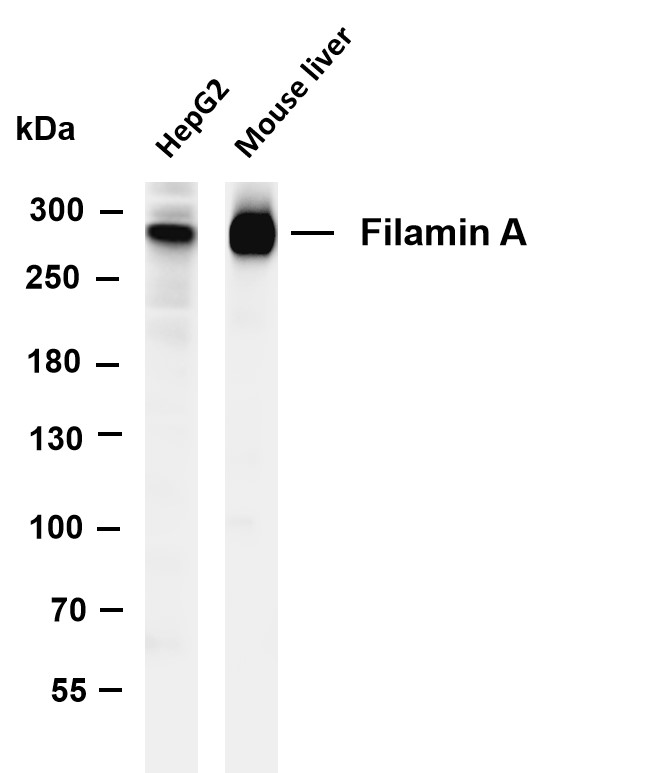
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-8% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-Filamin A (PT0388R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: HepG2 Lane 2: Mouse liver Predicted band size: 281kDa Observed band size: 281kDa



