β-Galactosidase (PT0312R) PT® Rabbit mAb
- Catalog No.:YM8184
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;IP;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human; Mouse; Rat;
- Target:
- Galactosidase β
- Fields:
- >>Galactose metabolism;>>Other glycan degradation;>>Glycosaminoglycan degradation;>>Sphingolipid metabolism;>>Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - ganglio series;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Lysosome
- Gene Name:
- GLB1
- Protein Name:
- Beta-galactosidase
- Human Gene Id:
- 2720
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P16278
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P23780
- Specificity:
- endogenous
- Formulation:
- PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
- Source:
- Monoclonal, rabbit, IgG, Kappa
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:2000-1:10000;WB 1:1000-1:5000;IF 1:200-1:1000;ELISA 1:5000-1:20000;IP 1:50-1:200;
- Purification:
- Protein A
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GLB1;ELNR1;Beta-galactosidase;Acid beta-galactosidase;Lactase;Elastin receptor 1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 76kD
- Observed Band(KD):
- 100kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the glycosyl hydrolase 35 family of proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature lysosomal enzyme. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of a terminal beta-linked galactose residue from ganglioside substrates and other glycoconjugates. Mutations in this gene may result in GM1-gangliosidosis and Morquio B syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:Hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing beta-D-galactose residues in beta-D-galactosides.,disease:Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 1 (GM1G1) [MIM:230500]; also known as infantile GM1-gangliosidosis. GM1-gangliosidosis is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease marked by the accumulation of GM1 gangliosides, glycoproteins and keratan sulfate primarily in neurons of the central nervous system. GM1G1 is characterized by onset within the first three months of life, central nervous system degeneration, coarse facial features, hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal dysmorphology reminiscent of Hurler syndrome, and rapidly progressive psychomotor deterioration. Urinary oligosaccharide levels are high. It leads to death usually between the first and second year of life.,disease:Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 2 (GM1G2) [MIM:230600];
- Subcellular Location:
- Lysosome
- Expression:
- Detected in placenta (at protein level) (PubMed:8383699). Detected in fibroblasts and testis (PubMed:2511208).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
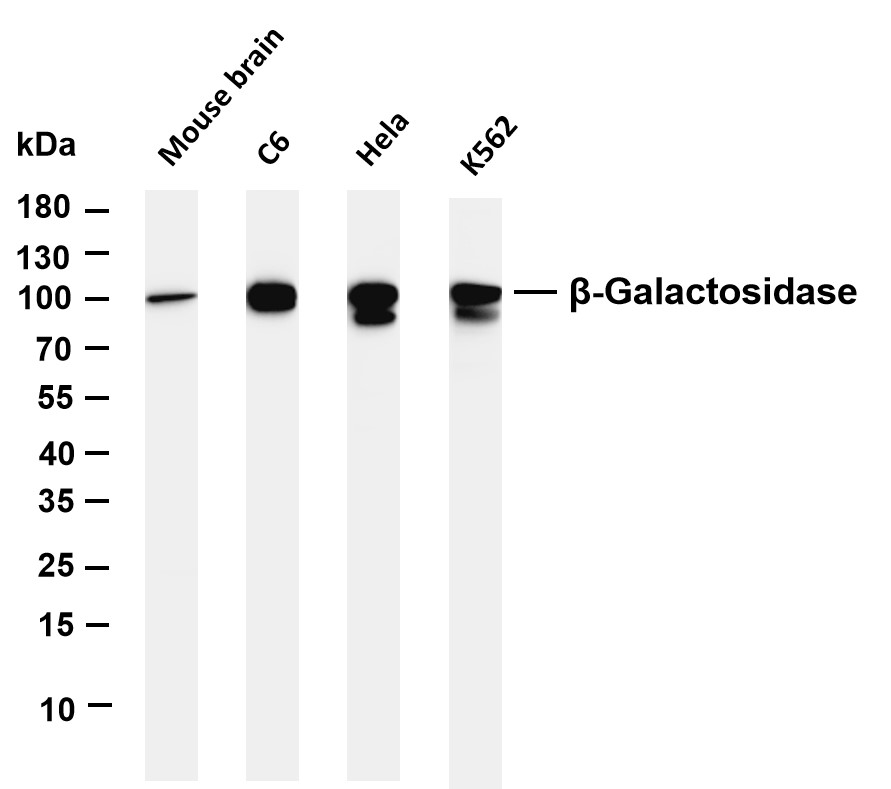
- Various whole cell lysates were separated by 4-20% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-β-Galactosidase (PT0312R) antibody. The HRP-conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG(H + L) antibody was used to detect the antibody. Lane 1: Mouse brain Lane 2: C6 Lane 3: Hela Lane 4: K562 Predicted band size: 76kDa Observed band size: 100kDa

- Mouse liver was stained with anti-β-Galactosidase (PT0312R) rabbit antibody
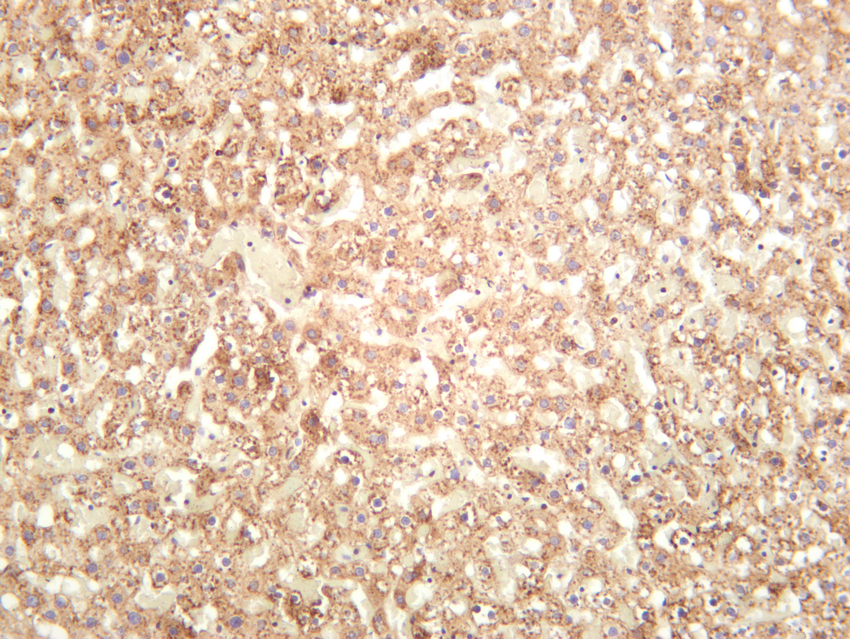
- Rat liver was stained with anti-β-Galactosidase (PT0312R) rabbit antibody



